目录标题
unordered_map关联式容器
1. 文档介绍
- unorder_map是存储<key, value>键值对的关联式容器,其允许通过key快速的索引到与其对应的value
- 键和映射值的类型可能不同,键值通常用于唯一的标识元素,而映射值是一个对象
- 在内部unorder_map没有对<key, value>按照任何特定的顺序排序,为了在常数范围内找到key所对应的value,unorder_map将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中
- unorder_map容器通过key访问单个元素要比map快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低
- unorder_map实现了直接访问操作符(operator[]),它允许使用key作为参数直接访问value,map也可以
- 它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器
- hash的性能非常出色:拥有高达O(1)的插入和查找复杂度.这比map(平衡二叉树)的O(logn)要快
2. 接口说明
2.1 构造
#include<unordered_map>
unordered_map<T1, T2> mp;
2.2 容量
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| bool empty() const | 检测容器是否为空 |
| size_t size() const | 获取容器中的有效元素个数 |
2.3 迭代器
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| begin | 返回第一个元素的迭代器 |
| end | 返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| cbegin | 返回第一个元素的const迭代器 |
| cend | 返回最后一个元素下一个位置的const迭代器 |
2.4 元素访问
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| operator[] | 返回与key对应的value,没有一个默认值 |
2.5 查询
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| iterator find(const K& key) | 返回key在哈希桶中的位置 |
| size_t count(const K& key) | 返回哈希桶中关键码为key的键值对的个数,查看是否存在 |
unordered_map中key是不能重复的,因此count函数的返回值最大为1
2.6 修改操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| insert | 向容器中插入键值对 |
| erase | 删除容器中的键值对 |
| void clear() | 清空容器中有效元素个数 |
| void swap(unorder_map&) | 交换两个容器中的元素 |
2.7 桶操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| size_t bucket_count() const | 返回哈希桶中桶的总个数 |
| size_t bucket_size(size_t n) const | 返回n号桶中有效元素的总个数 |
| size_t bucket(const K& key) | 返回元素key所在的桶号 |
3. 底层结构
unorder系列的关联式容器之所以效率比较高,是因为其底层使用了哈希结构
map/multimap属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现
4. 哈希表代码实现
1. 开放定址法中的删除
// 懒惰删除,增加一个删除标记
// 哈希表每个空间给个标记
// EMPTY此位置为空,EXIST此位置已经有元素,DELETE元素已经删除
enum Status{EMPTY, EXIST, DELETE};
2. 线性探测的实现

#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// hash设计时要尽可能少冲突,非素数有一对公约数,冲突概率暴涨,因此capacity要是素数(质数)
// 素数列表,num_prime是个数
static const int num_prime = 32;
static const unsigned long prime_list[num_prime] =
{
3, 7, 13, 19,
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// 根据输入的数得到比它大的素数
unsigned long GetNextPrime(size_t num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num_prime; i++)
{
if(prime_list[i] > num)
{
return prime_list[i]; // 返回第一个比num大的数
}
}
// 如果没有比num大的素数, 返回列表中最后一个数
return prime_list[num_prime - 1];
};
// 闭散列处理哈希冲突,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有的元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索
// 所以每个空间要给个标记
enum Status
{
EMPTY, // 空
EXIST, // 有元素
DELETE // 已经删除
};
template<class key, class value>
class HashTable{
struct Elem
{
pair<key, value> _val; // 键值对
Status _status;
};
public:
// 形参设置默认值,函数调用时,不传递任何实参就使用默认参数,有实参则进行实参传递
// 初始化列表中,(number)是为容器开辟了number大小的空间
HashTable(size_t capacity = 3) : _ht(capacity), _size(0)
{
for(size_t i= 0; i<capacity; ++i)
_ht[i]._status = EMPTY;
}
public:
// 插入方法
// 闭散列,线性探测法
bool Insert(const pair<key, value>& val)
{
// 检测哈希表底层空间是否充足
CheckCapacity();
size_t hashAddr = HashFunc(val.first);
// 找到空的位置才可以插入
while(_ht[hashAddr]._status != EMPTY)
{
// 重复键值的元素是无法插入的
if(_ht[hashAddr]._status == EXIST && _ht[hashAddr]._val.first == val.first)
return false;
// 删除标记的地方可以重用
if(_ht[hashAddr]._status == DELETE)
