原文链接:https://www.gbase.cn/community/post/4917
更多精彩内容尽在南大通用GBase技术社区,南大通用致力于成为用户最信赖的数据库产品供应商。
分区表的概述
-
分区表通过使用分区技术,将一张大表,拆分成多个表分区(独立的segment),从而提升数据访问的性能,以及日常的可维护性。
-
分区表中,每个分区的逻辑结构必须相同。如:列名、数据类型。
-
分区表中,每个分区的物理存储参数可以不同。如:各个分区所在的表空间。
-
对于应用而言完全透明,分区前后没有变化,不需要进行修改。
分区表的注意事项
-
目前支持的分区有 RANGE 分区、LIST 分区、HASH 分区、KEY 分区。
-
RANGE 分区表和 LIST 分区表支持子分区,子分区只可以是 HASH 分区或者 KEY分区,每个分区的子分区个数必须相同。
-
包括子分区在内所有分区总和个数不大于 8192,生产环境中最少保持单表分区总和在50个以下。
-
分区列不支持 update 操作。
分区表的性能测试
1. 分别创建一个分区的表和非分区的表,进行性能测试。
##创建测试库##
create database testdb;
use testdb;
##创建普通表##
create table no_part_tab ( c1 int default NULL, c2 varchar(30) default null, c3 date default null);
##创建分区表##
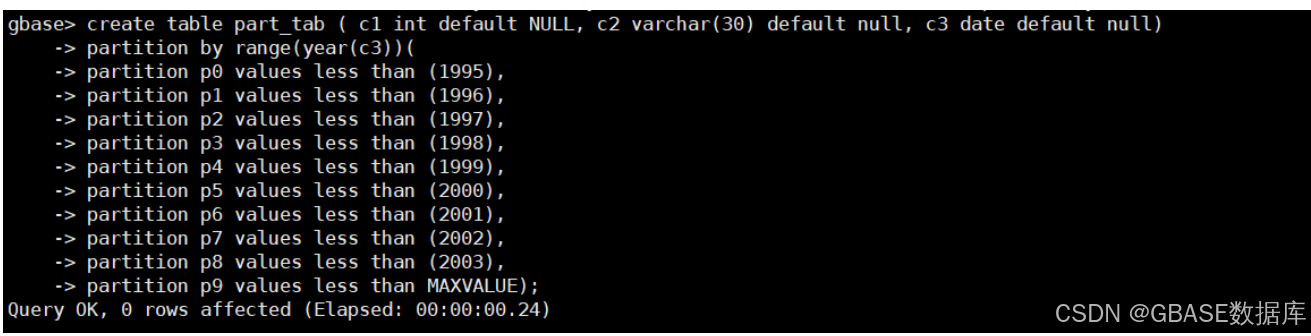
create table part_tab ( c1 int default NULL, c2 varchar(30) default null, c3 date default null)
partition by range(year(c3))(
partition p0 values less than (1995),
partition p1 values less than (1996),
partition p2 values less than (1997),
partition p3 values less than (1998),
partition p4 values less than (1999),
partition p5 values less than (2000),
partition p6 values less than (2001),
partition p7 values less than (2002),
partition p8 values less than (2003),
partition p9 values less than MAXVALUE);示例如下:

