1.Servlet介绍
- Servlet(Server Applet)服务器小程序,主要功能用于生成动态Web内容。
- Servlet是J2EE最重要的组成部分。(J2EE13个功能模块之一)
2.Servlet开发步骤
- 创建Servlet类,继承HttpServlet
- 重写doGet()/doPost()方法,编写程序代码
- 配置web.xml,绑定url
3.Servlet访问方法
- http://IP地址:端口/context-path/url-mapping
- 远程访问使用ip地址,本地访问localhost(127.0.0.1)
- context-path“上下文路径”,默认为工程名
4.servlet接收请求参数
- 请求参数是浏览器通过请求向tomcat提交的数据,通常是用户输入,servlet进行处理。
- 参数名1=值1&参数名2=值2&…
- servet中的request.getParameter() -接收单个参数,request.getParameterValues() -接收多个同名参数
这里举个例子。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>学生信息登记表</h1>
<form action="/myservlet/sample">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br/>
特长:
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="English">英语
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Program">编程
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Speech">演讲
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Swimming">游泳<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
这里设置action为/myservlet/sample,接着创建一个来接受这些参数的servlet类SampleServlet。 web.xml配置url,重写doGet()方法,乱码不慌,下面会讲。
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
String[] specs = request.getParameterValues("spec");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>" + name + "</h1>");
out.println("<h1>" + age + "</h1>");
for(int i = 0 ; i < specs.length ; i++){
out.println("<h2>spec:" + specs[i] + "</h2>");
}
}
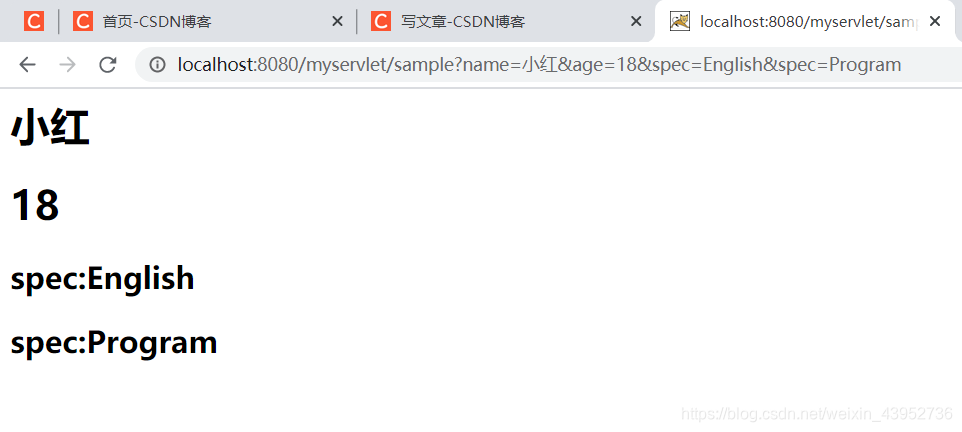
- 这里顺便讲一下Get和Post请求方法
在前面的表单中,< form action="/myservlet/sample">,这里如果没有写明method的话,就默认是get请求方法,所以servlet中重写doGet()方法。并且get的参数会显示在url上。
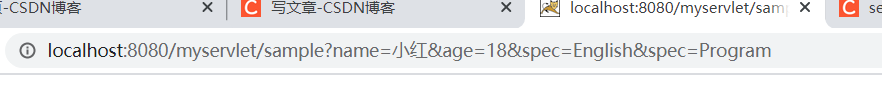
