数据结构:对一组数据而言,这组数据之间存在某种顺序关系,这种关系成为结构。
算法:是为实现某种功能而对数据结构所实施的有限处理步骤。
函数调用:包含头文件即可,一般为.h文件,文件中包含调用函数即可,名字可不一样,形如:
function.h文件中有
int vection(int ){}
调用则为:
int main()
{
int x = vection(int);
}
一、函数知识点:
阶乘:1*2*3*4*5....*n;
int Factorial(int n)
{
int fct = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
fct = fct*i;
return fct;
}
质数:指在大于1的自然数中,除了1和它本身以外不再有其他因数的自然数。
非质数判断:0或1不是质数,大于1且能被小于本身的整数整除,则不是质数
int Prime(int n)
{
if(n==0||n==1)
return 0;
for(int i=2;i<n;i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
return0
}
return 1;
}
最大公约数:
方法:辗转相除法:用second对first求余,若不为0,则second赋值first,余数赋值给second,直到余数为0.second即为最大公约数
int GCD(int first,int second)
{
int rem = first % second;
while(rem!=0)
{
first = second;
second = rem;
rem = first%second;
}
return second;
}
斐波那契数列:前两项都是1,从第3项开始,每项都是前两项之和
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
int fib1 = 1,fib2 = 1;
int fib3 = fib1+fib2;
for(int i=4;i<=n;i++)
{
fib1 = fib2;
fib2 = fib3;
fib3 = fib1+fib2;
}
return fib3;
}
π的近似值:格里高利公式:4*(1-1/3+1/5-1/7...)
double CircumRatio(double er)
{
double term; //用于存储单个项
double abs; //用于存储单个项的绝对值
double accum=0;//用于存储逐项累加结果
int i=1;
int sign=1;
while(1)
{
term=sign*(1.0/(2*i-1)); //分子为1.0
accum+=term;
abs=term>0?term:-term;
if(abs<er)
break;
i++;
sign = -sign;
}
accum = 4*accum;
return accum;
}
杂记:
指针理解:指针即指向地址,即可认为若p为指针,则*p为存储的值,&a为地址,类比为p = &a,即p也为地址
数组:int a[10] = {1,5,2,6} 等价于{1,5,2,6,0,0,0,0,0,0}
数组的传入也可用指针代替,如: **int Inter(int *p,int n){} 等价于int Inter(int a[],int n);**
const表示该数据只读取,不修改,且仅在该函数内有效,
动态数组的建立:new
函数指针: 类型(*函数指针名)(形参列表) //类型*(指针名)(形参列表),返回值为指针
结构指针:如有:
struct List L; //结构对象 struct List *l =&L;//结构指针l指向结构对象L,则有:
L.data,L.size,L.max等价于l->data,l->size,l->max/等价于(*l).data
typedef起别名: typedef int T; //将int等价于T
C++中引用为深复制,即对深层对象的复制
二、结构、联合、枚举、二维数组和指针
把一组有关联的对象封装在一起的是结构,把一组有关联的、共用 一个地址的对象封装在一起的是联合,把一组有关联的命名常量封装在一起是枚举。
结构数组:Date a[3]={{20,1,4},{24,5,8},{16,4,1}};//a[i].data;等价于(a+i)->data;
二维数组:int a[][3] = {};//列数必须有
二维数组指针:int a[2][3]; int (*p)[3]; p=a; 或者 int (*p)[3] = a; 则p[i]+j与a[i]+j等价
p[i][j]=a[i][j];
指针数组:char * a[6]; 字符型指针数组,每个数组元素都是字符型指针,用来指向数组中每个元素
二级指针:char **p;p是指针的指针,其值为字符型指针的地址,即指向一个字符型指针,即p[i] = "字符串";
三、字符串、链表
字符串:特殊的数组、特殊的顺序表,结尾带有结束符\0
字符串长度是有效字符长度,不含结束符
字符串赋值: char str[]="abcd"; //char *p; p="china"; str[0]='a',p[0]='c';
条件结束符,str[i]='\0';
字符串输入输出:输入:char *gets(char* s); 输出: int puts(const char* s);
链表:可随机插入、删除数据元素的顺序表
结点结构: //一个结点是一个结构对象,有三个数据成员,数据元素、前驱和后继指针
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
int struct Node Node;
链表有三个数据成员:size:数据结点个数、还有两个结点指针,一个是head,指向头结点,一个是tail,指向尾结点
链表插入:(在itr前插入q)
Node *p = itr;
p->pre->next = new Node *q;
p->pre = p->pre->next;
链表删除:(删除itr)
Node *p=itr;
Node *re=p->next;
p->pre->next=p->next;
p->next->pre=p->pre;
delete(p);
链表逆置:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=6;
typedef int DataType;//类型定义
typedef struct node{ //单链表
DataType data;
struct node* next;
}LinkedNode,*LinkList;
/****由数组创建单链表****/
LinkList CreateList(DataType a[N])
{
LinkedNode* ListHead=new LinkedNode();
ListHead->data=a[0];
ListHead->next=NULL;
for(int i=N-1;i>=1;i--)
