1. @Getter 和 @Setter
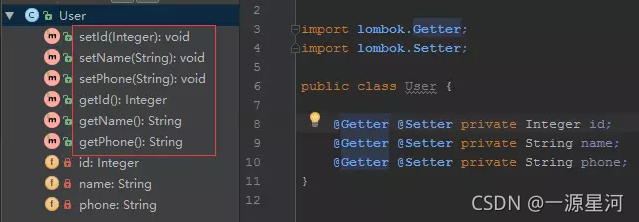
可以用@Getter或@Setter注解任何属性(也可以注释到类上),让lombok自动生成默认的getter/setter方法。
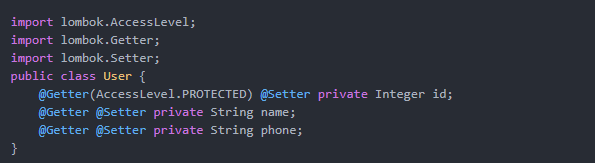
注:默认生成的方法是public,如果要修改方法修饰符可以设置AccessLevel的值,如:
@Getter(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
private Integer uid;
2. @ToString
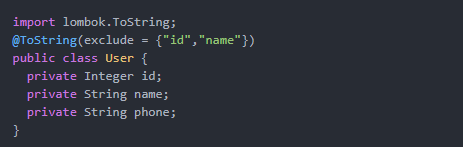
生成toString()方法,默认情况下,它会按顺序(以逗号分隔)打印你的类名称以及每个属性。
可以这样设置不包含哪些字段:
@ToString(exclude = "id")
// 或者:
@ToString(exclude = {"id","name"})
如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的toString()方法,如:
@ToString(callSuper = true)
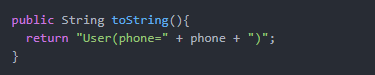
生成toString方法如下:
3. @EqualsAndHashCode
生成hashCode()和equals()方法。默认情况下,它将使用所有非静态,非transient字段。但可以通过在可选的exclude参数中来排除更多字段。或者,通过在parameter参数中命名它们来准确指定希望使用哪些字段。
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude={"id", "shape"})
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
private transient int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper=true)
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
}
}
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
private transient int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)){
return false;
}
EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.score, other.score) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.tags, other.tags)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.score);
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.name == null ? 43 : this.name.hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32));
result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.tags);
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample;
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Square)) return false;
Square other = (Square) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (!super.equals(o)) return false;
if (this.width != other.width) return false;
if (this.height != other.height) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
result = (result*PRIME) + super.hashCode();
result = (result*PRIME) + this.width;
result = (result*PRIME) + this.height;
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Square;
}
}
}
4. @NoArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor生成一个无参构造方法。当类中有final字段没有被初始化时,编译器会报错,此时可用@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),然后就会为没有初始化的final字段设置默认值 0 / false / null。对于具有约束的字段(例如@NonNull字段),不会生成检查或分配,因此请注意,正确初始化这些字段之前,这些约束无效。
@NoArgsConstructor(force = true)
public class User {
@NonNull
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String name;
private final String phone ;
}
5.@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequiredArgsConstructor会生成构造方法(可能带参数也可能不带参数),如果带参数,这参数只能是以final修饰的未经初始化的字段,或者是以@NonNull注解的未经初始化的字段。
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = “of”)会生成一个of()的静态方法,并把构造方法设置为私有的。
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User {
@NonNull
private Integer id ;
@NonNull
private String name = "bbbb";
private final String phone;
}
//另外一个
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
public class User {
@NonNull
private Integer id ;
@NonNull
private String name = "bbbb";
private final String phone;
}
6.@AllArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor 生成一个全参数的构造方法。
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
@NonNull
private Integer id ;
@NonNull
private String name = "bbbb";
private final String phone;
}
7. @Data
@Data包含了@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@Getter / @Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的功能。
@Data
public class DataExample {
private final String name;
@Setter(AccessLevel.PACKAGE)
private int age;
private double score;
private String[] tags;
@ToString(includeFieldNames=true)
@Data(staticConstructor="of")
