Mapper注册与绑定
我们都知道 Mapper 是一个接口,它是我们与数据库交互的入口,每个 Mapper 都有与之相对应的一个 XML 文件,我们可以在 XML 里面自由快活地写 sql,当然我们也可以用注解的形式写在接口方法上,但终究还是没 XML 灵活,那么问题来了,Mybatis 是如何注册与绑定 Mapper 的呢?
Mybatis 执行 sql 的两种方法
直接操作 SqlSession 方法
public User findUserById(Integer userId) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
// namespace + statementId
return sqlSession.selectOne("com.objcoding.mybatis.UserMapper.findUserById", userId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
通过 Mapper 接口
public User findUserById(Integer userId) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return userMapper.findUserById(userId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
public class UserMapper {
User findUserById(@Param("userId") String userId);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.objcoding.mybatis.UserMapper">
<select id="findUserById" resultType="com.objcoding.mybatis.User">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE user_id=#{userId}
</select>
</mapper>
很明显,第二种方法可以大大降低了手工写 namespace 出现错误的概率,且用 Mapper 可以直接操作方法来实现数据链接,看起来优雅很多。
那么 Mapper 是如何示例化的,它是通过 Java 动态代理生成的一个代理类,并与 sqlSession 关联一起,看如下图:
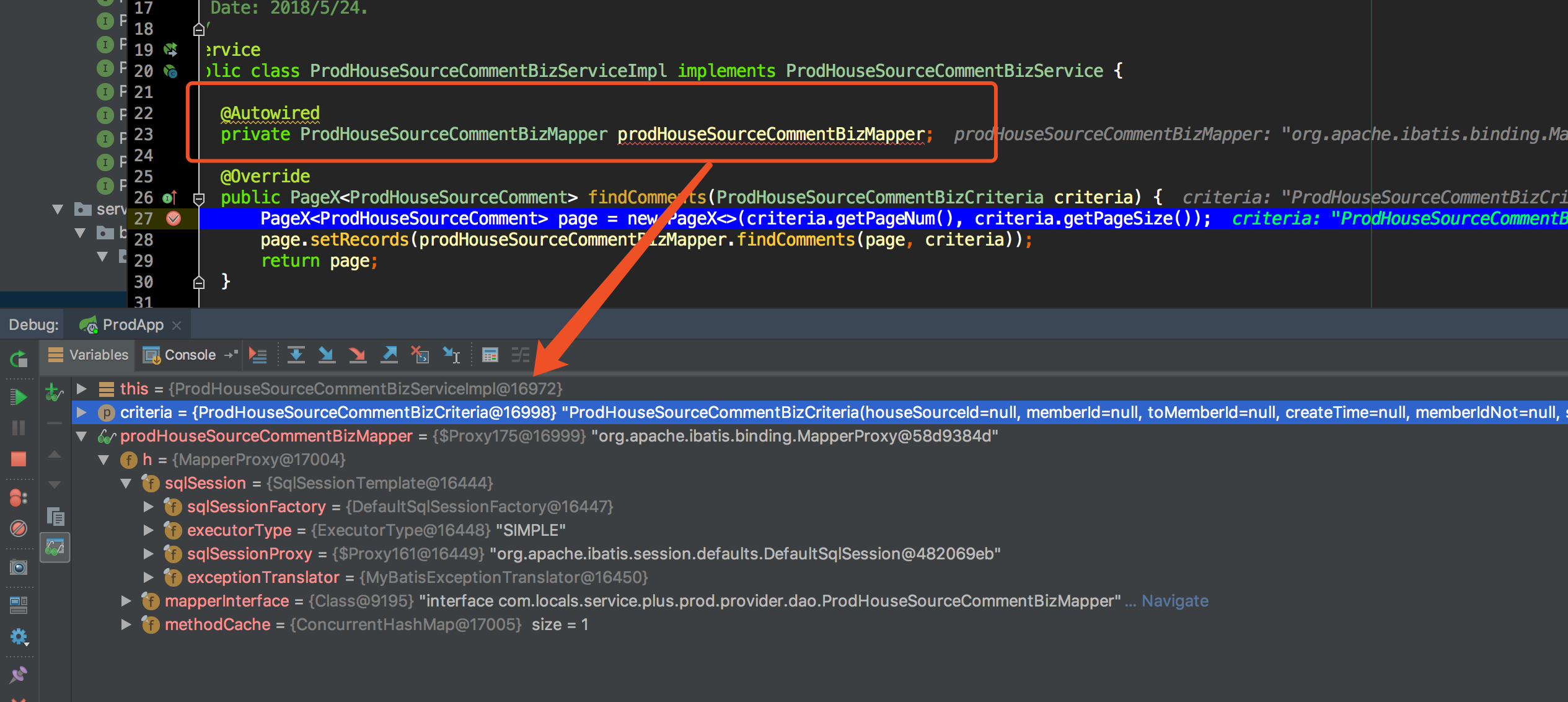
源码解析
XMLMapperBuilder
mapperElement
XMLMapperBuilder 这个类主要是用于解析 mybatis 中的 <mapper>标签里边的内容,功能与 XMLConfigBuilder 类似,都是解析 xml 内容,从源码看,拿到 mapperLocation 的输入流和 configuration 来初始化本身,mapperLocation 即是我们从配置文件配的 mapper XML 地址的封装类
parse()
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
/**
* 1.解析xml中的节点信息,并生成 MappedStatement
*/
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
/**
* 2.根据 Namespace 绑定 Mapper,也会解析 Mapper 注解中的信息生成 MappedStatement
*/
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
该方法即是 Mapper xml 节点解析与 Mapper 注解解析以及注册于绑定的入口。
configurationElement(XNode context)
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析 xml 中的 sql 片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析与 Mapper 方法对应的 sql
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
该方法将 Mapper xml 的各个节点进行读取,并生成 MapperStatement 添加到 Configuration 中,根据 Namespace 对 Mapper 进行注册绑定。
bindMapperForNamespace()
