JAVA的半关闭服务器
最近学习到JAVA网络编程的Socket半关闭,对于流的关闭与Soket的关闭的认识有些模糊,改进了一下教材的代码进行了一下实验
- Receiver类
public class Receiver {
private int port=8000;
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
private static int stopWay=1; //结束通信的方式
private final int NATURAL_STOP=1; //自然结束
private final int SUDDEN_STOP=2; //突然关闭程序
private final int SOCKET_STOP=3; //关闭Socket,再结束程序
private final int INPUT_STOP=4; //关闭输入流,再结束程序
private final int STREAM_STOP=5; //关闭输入流
private final int SERVERSOCKET_STOP=6; //关闭ServerSocket,再结束程序
public Receiver() throws IOException{
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("服务器已经启动");
}
private BufferedReader getReader(Socket socket) throws IOException {
InputStream socketIn=socket.getInputStream();
return new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socketIn));
}
public void receive() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Socket socket=null;
socket=serverSocket.accept();
BufferedReader br=getReader(socket);
for (int i=0 ; i<20 ;i++){
String msg=br.readLine();
System.out.println("receive:"+msg);
Thread.sleep(1000);
if (i==2){
//终止程序,结束通信
if (stopWay==SUDDEN_STOP){
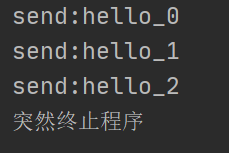
System.out.println("突然终止程序");
System.exit(0);
}
else if (stopWay==SOCKET_STOP){
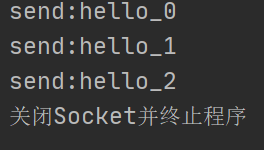
System.out.println("关闭Socket并终止程序");
socket.close();
break;
}
else if (stopWay==INPUT_STOP){
socket.shutdownInput();
System.out.println("关闭输入流并终止程序");
break;
}
else if (stopWay==STREAM_STOP){
br.close();
System.out.println("关闭输出流");
break;
}
else if (stopWay==SERVERSOCKET_STOP){
System.out.println("关闭ServerSocket并终止程序");
serverSocket.close();
break;
}
}
}
if (stopWay==NATURAL_STOP){
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length>0)
stopWay=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
new Receiver().receive();
}
}
- Sender类
public class Sender {
private String host="localhost";
private int port=8000;
private Socket socket;
private static int stopWay=1; //结束通信的方式
private final int NATURAL_STOP=1; //自然结束
private final int SUDDEN_STOP=2; //突然关闭程序
private final int SOCKET_STOP=3; //关闭Socket,再结束程序
private final int OUTPUT_STOP=4; //关闭输出流,再结束程序
private final int STREAM_STOP=5; //关闭输出流
public Sender() throws IOException {
socket=new Socket(host,port);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length>0)
stopWay=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
new Sender().send();
}
private PrintWriter getWriter(Socket socket) throws IOException {
OutputStream socketOut=socket.getOutputStream();
return new PrintWriter(socketOut,true);
}
public void send() throws Exception{
PrintWriter pw=getWriter(socket);
for (int i=0;i<20;i++){
String msg="hello_"+i;
pw.println(msg);
System.out.println("send:"+msg);
Thread.sleep(500); //睡眠500ms
if (i==2){
//终止程序,结束通信
if (stopWay==SUDDEN_STOP){
System.out.println("突然终止程序");
System.exit(0);
}
else if (stopWay==SOCKET_STOP){
System.out.println("关闭Socket并终止程序");
socket.close();
break;
}
else if (stopWay==OUTPUT_STOP){
socket.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("关闭输出流并终止程序");
break;
}
else if (stopWay==STREAM_STOP){
pw.close();
System.out.println("关闭输出流");
break;
}
}
}
if (stopWay==NATURAL_STOP){
socket.close();
}
}
}
Sender用来向Receiver连续发送20条数据,在发送第三条数据时,根据不同情况中断Sender或Receiver
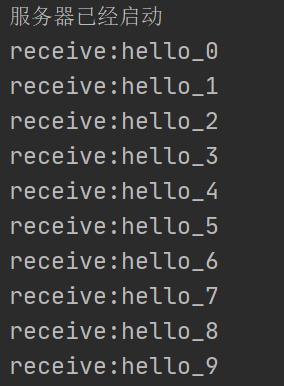
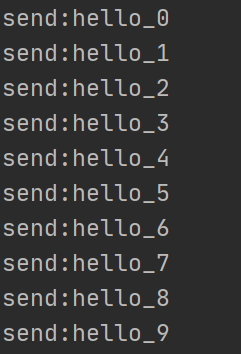
- 情况一:Sender和Receiver正常结束(Sender正常发送了20条数据,Receiver正常发送了20条数据)
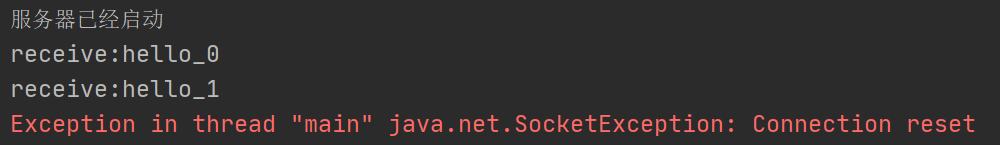
- 情况二:Sender正常发送,Receiver出现异常,提前结束(服务器提前终止,因参数设置原因,底层客户端Socket并不立即释放端口,操作系统探测到还有发送给服务器Socket的数据,会继续向服务器发送数据,尽管服务器已经不能接收)