2. 生成模拟数据
use testdb;
##创建存储过程生成测试数据##
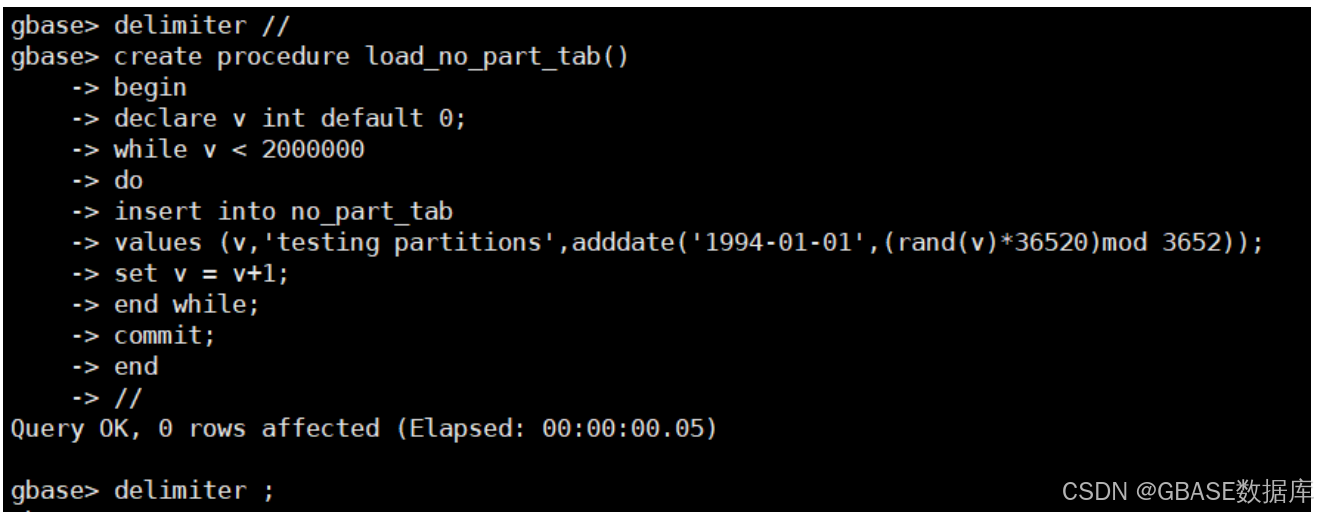
delimiter //
create procedure load_no_part_tab()
begin
declare v int default 0;
while v < 2000000
do
insert into no_part_tab
values (v,'testing partitions',adddate('1994-01-01',(rand(v)*36520)mod 3652));
set v = v+1;
end while;
commit;
end
//
delimiter ;示例如下:
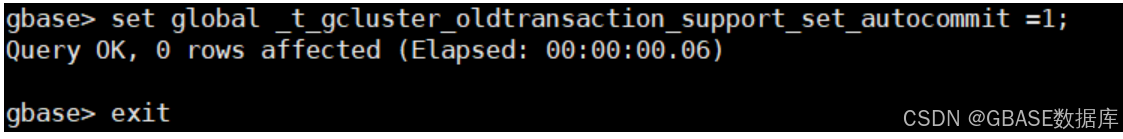
- 关闭事务自动提交参数,使数据插入更快速。
use testdb;
set global _t_gcluster_oldtransaction_support_set_autocommit =1;示例如下:
##重新登陆后使参数生效,执行存储并生成模拟数据##
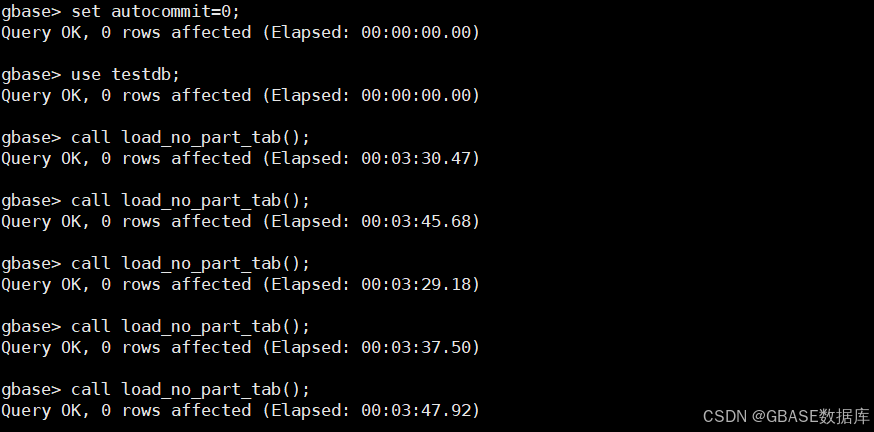
set autocommit=0;
##多执行几次,使数据均匀分布##
call load_no_part_tab();
call load_no_part_tab();
call load_no_part_tab();
call load_no_part_tab();
call load_no_part_tab();
set autocommit=1;示例如下:
- 生成更多数据,使后续查询结果更明显
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;
insert into no_part_tab select * from no_part_tab;示例如下:

