TCP通信程序
概述
TCP通信能实现两台计算机之间的数据交互,通信的两端,要严格区分为客户端(Client)与服务端(Server)。
两端通信时步骤:
- 服务端程序,需要事先启动,等待客户端的连接。
- 客户端主动连接服务器端,连接成功才能通信。
- 服务端不可以主动连接客户端。
在Java中,提供了两个类用于实现TCP通信程序:
- 客户端:
java.net.Socket类表示。创建Socket对象,向服务端发出连接请求,服务端响应请求,两者建立连接开始通信。 - 服务端:
java.net.ServerSocket类表示。创建ServerSocket对象,相当于开启一个服务,并等待客户端的连接。
Socket类
Socket 类:该类实现客户端套接字,套接字指的是两台设备之间通讯的端点。
构造方法
public Socket(String host, int port):创建套接字对象并将其连接到指定主机上的指定端口号。如果指定的host是null ,则相当于指定地址为回送地址。
成员方法
public InputStream getInputStream(): 返回此套接字的输入流。- 如果此Scoket具有相关联的通道,则生成的InputStream 的所有操作也关联该通道。
- 关闭生成的InputStream也将关闭相关的Socket。
public OutputStream getOutputStream(): 返回此套接字的输出流。- 如果此Scoket具有相关联的通道,则生成的OutputStream 的所有操作也关联该通道。
- 关闭生成的OutputStream也将关闭相关的Socket。
public void close():关闭此套接字。- 一旦一个socket被关闭,它不可再使用。
- 关闭此socket也将关闭相关的InputStream和OutputStream 。
public void shutdownOutput(): 禁用此套接字的输出流。- 任何先前写出的数据将被发送,随后终止输出流。
getOutputStream()源码
/**
* Returns an output stream for this socket.
*
* <p> If this socket has an associated channel then the resulting output
* stream delegates all of its operations to the channel. If the channel
* is in non-blocking mode then the output stream's {@code write}
* operations will throw an {@link
* java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException}.
*
* <p> Closing the returned {@link java.io.OutputStream OutputStream}
* will close the associated socket.
*
* @return an output stream for writing bytes to this socket.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs when creating the
* output stream or if the socket is not connected.
* @revised 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isConnected())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not connected");
if (isOutputShutdown())
throw new SocketException("Socket output is shutdown");
final Socket s = this;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<OutputStream>() {
public OutputStream run() throws IOException {
return impl.getOutputStream();
}
});
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getException();
}
return os;
}
getInputStream()源码
/**
* Returns an input stream for this socket.
*
* <p> If this socket has an associated channel then the resulting input
* stream delegates all of its operations to the channel. If the channel
* is in non-blocking mode then the input stream's {@code read} operations
* will throw an {@link java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException}.
*
* <p>Under abnormal conditions the underlying connection may be
* broken by the remote host or the network software (for example
* a connection reset in the case of TCP connections). When a
* broken connection is detected by the network software the
* following applies to the returned input stream :-
*
* <ul>
*
* <li><p>The network software may discard bytes that are buffered
* by the socket. Bytes that aren't discarded by the network
* software can be read using {@link java.io.InputStream#read read}.
*
* <li><p>If there are no bytes buffered on the socket, or all
* buffered bytes have been consumed by
* {@link java.io.InputStream#read read}, then all subsequent
* calls to {@link java.io.InputStream#read read} will throw an
* {@link java.io.IOException IOException}.
*
* <li><p>If there are no bytes buffered on the socket, and the
* socket has not been closed using {@link #close close}, then
* {@link java.io.InputStream#available available} will
* return {@code 0}.
*
* </ul>
*
* <p> Closing the returned {@link java.io.InputStream InputStream}
* will close the associated socket.