{
LinkedNode* p=new LinkedNode();
p->data=a[i];
p->next=ListHead->next;
ListHead->next=p;
}
return ListHead;
}
/****输出单链表****/
void PrintList(LinkList ListHead)
{
if(NULL==ListHead)cout<<"The List is empty!"<<endl;
else
{
LinkedNode* p=ListHead;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
void ReverseList(LinkedNode* pCur,LinkList& ListHead)
{
if( (NULL==pCur)||(NULL==pCur->next) )
{
ListHead=pCur;
}
else
{
LinkedNode* pNext=pCur->next;
ReverseList(pNext,ListHead); //递归逆置后继结点
pNext->next=pCur; //将后继结点指向当前结点。
pCur->next=NULL;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
LinkedNode* list=CreateList(a);
PrintList(list);
LinkedNode*pTemp=list;
ReverseList(pTemp,list);
PrintList(list);
return 0;
}
著名问题:约瑟夫环(Josephus):待更新(链表、栈、队列、数组)
数组方法:
// 每出列一个,就往前移动数组
// 用求余解决到尾问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void JosePhus(int n, int m, int start) {
int i, *arr = new int[n]; // 动态分配数组
int count; // 保存当前已站出来的人数
for(i = 0;i < n; i++) // 初始化,把各位置号存入数组中
arr[i] = i + 1;
count = 1;
start--; // 因为数组下标从0开始,所以要减1
while(count < n) { // 当前已站出来的人数
cout << arr[start] << ","; // 输出当前要站出来的人的位置号
for(i = start; i < (n - count); i++)
arr[i] = arr[i+1]; // 把位置号前移
// start + m - 1:减1是因为该位置号的人已出列,位置号前移了一位
// n - count: 当前剩下的人数
start = (start + m - 1) % (n - count); // 考虑到尾了,要从头开始,所以用取余,或者用判断方法
count++;
}
cout << arr[0] << "\n";
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
int n, m, start; // n:人数 m:数到多少出列 start:开始位置
cout << "请输入n,m,start:\n";
while(cin >> n >> m >> start) {
JosePhus(n, m, start); // 调用解决约瑟夫问题的函数
cout << "请输入n,m,start:\n";
}
return 0;
}
四、string类
插入、删除、取子串、比较、查找、
初始化:使用等号的初始化叫做拷贝初始化,不使用等号的初始化叫做直接初始化。
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;//默认初始化,一个空字符串
string s1("ssss");//s1是字面值“ssss”的副本
string s2(s1);//s2是s1的副本
string s3=s2;//s3是s2的副本
string s4(10,'c');//把s4初始化
string s5="hiya";//拷贝初始化
string s6=string(10,'c');//拷贝初始化,生成一个初始化好的对象,拷贝给s6
char cs[]="12345";
string s7(cs,3);//复制字符串cs的前3个字符到s当中
//string s(s2,pos2)
string s8="asac";
string s9(s8,2);//从s2的第二个字符开始拷贝,不能超过s2的size
//string s(s2,pos2,len2)
string s10="qweqweqweq";
string s11(s10,3,4);//s4是s3从下标3开始4个字符的拷贝,超过s3.size出现未定义
return 0;
}
插入操作:
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str="to be question";
string str2="the ";
string str3="or not to be";
string::iterator it;
//s.insert(pos,str)//在s的pos位置插入str
str.insert(6,str2); // to be the question
//s.insert(pos,str,a,n)在s的pos位置插入str中插入位置a到后面的n个字符
str.insert(6,str3,3,4); // to be not the question
//s.insert(pos,cstr,n)//在pos位置插入cstr字符串从开始到后面的n个字符
str.insert(10,"that is cool",8); // to be not that is the question
//s.insert(pos,cstr)在s的pos位置插入cstr
str.insert(10,"to be "); // to be not to be that is the question
//s.insert(pos,n,ch)在s.pos位置上面插入n个ch
str.insert(15,1,':'); // to be not to be: that is the question
//s.insert(s.it,ch)在s的it指向位置前面插入一个字符ch,返回新插入的位置的迭代器
it = str.insert(str.begin()+5,','); // to be, not to be: that is the question
//s.insert(s.it,n,ch)//在s的it所指向位置的前面插入n个ch
str.insert (str.end(),3,'.'); // to be, not to be: that is the question...