- 将普通表数据同步给分区表
insert into part_tab select * from no_part_tab;示例如下:
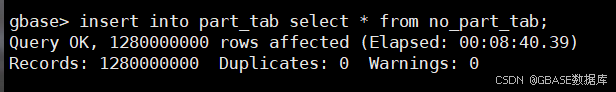
3. 执行查询,对比分区表和普通表的查询速度。
select count(*) from part_tab where c3 > to_date('1995-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1995-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd') and c1 like '252%';
select count(*) from no_part_tab where c3 > to_date('1995-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1995-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd') and c1 like '252%';示例如下:
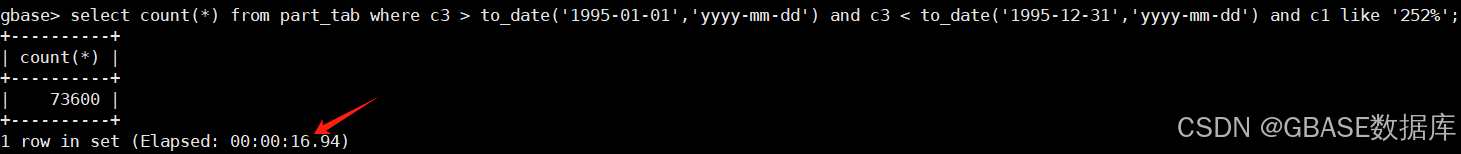
- 跨单个分区表查询只需要16秒,而普通表则需要158秒的时间。
select count(*) from part_tab where c3 > to_date('1995-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1996-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd');
select count(*) from no_part_tab where c3 > to_date('1995-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1996-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd');示例如下: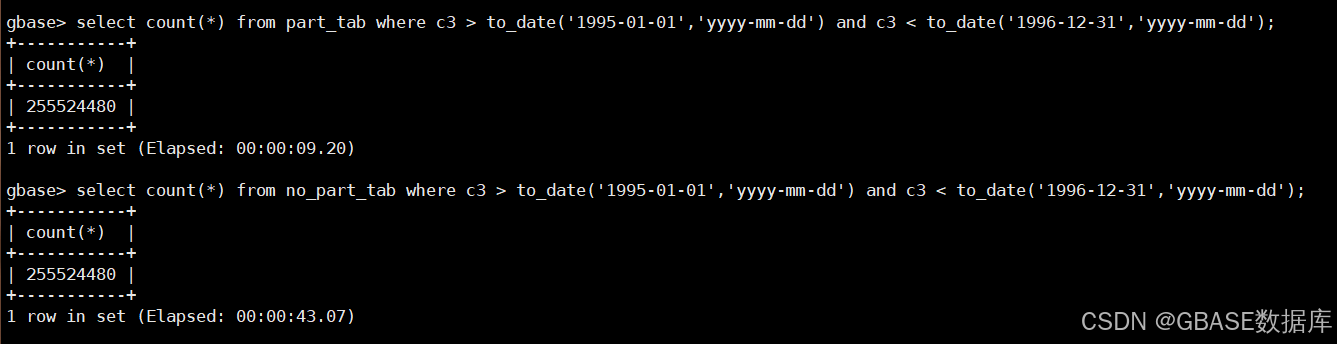
- 跨两个分区表查询只需要9秒,而普通表则需要43秒的时间。
##调整并行度防止内存超出##
set gbase_parallel_degree=8;
##测试update所需时间##
update part_tab set c2='test update' where c3 > to_date('1997-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1997-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd') and c1=151;
update no_part_tab set c2='test update' where c3 > to_date('1997-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and c3 < to_date('1997-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd') and c1=151;示例如下:

跨单个分区的update所需时间为8秒,普通表的整个update更新时间为78秒。
结论
当前数据库版本为953.27.20_patch 9

查询分区表每个分区数据:
select count(*) from part_tab partition(p0);
select count(*) from part_tab partition(p1);
...
...
select count(*) from part_tab partition(p8);
select count(*) from part_tab partition(p9);示例如下:


为方便验证,数据生成的时候设计的就是每个分区数据尽量均匀分布,总共十个分区,所以根据跨单个分区表查询只需要16秒,而普通表则需要158秒,大约十倍;跨两个分区表查询只需要9秒,而普通表则需要43秒的时间,大约5倍;跨单个分区的update也大概为普通表update 的十分之一,即可验证Gbase 8a 分区表的查询只会检索当前分区内的数据,而普通表检索整表数据,性能上会大大优化。
原文链接:https://www.gbase.cn/community/post/4917
更多精彩内容尽在南大通用GBase技术社区,南大通用致力于成为用户最信赖的数据库产品供应商。




















 1751
1751

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








