本文开始手写源码系列学习,通过手写各大框架的源码了解底层逻辑。
流程
应用程序容器启动—>解析配置类—>扫描
准备工作
回顾之前学习Spring,启动时候首先需要注册bean。**那么如何加载bean?**以前是通过beans.xml配置文件的方式,让容器读取到配置文件中的配置来加载对应的bean。如下代码
@Test
public void test(){
//解析beans.xml文件 , 生成管理相应的Bean对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//getBean : 参数即为spring配置文件中bean的id .
Hello hello = (Hello) context.getBean("hello");
hello.show();
}
因为随着Spring发展我们都用注解的方式进行bean的标注,所以手写源码方式就基于注解了。
基础类
MyApplicationContext
public class MyApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
}
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
//...
return null;
}
}
AppConfig
Spring中有一个这样的配置类来进行类的注册
@ComponentScan("com.wangqun.service")
public class AppConfig {
}
注解
@ComponentScan
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value();
}
@Component
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
@Scope
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {
String value();
}
容器启动
构建
applicationContext将配置文件注入
MyApplicationContext applicationContext = new MyApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
注入之后的后面需要进行解析配置类,那么解析类解析的是什么?
并不是解析类的属性、限定符,而是解析这个配置类AppConfig的注解@ComponentScan,从而判断接下来需要扫描哪些类
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
// 解析配置类
// ComponentScan ---> 扫描路径 ---> 扫描
}
解析配置类
获取注解@ComponentScan得到路径
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value(); // 扫描路径 com.wangqun.service
扫描
是不是得到了扫描路径后加载全部就可以了?
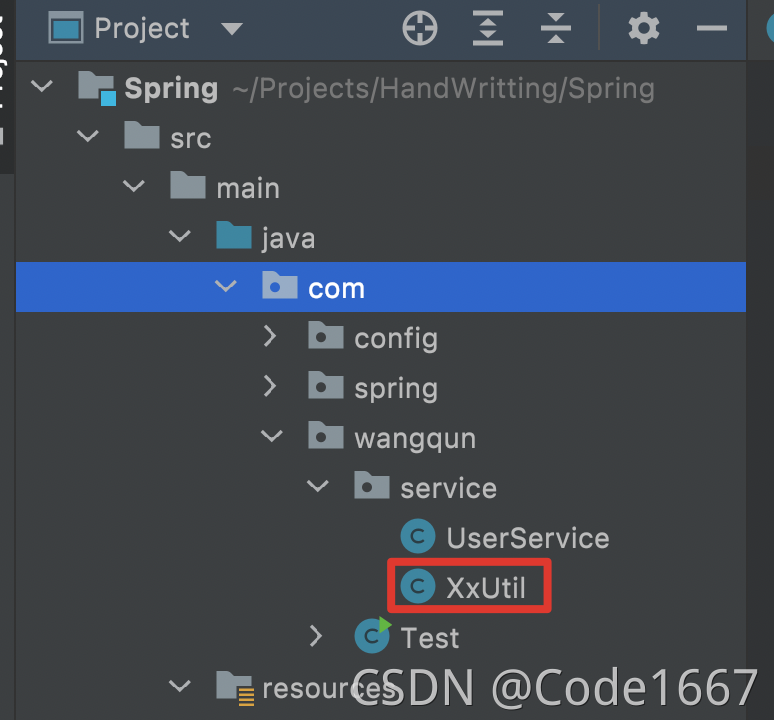
可以看到service下的类并不都是xxxService的情况下,加载全部类是不正确的,而且在Spring的应用中,我们需要加载的是被@Component注解的类。
现在又有一个问题,如何获得这些类?