public static class Exercise<T> {
private final String name;
private final T value;
}
}
8. @Accessors
@Accessors 主要用于控制生成的getter和setter。
主要参数介绍:
fluent boolean值,默认为false。此字段主要为控制生成的getter和setter方法前面是否带get/set
chain boolean值,默认false。如果设置为true,setter返回的是此对象,方便链式调用方法
prefix 设置前缀 例如:@Accessors(prefix = “abc”) private String abcAge 当生成get/set方法时,会把此前缀去掉。
9.@Synchronized
给方法上加锁。
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object readLock = new Object();
@Synchronized
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
@Synchronized
public int answerToLife() {
return 42;
}
@Synchronized("readLock")
public void foo() {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}
# 10. @Wither 给final属性赋值的一种方式。
public class WitherExample {
@Wither
private final int age;
@Wither(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@NonNull
private final String name;
public WitherExample(String name, int age) {
if (name == null) throw new NullPointerException();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
11. @NonNull
作用在方法、构造方法的参数上,帮我们避免空指针。
public class NonNullExample extends Something {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) {
super("Hello");
this.name = person.getName();
}
}
12. @Cleanup
帮我们自动调用close()。
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
@Cleanup
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
@Cleanup
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
}
}
13. @Log4j2
注解在类上为类提供一个属性名为log 的 log4j 日志对象,和@Log4j注解类似。
14. 其它
@Entity // 这是hibernate的注解
@Table(name= Constants.TABLE_SCHOOL_DOWNLOAD_LIMIT)
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of") // 生成一个叫of的静态方法,同时私有化构造方法
@Accessors(chain = true) // 控制生成的set/get方法前缀,设置true表示前面用get和set
@ToString
public class SchoolDownloadLimit implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -196412797757026250L;
@Getter(onMethod = @_({@Id,@Column(name="id",nullable=false),@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)}))
@Setter
private Integer id;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name="school_id")))
@Setter
private Integer schoolId;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "per_download_times")))
@Setter
private Integer perDownloadTimes;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "limit_time")))
@Setter
private Integer limitTime;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "download_to_limit_an_hour")))
@Setter
private Integer downloadToLimitInHour;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "available")))
@Setter
private Integer available = 1;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "create_time")))
@Setter
private Date createTime;
@Getter(onMethod = @_(@Column(name = "update_time")))
@Setter
private Date updateTime;
}
@Data:注解在类上;提供类所有属性的 getting 和 setting 方法,此外还提供了equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法
@Setter:注解在属性上;为属性提供 setting 方法
@Getter:注解在属性上;为属性提供 getting 方法
@Log4j2 :注解在类上;为类提供一个 属性名为log 的 log4j 日志对象,和@Log4j注解类似
@NoArgsConstructor:注解在类上;为类提供一个无参的构造方法
@AllArgsConstructor:注解在类上;为类提供一个全参的构造方法
@EqualsAndHashCode:默认情况下,会使用所有非瞬态(non-transient)和非静态(non-static)字段来生成equals和hascode方法,也可以指定具体使用哪些属性。
@toString:生成toString方法,默认情况下,会输出类名、所有属性,属性会按照顺序输出,以逗号分割。
@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @AllArgsConstructor:
无参构造器、部分参数构造器、全参构造器,当我们需要重载多个构造器的时候,只能自己手写了。
@NonNull:注解在属性上,如果注解了,就必须不能为Null。
@val:注解在属性上,如果注解了,就是设置为final类型,可查看源码的注释知道。





 本文介绍了Lombok库中常用的注解如@Getter, @Setter, @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode等,展示了如何自动生成方法并控制其行为,包括访问修饰符、字段排除、构造器生成等。
本文介绍了Lombok库中常用的注解如@Getter, @Setter, @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode等,展示了如何自动生成方法并控制其行为,包括访问修饰符、字段排除、构造器生成等。
















 347
347

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