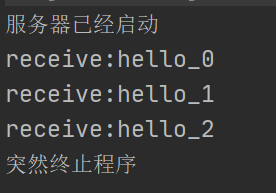
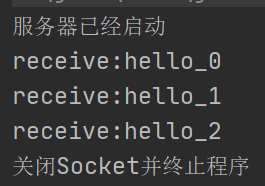

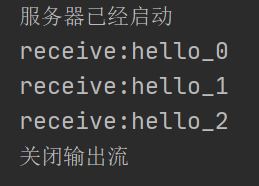
- 情况三:突然停止Sender(半关闭或关闭客户端Socket时,服务器端的输入流并不受影响,但接收到的数据为null,因为此时客户端已经无法继续发送数据)
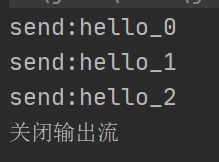
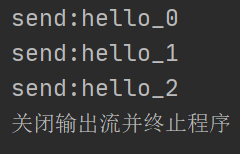

另有一种特殊情况,上述实验是基于客户端只发送数据,而服务器端只接收数据,关闭和半关闭Socket产生的效果是相同的,如果客户端和服务器端都要彼此互相发送数据呢?
代码如下:
public class socketServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务器端监听9999端口,等待客户端连接");
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接建立");
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int readLen=0;
while ((readLen=inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,readLen));
}
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello,client".getBytes());
//socket.shutdownOutput();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
public class socketClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(),9999);
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello,server".getBytes());
//socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String msg=null;
while((msg=bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(msg);
}
socket.close();
}
}
上述代码客户端向服务器端发送hello,server,服务器端接收到消息后给服务器端发送hello,client,当不使用半关闭的socket时
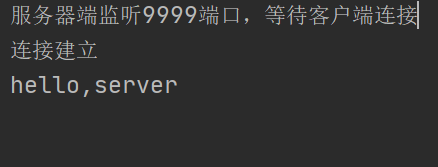
服务器端和客户端都阻塞,原因是服务器端和客户端的输出流都不知道什么时候数据的输出结束,于是阻塞,此时半关闭socket和全关闭socket就会产生不同的结果,当全关闭socket时,输入流和输出流都被关闭,服务器在接收到数据后因为socket关闭,客户端无法接收来自服务器的数据(outputstream.close()会使socket关闭)
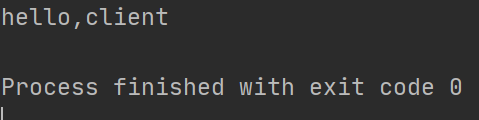
使用半关闭后,通信正常
























 225
225

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