//s.insert(it,str.ita,str.itb)在it所指向的位置的前面插入[ita,itb)的字符串
str.insert (it+2,str3.begin(),str3.begin()+3); // to be, or not to be: that is the question...
return 0;
}
删除操作:(迭代器左闭右开)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string str ("This is an example sentence.");
cout << str << '\n'; // "This is an example sentence."
str.erase (10,8); // ^^^^^^^^
//直接指定删除的字符串位置第十个后面的8个字符
cout << str << '\n'; // "This is an sentence."
str.erase (str.begin()+9);// ^//删除迭代器指向的字符
cout << str << '\n';
str.erase (str.begin()+5, str.end()-9);
//删除迭代器范围的字符
cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
子串:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s="abcdefg";
//s.substr(pos1,n)返回字符串位置为pos1后面的n个字符组成的串
string s2=s.substr(1,5);//bcdef
//s.substr(pos)//得到一个pos到结尾的串
string s3=s.substr(4);//efg
return 0;
}
append和replace操作:
append函数可以用来在字符串的末尾追加字符和字符串。由于string重载了运算符,也可以用+=操作实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
string str;
string str2="Writing ";
string str3="print 10 and then 5 more";
//直接追加一个str2的字符串
str.append(str2); // "Writing "
//后面追加str3第6个字符开始的3个字符串
str.append(str3,6,3); // "10 "
//追加字符串形参的前5个字符
str.append("dots are cool",5); // "dots "
//直接添加
str.append("here: "); // "here: "
//添加10个'.'
str.append(10u,'.'); // ".........."
//添加str3迭代器范围的字符串
str.append(str3.begin()+8,str3.end()); // " and then 5 more"
//最后这个比较特殊,意思是添加5个'A',实际上参数里面的65对应的asc码就是65
str.append<int>(5,65); // "....."
//字符串追加也可以用重载运算符实现
str+="lalala";
cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
repalce顾名思义,就是替换的意思,先删除,后增加。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
string base="this is a test string.";
string str2="n example";
string str3="sample phrase";
string str4="useful.";
// replace signatures used in the same order as described above:
// Using positions: 0123456789*123456789*12345
string str=base; // "this is a test string."
//第9个字符以及后面的4个字符被str2代替
str.replace(9,5,str2); // "this is an example string." (1)
//第19个字符串以及后面的5个字符用str的第7个字符以及后面的5个字符代替
str.replace(19,6,str3,7,6); // "this is an example phrase." (2)
//第8个字符以及后面的9个字符用字符串参数代替
str.replace(8,10,"just a"); // "this is just a phrase." (3)
//第8个字符以及后面的5个字符用字符串参数的前7个字符替换
str.replace(8,6,"a shorty",7); // "this is a short phrase." (4)
//第22以及后面的0个字符用3个叹号替换
str.replace(22,1,3,'!'); // "this is a short phrase!!!" (5)
//迭代器的原理同上
// Using iterators: 0123456789*123456789*
str.replace(str.begin(),str.end()-3,str3); // "sample phrase!!!" (1)
str.replace(str.begin(),str.begin()+6,"replace"); // "replace phrase!!!" (3)
str.replace(str.begin()+8,str.begin()+14,"is coolness",7); // "replace is cool!!!" (4)
str.replace(str.begin()+12,str.end()-4,4,'o'); // "replace is cooool!!!" (5)
str.replace(str.begin()+11,str.end(),str4.begin(),str4.end());//"replace is useful."(6)
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
assign操作:
assign操作在一起列容器当中都存在,比如vector等等。是一个很基本的操作函数,string使用assign可以灵活的对其进行赋值。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
string str;
string base="The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.";
// used in the same order as described above:
//直接把base赋值给str
str.assign(base);
cout << str << '\n';
//把base第10个字符以及后面的8个字符赋给str
str.assign(base,10,9);
cout << str << '\n'; // "brown fox"
//把参数中的0到6个字符串赋给str