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// 获取 mapper.xml 中 namespace 的 mapper 类名
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 根据类名加载 class 对象
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 绑定操作
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
该方法找到 mapper.xml 的 mapper 类名,再根据类名找到加载 class 对象,最后进行绑定操作
MapperRegistry.addMapper()
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// mapper 与 MapperProxyFactory 进行映射
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// mapper注解构建器
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
MapperRegistry 类是一个 Mapper 类注册工厂,把与 MapperProxyFactory 映射过的 Mapper 类添加到它的属性 knownMappers 中;
MapperProxy
MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory 类是 生产Mapper 代理类的工厂,用 Java 动态代理实现:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
从方法 newInstance 方法终于看出来了,从这里生产出来的 Mapper 代理类,是与 SqlSession 关联起来的,我们继续往下看:
MapperProxy.invoke()
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
MapperMethod
mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 参数解析,依据时接口方法入参的注解
// 如果有一个参数就是单个对象,如果有多个参数会解析成 paramMap
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 此处省略部分代码
}
return result;
}
谜底揭开了,我们每次调用 Mapper 的方法,其实是调用这个 execute 方法,而这个方法实则在调用 SqlSession 的方法与数据库交互,通过cachedMapperMethod(method);
这个方法拿到执行 sql 相关信息,其实它就是从 congfiguration 类的属性 MappedStatement 中获取的:
MapperMethod.resolveMappedStatement()
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName, Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
// 获取 MappedStatement
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
MappedStatement 类是保存 Mapper 一个执行方法映射的一个节点(select/insert/delete/update),包括配置的 sql,sql 的 id、缓存信息、resultMap、parameterType、resultType 等重要配置内容。
小结
从以上源码分析过程得出:Mybatis 在生成一个 SqlSessionFactory 的过程中,主要干了两件事情:
- 注册:将 Mapper xml 中的节点信息和 Mapper 类中的注解信息与 Mapper 类的方法一一对应,每个方法对应生成一个 MapperStatement,并添加到 Configuration 中;
- 绑定:根据 Mapper xml 中的 namespace 生成一个 Mapper class 对象,并与一个 MapperProxyFactory 代理工厂对应,用于 Mapper 代理对象的生成。





















 315
315











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