而当我们改为:< form action="/myservlet/sample" method=“post”>,参数就会被隐藏起来,点击f12
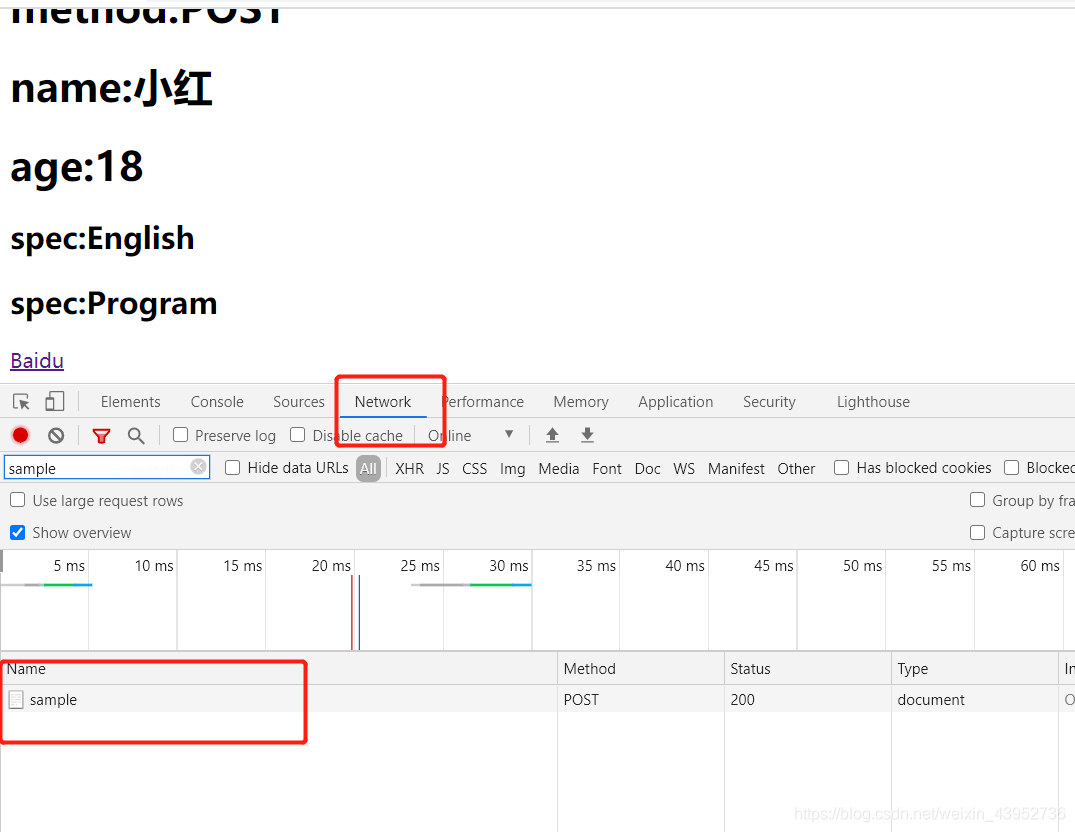
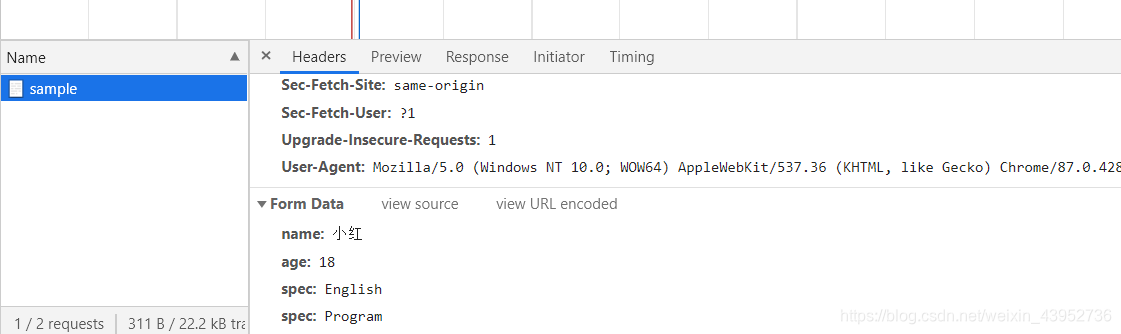
打开sample可以看到请求参数被放到请求体中。
Get和Post应用场景:
- Get常用于不包含敏感信息的查询功能。
- Post用于安全性要求较高的功能或者服务器的“写”操作。
Get和Post的乱码问题:
tomcat默认编码为西欧字符集:ISO-8859-1,需将其转为UTF-8,才能显示中文。
- 对于Get请求,tomcat8.x的版本,默认get请求发送中文就是utf-8格式,故对请求无需转换,如上面例子,只设置了响应浏览器的编码格式。
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
- 而对于Post请求,需要设置多一个 request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”),该方法用于将请求体中的字符集转换为UTF-8。故中文如果想要输出到浏览器,需要设置如下。
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
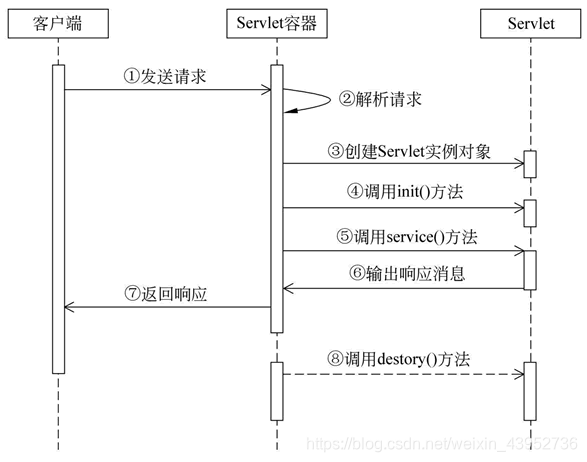
5.servlet生命周期图
6.使用注解配置servlet
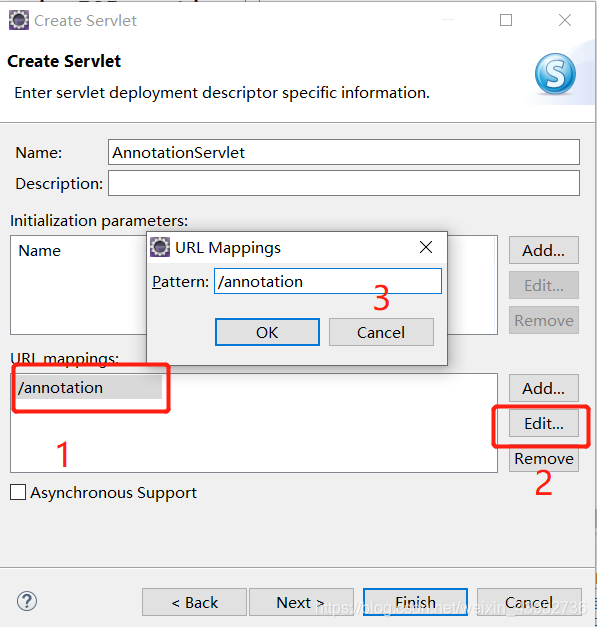
当我们新建了一个servlet后,每次都要去web.xml上配置url-pattern很麻烦,可以用注解的方式配置url。
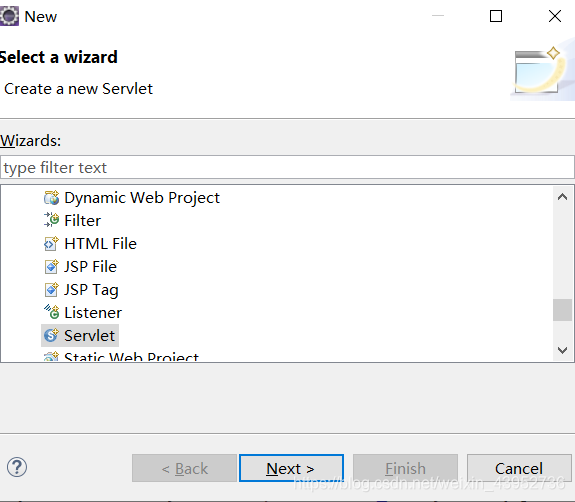
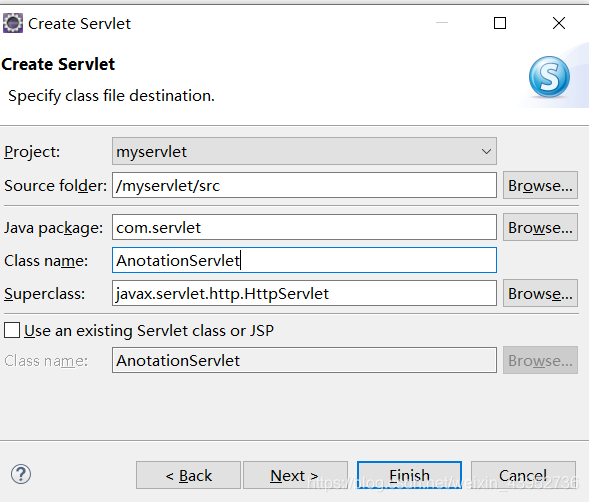
我们可以在包内新建一个servlet类, new -> web-> servlet
package com.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class AnnotationServlet
*/
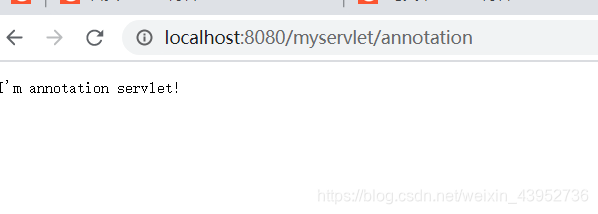
@WebServlet("/annotation")
public class AnnotationServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public AnnotationServlet() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.getWriter().println("I'm annotation servlet!");
}
}
7.启动时加载servlet
- web.xml使用< load-on-startup >设置启动时加载
- < load-on-startup > 0~9999 < /load-on-startup >
- 0~9999表示加载的优先级
- 启动时加载在工作中常用于系统的预处理,能够提高运行时的效率。例如游戏开始时候的进度条加载,就是在加载资源,也就是系统的预处理。