str.assign("pangrams are cool",7);
cout << str << '\n'; // "pangram"
//直接使用参数赋值
str.assign("c-string");
cout << str << '\n'; // "c-string"
//给str赋值10个'*'字符
str.assign(10,'*');
cout << str << '\n'; // "**********"
//赋值是10个'-'
str.assign<int>(10,0x2D);
cout << str << '\n'; // "----------"
//指定base迭代器范围的字符串
str.assign(base.begin()+16,base.end()-12);
cout << str << '\n'; // "fox jumps over"
return 0;
}
find和rfind函数:
find函数主要是查找一个字符串是否在调用的字符串中出现过,大小写敏感。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str ("There are two needles in this haystack with needles.");
string str2 ("needle");
// different member versions of find in the same order as above:
//在str当中查找第一个出现的needle,找到则返回出现的位置,否则返回结尾
size_t found = str.find(str2); //size_t为类型,一般与int类似,相当于unsigned
if (found!=string::npos)
cout << "first 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
//在str当中,从第found+1的位置开始查找参数字符串的前6个字符
found=str.find("needles are small",found+1,6);
if (found!=std::string::npos)
cout << "second 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
//在str当中查找参数中的字符串
found=str.find("haystack");
if (found!=std::string::npos)
cout << "'haystack' also found at: " << found << '\n';
//查找一个字符
found=str.find('.');
if (found!=std::string::npos)
cout << "Period found at: " << found << '\n';
//组合使用,把str2用参数表中的字符串代替
// let's replace the first needle:
str.replace(str.find(str2),str2.length(),"preposition");
cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
rfind函数就是找最后一个出现的匹配字符串,返回的位置仍然是从前往后数的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str ("The sixth sick sheik's sixth sheep's sick.");
string key ("sixth");// ^
//rfind是找最后一个出现的匹配字符串
size_t found = str.rfind(key);
if (found!=std::string::npos)
{
cout<<found<<endl;//输出23
str.replace (found,key.length(),"seventh");//找到的sixth替换成seventh
}
cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
参见:https://blog.csdn.net/tengfei461807914/article/details/52203202
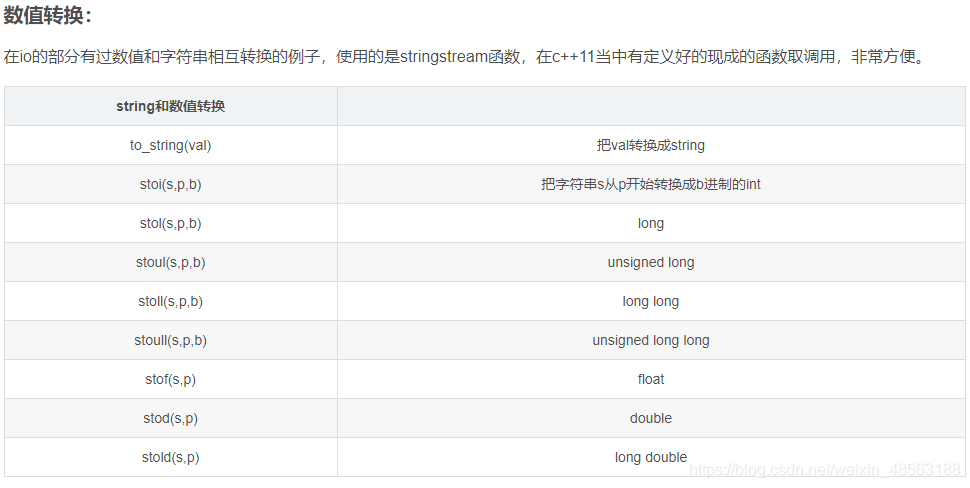
五、链表类
参见: https://blog.csdn.net/slimmm/article/details/84317806
增删改查
数据结构定义:
class node{
public:
node *prev;
node *next;
uint32_t data;
};
typedef class node Node,*pNode;
class list:public node{
public:
list(){ //构造一个链表头
head = new Node;
list_len = 0;
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
list_len++;
cout << "list Head:" << head << endl;
}
~list(){
head = NULL;
delete head;
}
//add and delete
pNode list_addhead(uint32_t dat); //头插
pNode list_addtail(uint32_t dat); //尾插
pNode list_add(uint16_t coord, uint32_t dat); //按位置插入
pNode list_delhead(void); //头删
pNode list_deltail(void); //尾删
pNode list_del(uint16_t coord); //按位置删除
pNode list_delnode(pNode node); //按节点地址删除
//find and change
pNode list_sortval(void); //值排序,交换值,不改变节点
pNode list_sortnode(void); //值排序,直接交换节点
pNode list_findval(uint32_t dat); //值查找
uint32_t list_findcursor(uint16_t cnt); //位置查找
pNode list_changeval(uint32_t src_dat, uint32_t des_dat){ //修改值
pNode tmp = NULL;
tmp = list_findval(src_dat);
if(tmp != head){ //find effective value
tmp->data = des_dat;
}
return head;
}
pNode list_changecursorval(uint16_t cnt, uint32_t des_dat){ //修改特定位置的值
if(cnt >= get_list_len()){
cout << "param error!!!" << endl;
return 0;
}
pNode tmp = head;
while(cnt--){
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->data = des_dat;