break;
hashAddr++;
if(hashAddr == _ht.capacity())
hashAddr = 0;
/* 转一圈也没有找到,注意:动态哈希表,该种情况可以不用考虑,哈希表中元素个数到达
*一定的数量,哈希冲突概率会增大,需要扩容来降低哈希冲突,因此哈希表中元素是不会存满的
*/
}
// 插入元素
_ht[hashAddr]._status = EXIST;
_ht[hashAddr]._val = val;
_size++;
return true;
}
// 获取size
size_t Size() const
{
return _size;
}
// 判断是否为空
bool Empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
// 查找
int Find(const key& t)
{
size_t hashAddr = HashFunc(t);
while(_ht[hashAddr]._status != EMPTY)
{
if(_ht[hashAddr]._val.first == t && _ht[hashAddr]._val.second != DELETE)
return hashAddr;
hashAddr++;
}
return -1;
}
// 删除
bool Erase(const key& k)
{
int index = Find(k);
if(index == -1)
return false;
_ht[index]._status = DELETE;
_size--;
return true;
}
// 交换
void Swap(HashTable<key, value>& ht)
{
swap(_ht, ht._ht);
swap(_size, ht._size);
}
private:
// 检查容量,不够就扩容
void CheckCapacity()
{
//载荷因子
if(_size * 10 / _ht.capacity() >= 7)
{
HashTable<key, value> newHt(GetNextPrime(_ht.capacity()));
for(size_t i=0; i<_ht.capacity(); i++)
{
if(_ht[i]._status == EXIST)
newHt.Insert(_ht[i]._val);
}
// 因为CheckCapacity()函数中的newHt对象是局部的,作用域只在这个函数中
// 局部变量存在栈区,编译器 编译结束后会释放掉
// 所以要将原来的对象和newHt对象进行交换
Swap(newHt);
}
}
// 哈希函数
size_t HashFunc(const key& k)
{
return k % _ht.capacity();
}
private:
vector<Elem> _ht;
size_t _size;
};
int main()
{
cout << "111" << endl;
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int ar[] = { 4, 6, 8, 3, 6, 13, 1, 2, 9};
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(int);
cout << n << endl; // 9
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout << "222" << endl;
ht.Insert(pair<int, int>(ar[i], ar[i]));
cout << "333" << endl;
}
// 因为不能有重复的元素,所以下面的结果是 8
cout << ht.Size() << endl; //当前元素个数
ht.Erase(8);
cout << ht.Size() << endl; //删除之后元素个数
cout <<"key = 6 : index = "<< ht.Find(6) << endl;
cout << "key = 8 : index = " << ht.Find(8) << endl;
cout <<"key = 13 : index = " << ht.Find(13) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
unordered系列关联式容器的底层实现是hashtable,
比如在undered_set中value就是key,而在unordered_map中value代表键值对的值
哈希函数使用除留余数法计算存放地址,那么key就必须是整形或者转换为整形才能取模==
*/
3. 链地址法
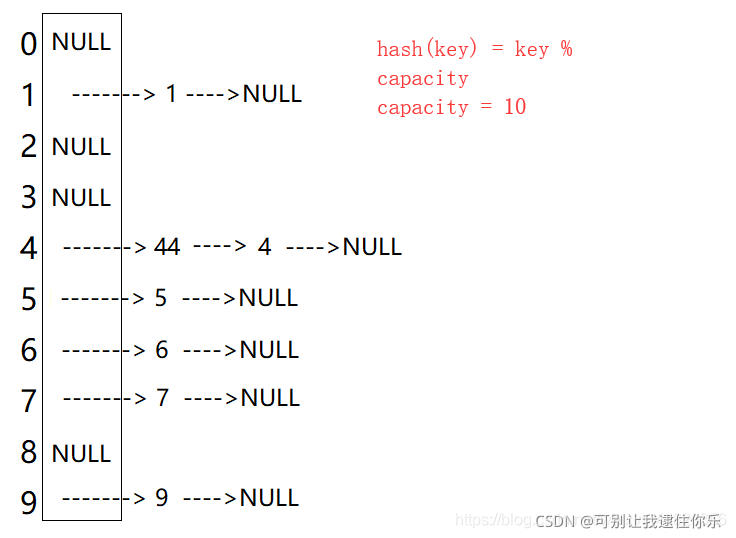
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
// 素数
static const int num_prime = 28;
static const unsigned long prime_list[num_prime] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// 扩容的长度
inline unsigned long next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
const unsigned long* first = prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = prime_list + num_prime;
// lower_bound()函数的功能:
// 在[first, last)区间上返回一个存放不小于n的数的内存地址
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
// 没找到返回最大值
return pos == last ? *(last-1) : *pos;
}
// 节点结构
template<class key_type, class value_type>
struct HashBucketNode
{
HashBucketNode<key_type, value_type>* _pNext; // 指向下个节点的指针
pair<key_type, value_type> _val; // 键值对
};
template<class key_type, class value_type>
class HashBucket
{
typedef struct HashBucketNode<key_type, value_type> Node;
public:
// 初始化
HashBucket(size_t capacity = 3) : _size(0)
{
const size_t n_buckets = next_prime(capacity);
// 预留空间
_ht.reserve(n_buckets);
// 插入节点结构的空指针
// insert(const_iterator pos, int count, ele); // 迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
_ht.insert(_ht.end(), n_buckets, (Node*)0);
}
// 开辟新节点