- 配置方式如下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>create</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.imooc.servlet.CreateServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>import</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.imooc.servlet.ImportServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
8.多个servlet(JSP)之间的跳转方式:
(应用场景:登录/注册页面跳转到主页等。)
请求转发:
- request.getRequestDispatcher(“映射路径”).forword(request, response) - 请求转发
- 请求转发是服务器跳转,只会产生一次请求。
- 这个服务器跳转说的是当浏览器向服务器发送请求,由servlet1接收信息,由于servlet1中包含了请求转发,servlet1会转向servlet2,由servlet2响应浏览器。因为这种跳转发生在服务器中,所以称为服务器跳转。
响应重定向:
- response.sendRedirect("/contentPath/映射路径")
- 响应重定向是浏览器端跳转,会产生两次请求。
- 浏览器端跳转是当浏览器向服务器发送请求,由servlet1接收信息,由于servlet1中包含了响应重定向,servlet1会响应浏览器,告诉它重新生成一个响应页面,浏览器再次以servet1告知的路径,再次向服务器发送请求,由servlet2响应浏览器。
9.设置请求自定义属性
- 请求允许创建自定义属性
- 设置请求属性:request.setAttribute(属性名,属性值);属性值可以是任何java有效对象
- 获取请求属性:Object attr = request.getAttribute(属性名)
10.ServletContext
- servletContext(servlet上下文对象),是web应用全局对象
- 一个Web应用只会创建一个ServletContext对象
- ServletContext随着Web应用启动而自动创建。
使用方法:
首先在web.xml配置
<context-param>
<param-name>copyright</param-name>
<param-value>© 2018 kkk.com 京ICP备 888888888号-88</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>title</param-name>
<param-value>servlet的详细讲解</param-value>
</context-param>
创建一个servlet类,initServlet类,初始化自定义属性
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ServletContext context = request.getServletContext();
String copyright = context.getInitParameter("copyright");
context.setAttribute("copyright", copyright);
String title = context.getInitParameter("title");
context.setAttribute("title", title);