类加载器分别加载的路径
- BootStrap -----> jre/lib
- Ext -----> jre/ext/lib
- App -----> classpath
所以我们要获取到MyApplicationContext的类加载器来加载
BeanDefinition 定义bean的描述
public class BeanDefinition {
private Class clazz;
private String scope;
public BeanDefinition(){
}
public BeanDefinition(Class clazz, String scope) {
this.clazz = clazz;
this.scope = scope;
}
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
}
scan()方法
private void scan(Class configClass) {
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value(); // 扫描路径 com.wangqun.service
ClassLoader classLoader = MyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); // app
path = path.replace(".", "/");
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);// 相对路径,相对的是classpath
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {// 判断是否是目录
File[] files = file.listFiles();// 获得目录下的所有文件
for (File f : files) {
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();// 获得文件的绝对路径 这里是编译后的target/classes下的绝对路径
// 如果是类文件才处理
if (absolutePath.endsWith(".class")) {
String name = toFullQualifiedName(absolutePath);// 需要将绝对路径变成全限定名
try {
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(name);// 通过类全限定名加载类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
// 表示当前这个类是一个Bean
// 解析类,判断单例还是原型 ----> BeanDefinition
Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
// bean的定义
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scopeAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scopeAnnotation.value());
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
// 将bean的描述放入map
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
通过绝对路径变为权限定名
/**
* 绝对路径变为全限定名
*
* @param absolutePath 绝对路径
* @return 全限定名
*/
private String toFullQualifiedName(String absolutePath) {
int com = absolutePath.indexOf("com");
int point = absolutePath.indexOf(".");
// 去掉.Class
String substring = absolutePath.substring(0, point);
// 去掉com之前
substring = substring.substring(com);
// 替换
substring = substring.replace("/", ".");
return substring;
}
创建bean对象
扫描后,从Map中去判断类描述信息,根据beanName和描述信息创建bean对象
最后将bean加入单例池
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
// 解析配置类,并不是解析限定符、属性,而是解析类上的注解
// ComponentScan ---> 扫描路径 ---> 扫描
scan(configClass);
// 创建bean对象
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : beanDefinitionMap.entrySet()) {
String beanName = entry.getKey();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
Object bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
创建bean
private Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object bean = null;
try {
bean = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
getBean()方法
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
Object o = singletonObjects.get(beanName);
return o;
} else {
// 创建Bean对象
return createBean(beanDefinition);
}
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("Bean " + beanName + " not exists");
}
}
总结
总结一下Spring从启动开始做了哪些事。
- 首先加载程序配置类
AppConfig,读取配置类的注解,从而获得扫描的包,通过包去加载包内的类 - 遍历包内文件是否为
class文件,如果是通过类加载器加载类,判断该类是否有@Component注解,如果有的话则该类为需要加载的bean - 将该类的描述(类信息、是否单例、是否懒加载等等)记录为
BeanDefinition,加载到BeanDefinitionMap - 遍历
BeanDefinitionMap判断每个BeanDefinition是否为单例,如果是单例则创建bean,将bean加入到单例池ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects getBean(beanName)方法判断beanDefinitionMap是否存在该beanName,判断是否单例,单例则直接从单例池中获取bean,原型则创建bean返回
完整代码
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyApplicationContext applicationContext = new MyApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("userService"));
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("userService"));
}
}
public class MyApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
// 解析配置类,并不是解析限定符、属性,而是解析类上的注解
// ComponentScan ---> 扫描路径 ---> 扫描
scan(configClass);
// 创建bean对象
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : beanDefinitionMap.entrySet()) {
String beanName = entry.getKey();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
Object bean = createBean(beanDefinition);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
private Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object bean = null;
try {
bean = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
private void scan(Class configClass) {
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value(); // 扫描路径 com.wangqun.service
// 扫描
// 包下面有些不是我们需要加载的类如XxUtil,所以我们要先拿到包下面的所有类,判断类上面是否有@Component注解
// 那么如何拿到所有类呢???
// BootStrap -----> jre/lib
// Ext -----> jre/ext/lib
// App -----> classpath 例如:/Users/wangqun03/Projects/HandWritting/Spring/target/classes com.wangqun.Test
ClassLoader classLoader = MyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); // app
path = path.replace(".", "/");
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);// 相对路径,相对的是classpath
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
// 如果是类文件才处理
if (absolutePath.endsWith(".class")) {
String name = toFullQualifiedName(absolutePath);
try {
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(name);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
// 表示当前这个类是一个Bean
// 解析类,判断单例还是原型 ----> BeanDefinition
Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
// bean的定义
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scopeAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scopeAnnotation.value());
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 绝对路径变为全限定名
*
* @param absolutePath 绝对路径
* @return 全限定名
*/
private String toFullQualifiedName(String absolutePath) {
int com = absolutePath.indexOf("com");
int point = absolutePath.indexOf(".");
// 去掉.Class
String substring = absolutePath.substring(0, point);
// 去掉com之前
substring = substring.substring(com);
// 替换
substring = substring.replace("/", ".");
return substring;
}
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
Object o = singletonObjects.get(beanName);
return o;
} else {
// 创建Bean对象
return createBean(beanDefinition);
}
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("Bean " + beanName + " not exists");
}
}
}





















 1008
1008

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