Node* new_node(const pair<key_type, value_type>& val)
{
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->_pNext = (Node*)0;
n->_val = val;
return n;
}
// 哈希桶中的元素不能重复
Node* Insert(const pair<key_type, value_type>& val)
{
// 确认是否需要扩容
CheckCapacity(_size+1);
// 计算元素所在的桶号
size_t bucketNow = HashFunc(val.first);
// 检测该元素是否在桶中
Node* pCur = _ht[bucketNow];
while(pCur)
{
if(pCur->_val.first == val.first && pCur->_val.second == val.second)
return pCur;
pCur = pCur->_pNext;
}
// 插入新元素
pCur = new_node(val);
pCur->_pNext = _ht[bucketNow];
_ht[bucketNow] = pCur;
_size++;
return pCur;
}
// 删除
bool Erase(const key_type& k)
{
size_t bucketNow = HashFunc(k);
Node* pCur = _ht[bucketNow];
Node* pPrev = nullptr, pRet = nullptr;
while (pCur)
{
if (pCur->_val.first == k)
{
if (pCur == _ht[bucketNow]) // 如果当前指针指向的节点是头一个
_ht[bucketNow] = pCur->_pNext;
else
pPrev->_pNext = pCur->_pNext; // 如果不是,就用一个指针记录其后面的节点
pRet = pCur->_pNext;
delete pCur;
_size--;
return pRet;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
Node* Find(const key_type& data);
// 交换
void Swap(HashBucket<key_type, value_type>& ht)
{
swap(_ht, ht._ht);
swap(_size, ht._size);
}
// 判断是否需要扩容
void CheckCapacity(size_t num_elements_hint)
{
size_t bucketCount =_ht.capacity();
// 看有没有超过容量
if (num_elements_hint > bucketCount)
{
const size_t n = next_prime(num_elements_hint);
HashBucket<key_type, value_type> newHt(n);
for (size_t bucketIdx = 0; bucketIdx < _ht.size(); ++bucketIdx)
{
Node* pCur = _ht[bucketIdx];
while (pCur)
{
// 将该节点从原哈希表中拆出来
_ht[bucketIdx] = pCur->_pNext;
// 将该节点插入到新哈希表中
size_t bucketNo = newHt.HashFunc(pCur->_val.first);
// 先拼接起来,再移动
pCur->_pNext = newHt._ht[bucketNo];
newHt._ht[bucketNo] = pCur;
pCur = _ht[bucketIdx];
}
}
newHt._size = _size;
this->Swap(newHt);
}
}
// 求size
size_t Size() const
{
return _size;
}
// 判空
bool Empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
// 展示
void show_hashtable()
{
for(size_t i=0; i< _ht.size(); i++)
{
Node* p = _ht[i];
cout << "_ht[" << i << "]:";
while(p != NULL)
{
cout << "key: " << p->_val.first << " value: " << p->_val.second << " ->";
p = p->_pNext;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
private:
// 哈希函数
size_t HashFunc(const key_type& data)
{
return data % _ht.capacity();
}
private:
// 数组存放指向Node的指针
vector<Node*> _ht;
size_t _size;
};
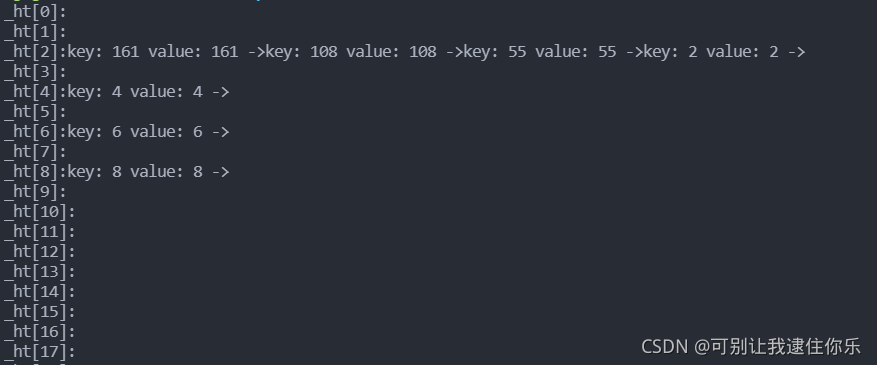
int main()
{
int ar[] = {2, 55, 108, 161, 6, 8, 6, 8, 4};
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(int);
HashBucket<int, int> ht(3);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ht.Insert(pair<int, int>(ar[i], ar[i]));
}
ht.show_hashtable();
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
4. 开散列与闭散列的比较
用链地址法处理哈希冲突,需要增加链接的指针,似乎增加了存储开销。事实上:由于开地址法必须保持大量的空闲空间来确保搜索效率,如二次探查法要求装载因子a<=0.7,而表项所占空间又比指针大的多,所以使用链地址法反而比开地址法节省存储空间
5. 存储其他类型
// 哈希函数可以采用处理余数法,key要化为整型才可以处理
// 仿函数
template<class T>
class DefHashF
{
public:
size_t operator()(const T& val)
{
return val;
}
};
// key为字符串类型,需要将其转化为整型
class Str2Int
{
public:
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
// 将string类型转化为char*类型
const char* str = s.c_str();
unsigned int seed = 131;
unsigned int hash = 0;
while(*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
};
// 关键是s.c_str()函数





















 79
79











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