response.getWriter().println("init success");
}
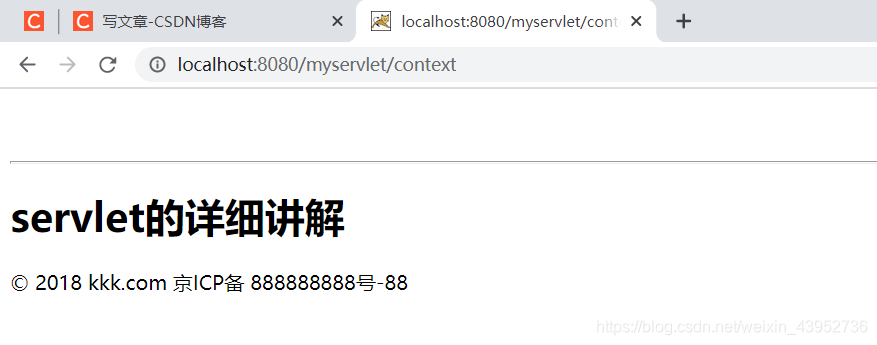
创建另外一个servlet类,contextServlet类,显示context内容。
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = (ServletContext)request.getServletContext();
String copyright = (String)context.getAttribute("copyright");
String title = (String)context.getAttribute("title");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().println("<br><br>");
response.getWriter().println("<hr/>");
response.getWriter().println("<h1>" + title + "</h1>" + copyright);
}
11.JavaWeb三大作用域对象:
- HttpServletRequest - 请求对象
- HttpSession - 用户会话对象
- ServletContext - web应用全局对象
作用域从上到下,是小到大。tips:能用小的就不用大的,耗费资源。
12.错误页面处理
- 因为404或500,会把错误信息等,显示在页面上,安全性不够好,我们可以在web.xml中,设置其错误时加载显示的页面,显示我们想要显示的数据。
例如:
<!-- 指定错误页面 -->
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error/404.html</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/error/500.jsp</location>
</error-page>
13.Java Web打包与发布
项目做好要上线怎么打包呢?
对项目右键 -> Export -> Web -> WAR file,
Desination选择打包到 E:\Program Files (x86)\tomcat\apache-tomcat-8.5.61\webapps 即tomcat的webapps路径下。
然后打开tomcat文件夹
点击startup.bat即可成功运行项目。





 本文详细介绍了Servlet的原理与应用,包括Servlet的介绍、开发步骤、访问方法、接收请求参数的方式,以及Get和Post请求的区别。此外,还讲解了Servlet的生命周期、注解配置、启动时加载、servlet间跳转、请求自定义属性、ServletContext对象以及JavaWeb的作用域对象。最后,讨论了错误页面处理和项目打包发布的流程。
本文详细介绍了Servlet的原理与应用,包括Servlet的介绍、开发步骤、访问方法、接收请求参数的方式,以及Get和Post请求的区别。此外,还讲解了Servlet的生命周期、注解配置、启动时加载、servlet间跳转、请求自定义属性、ServletContext对象以及JavaWeb的作用域对象。最后,讨论了错误页面处理和项目打包发布的流程。
















 88
88

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