return head;
}
pNode list_getnode(uint16_t cnt){ //获取节点位置
if(cnt == 0 || cnt >= get_list_len()){
cout << "param error!!!" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << "cnt: " << cnt <<"\t";
pNode tmp = head;
while(cnt--){
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return tmp;
}
pNode list_changenode(pNode src_node, pNode des_node); //交换节点
uint32_t get_list_len(void){ //获取链表长度
return list_len;
}
pNode list_clear(void){ //清除链表
pNode cursor = head->next;
while(cursor != head){
head->next = cursor->next;
cursor->next->prev = head;
list_len--;
cursor = cursor->next;
delete(cursor);
}
return head;
}
void list_print(void){ //链表打印
if(NULL == head){
cout << "head point empty!!!" << endl;
return;
}
if(head == head->next){
cout << "List empty" << endl;
return;
}
pNode tmp = head->next;
while(tmp != head){
cout << "P:" << tmp << "\tData:" << tmp->data+0 << endl;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
protected:
private:
pNode head = NULL;
uint16_t list_len;
};
链表插入:
pNode list::list_addhead(uint32_t dat){
if(NULL == head) list();
pNode tmp = new Node;
if(tmp == head) tmp = new Node;
list_len++;
tmp->next = head->next;
tmp->prev = head;
head->next->prev = tmp;
head->next = tmp;
tmp->data = dat;
return head;
}
pNode list::list_addtail(uint32_t dat){
if(NULL == head) list();
pNode tmp = new Node;
list_len++;
tmp->prev = head->prev;
tmp->next = head;
head->prev->next = tmp;
head->prev = tmp;
tmp->data = dat;
return head;
}
pNode list::list_add(uint16_t coord, uint32_t dat){
if(NULL == head) list();
pNode tmp = new Node;
pNode cursor = head->next;
list_len++;
while(coord--){
cursor = cursor->next;
}
tmp->prev = cursor->prev;
tmp->next = cursor;
cursor->prev->next = tmp;
cursor->prev = tmp;
tmp->data = dat;
return head;
}
链表删除:
pNode list::list_delhead(void){
if((NULL==head) || (head->next==head)){
cout << "List is empty" << endl;
return head;
}
pNode tmp = head->next;
head->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next->prev = head;
list_len--;
delete tmp;
}
pNode list::list_deltail(void){
if((NULL==head) || (head->next==head)){
cout << "List is empty" << endl;
return head;
}
pNode tmp = head->prev;
head->prev = tmp->prev;
tmp->prev->next = head;
list_len--;
delete tmp;
}
pNode list::list_del(uint16_t coord){
if((NULL==head) || (head->next==head)){
cout << "List is empty" << endl;
return head;
}
if(coord >= get_list_len()){
cout << "param error!!!" << endl;
return head;
}
pNode cursor = head->next;
pNode tmp = NULL;
while(coord--){
cursor = cursor->next;
}
tmp = cursor;
cursor->prev->next = cursor->next;
cursor->next->prev = cursor->prev;
list_len--;
delete cursor;
}
pNode list::list_delnode(pNode node){
pNode tmp = head->next;
while(tmp != head){
if(node == tmp){
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
list_len--;
delete node;
cout << "delete Node success" << endl;
return head;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
cout << "Not find this Node" << endl;
return head;
}
链表查找:
pNode list::list_findval(uint32_t dat){ //值查找:检索链表是是否有该值,有的话返回该节点的位置;
pNode tmp = head->next;
while(tmp != head){
if(dat == tmp->data){
cout << "find dat:" << dat << "\taddr:" << tmp << endl;