*
* @return an input stream for reading bytes from this socket.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs when creating the
* input stream, the socket is closed, the socket is
* not connected, or the socket input has been shutdown
* using {@link #shutdownInput()}
*
* @revised 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isConnected())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not connected");
if (isInputShutdown())
throw new SocketException("Socket input is shutdown");
final Socket s = this;
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<InputStream>() {
public InputStream run() throws IOException {
return impl.getInputStream();
}
});
} catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getException();
}
return is;
}
- 创建一个客户端对象Socket,构造方法绑定服务器的IP地址和端口号
- 使用Socket对象中的方法getOutputStream()获取网络字节输出流OutputStream对象
- 使用网络字节输出流OutputStream对象中的方法write,给服务器发送数据
- 使用Socket对象中的方法getInputStream()获取网络字节输入流InputStream对象
- 使用网络字节输入流InputStream对象中的方法read,读取服务器回写的数据
- 释放资源(Socket)
ServerSocket类
ServerSocket类:这个类实现了服务器套接字,该对象等待通过网络的请求。
构造方法
public ServerSocket(int port):使用该构造方法在创建ServerSocket对象时,就可以将其绑定到一个指定的端口号上,参数port就是端口号。
成员方法
public Socket accept():侦听并接受连接,返回一个新的Socket对象,用于和客户端实现通信。该方法会一直阻塞直到建立连接。
1.创建服务器ServerSocket对象和系统要指定的端口号
2.使用ServerSocket对象中的方法accept,获取到请求的客户端对象Socket
3.使用Socket对象中的方法getInputStream()获取网络字节输入流InputStream对象
4.使用网络字节输入流InputStream对象中的方法read,读取客户端发送的数据
5.使用Socket对象中的方法getOutputStream()获取网络字节输出流OutputStream对象
6.使用网络字节输出流OutputStream对象中的方法write,给客户端回写数据
7.释放资源(Socket,ServerSocket)
简单的TCP网络程序
TCP通信分析图解
- 【服务端】启动,创建ServerSocket对象,等待连接。
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
- 【客户端】启动,创建Socket对象,请求连接。
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
- 【服务端】接收连接,调用accept方法,并返回一个Socket对象。
Socket socket = server.accept();
- 【客户端】Socket对象,获取OutputStream,向服务端写出数据。
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好服务器".getBytes());
- 【服务端】Scoket对象,获取InputStream,读取客户端发送的数据。
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bytes);

到此,客户端向服务端发送数据成功。
自此,服务端向客户端回写数据。
- 【服务端】Socket对象,获取OutputStream,向客户端回写数据。
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("收到谢谢".getBytes());
- 【客户端】Scoket对象,获取InputStream,解析回写数据。
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bytes);
- 【客户端】释放资源,断开连接。
socket.close();
客户端向服务器发送数据
服务端实现:
package com.itheima.demo01.TCP;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);//1
Socket socket = server.accept();//3
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//5
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//5
int len = is.read(bytes);//5
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));//5
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//6
os.write("收到谢谢".getBytes());//6
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
客户端实现:
package com.itheima.demo01.TCP;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);//2
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//4
os.write("你好服务器".getBytes());//4
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//7
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//7
int len = is.read(bytes);//7
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));//7
socket.close();//8
}
}
运行结果
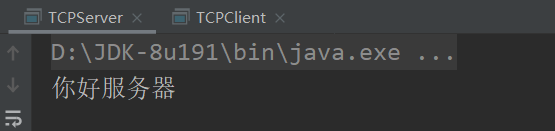
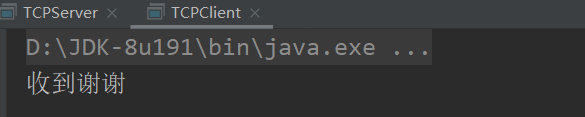





 本文详细介绍了Java中TCP通信的基本原理和实现步骤,包括客户端Socket和服务器端ServerSocket的使用。通过示例代码展示了如何创建连接,发送和接收数据,以及资源的释放。此外,还提供了客户端和服务端的简单程序示例,帮助理解TCP通信过程。
本文详细介绍了Java中TCP通信的基本原理和实现步骤,包括客户端Socket和服务器端ServerSocket的使用。通过示例代码展示了如何创建连接,发送和接收数据,以及资源的释放。此外,还提供了客户端和服务端的简单程序示例,帮助理解TCP通信过程。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