return tmp;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
cout << "Not find dat" << endl;
return head;
}
uint32_t list::list_findcursor(uint16_t cnt){ //位置查找:查找链表的第n个节点的值是多少,并返回该值;
if(cnt >= get_list_len()){
cout << "param error!!!" << endl;
return 0;
}
pNode tmp = head;
while(cnt--){
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return tmp->data;
}
链表的节点替换:
pNode list::list_changenode(pNode src_node, pNode des_node){
pNode tmp = head->next;
uint8_t flag = 0;
cout << "\n\nsrc_node:" << src_node << "\tdes_node:" << des_node << endl;
if(src_node == des_node){
cout << "desNode equel desNode" << endl;
return head;
}
while(tmp != head){
if((tmp==src_node) || (tmp==des_node)){
flag++;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if(2 != flag){
cout << "pNode param error" << endl;
return head;
}
if(src_node->next == des_node){
src_node->prev->next = src_node->next;
src_node->next->prev = src_node->prev;
src_node->next = des_node->next;
src_node->prev = des_node;
des_node->next->prev = src_node;
des_node->next = src_node;
}else if(des_node->next == src_node){
des_node->prev->next = des_node->next;
des_node->next->prev = des_node->prev;
des_node->next = src_node->next;
des_node->prev = src_node;
src_node->next->prev = des_node;
src_node->next = des_node;
}else{
pNode pSrc = src_node->prev;
pNode pDes = des_node->prev;
src_node->prev->next = src_node->next;
src_node->next->prev = src_node->prev;
src_node->next = pDes->next;
src_node->prev = pDes;
pDes->next->prev = src_node;
pDes->next = src_node;
des_node->prev->next = des_node->next;
des_node->next->prev = des_node->prev;
des_node->next = pSrc->next;
des_node->prev = pSrc;
pSrc->next->prev = des_node;
pSrc->next = des_node;
}
return head;
}
链表的排序:
pNode list::list_sortval(void){ //进行升序排序,只交换值,节点不做更改;
uint16_t len = get_list_len();
for(uint16_t i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(uint16_t j=0;j<len-i-1;j++){
if(list_findcursor(j) > list_findcursor(j+1)){
uint32_t tmp = list_findcursor(j+1);
list_changecursorval(j+1, list_findcursor(j));
list_changecursorval(j, tmp);
}
}
}
return head;
}
pNode list::list_sortnode(void){ //进行升序排序,直接交换节点的位置。
uint16_t len = get_list_len();
for(uint16_t i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(uint16_t j=0;j<len-i-1;j++){
if(list_findcursor(j) > list_findcursor(j+1)){
list_changenode(list_getnode(j), list_getnode(j+1));
}
}
}
return head;
}
插入:定点插入、首插和尾插
删除:定点删除、首删和尾删
清表和析构
链栈
链队列
链表类模板:
template<class T>
class List
{
struct Node
{
T data;
Node *pre,*next;
Node(const T& d=T(),Node *p=0,Node *n=0):
data(d),pre(p),next(n){} //默认构造
};
int size;
Node *head;
Node *tail;
void Init(){size=0;head =new Node;tail=new Node;head->next=tail;tail->pre=head;} //初始化函数
public:
List(){Init(;)
}
int Size()const{return size;}
int Empty()const{return size=0;}
};
后续补充:
命名空间 using namespace std 为 using namespace 空间名: std::cout限制域




 本文详细介绍了数据结构中的关键概念,包括阶乘、质数判断、最大公约数、斐波那契数列和π的近似值等。此外,深入剖析了函数、指针、数组、结构、联合、枚举、链表、字符串和字符串处理技巧。重点讲解了链表操作,如插入、删除、查找和排序,以及string类中的插入、删除、子串和字符串操作。还涉及了链表类模板,包括增删改查和排序算法。
本文详细介绍了数据结构中的关键概念,包括阶乘、质数判断、最大公约数、斐波那契数列和π的近似值等。此外,深入剖析了函数、指针、数组、结构、联合、枚举、链表、字符串和字符串处理技巧。重点讲解了链表操作,如插入、删除、查找和排序,以及string类中的插入、删除、子串和字符串操作。还涉及了链表类模板,包括增删改查和排序算法。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








