第一版:是不同的线程各卖各的,会导致最终买了300张票
因为 100 放在局部变量,每个线程人手一个
/*
使用多线程来买票的案例
有 3 个窗口,一共是 100 张票
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void *sellticket(void*arg){
int ticket = 100;
while (ticket > 0)
{
printf("%ld is selling the %d ticket.\n",pthread_self(),ticket);
ticket--;
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void){
//创建3个子线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
//回收子线程的资源
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
//设置线程分离
// pthread_detach(tid1);
// pthread_detach(tid2);
// pthread_detach(tid3);
//退出主线程
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
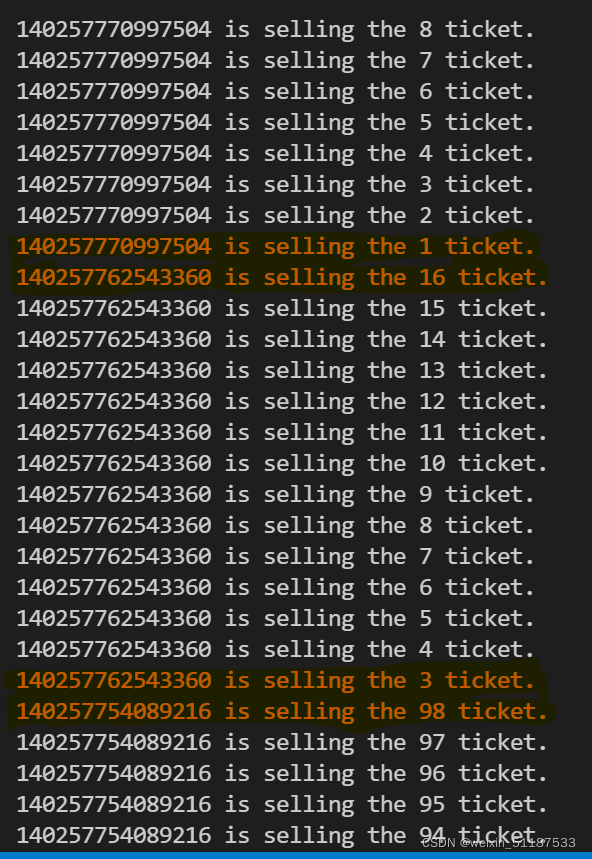
第二版:即使设置了全局变量,也会出现前一个线程更改了但是后面的线程没有得到更改后的数据的情况。
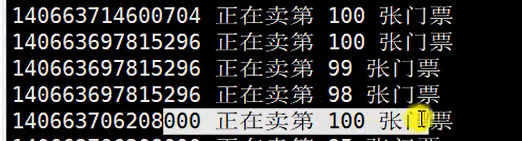
第三版:让每个线程休眠 3000 ms ,结果之前重复更改某个数据的效果更明显了
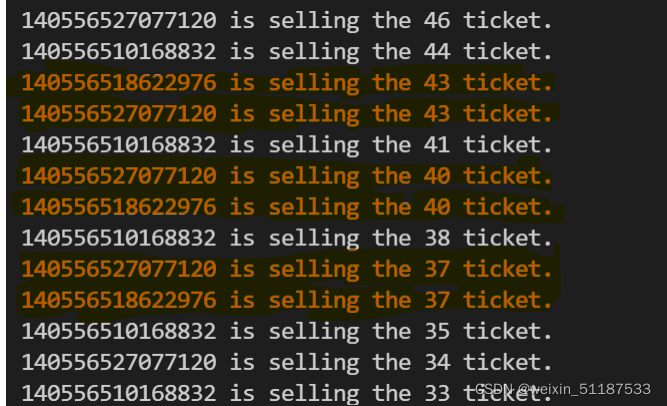
第四版:改成 sleep 6000 ms 有惊喜,居然出现了负数!!!
/*
使用多线程来买票的案例
有 3 个窗口,一共是 100 张票
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int ticket = 100;
void *sellticket(void*arg){
while (ticket > 0)
{
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld is selling the %d ticket.\n",pthread_self(),ticket);
ticket--;
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void){
//创建3个子线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
//回收子线程的资源
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
//设置线程分离
// pthread_detach(tid1);
// pthread_detach(tid2);
// pthread_detach(tid3);
//退出主线程
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
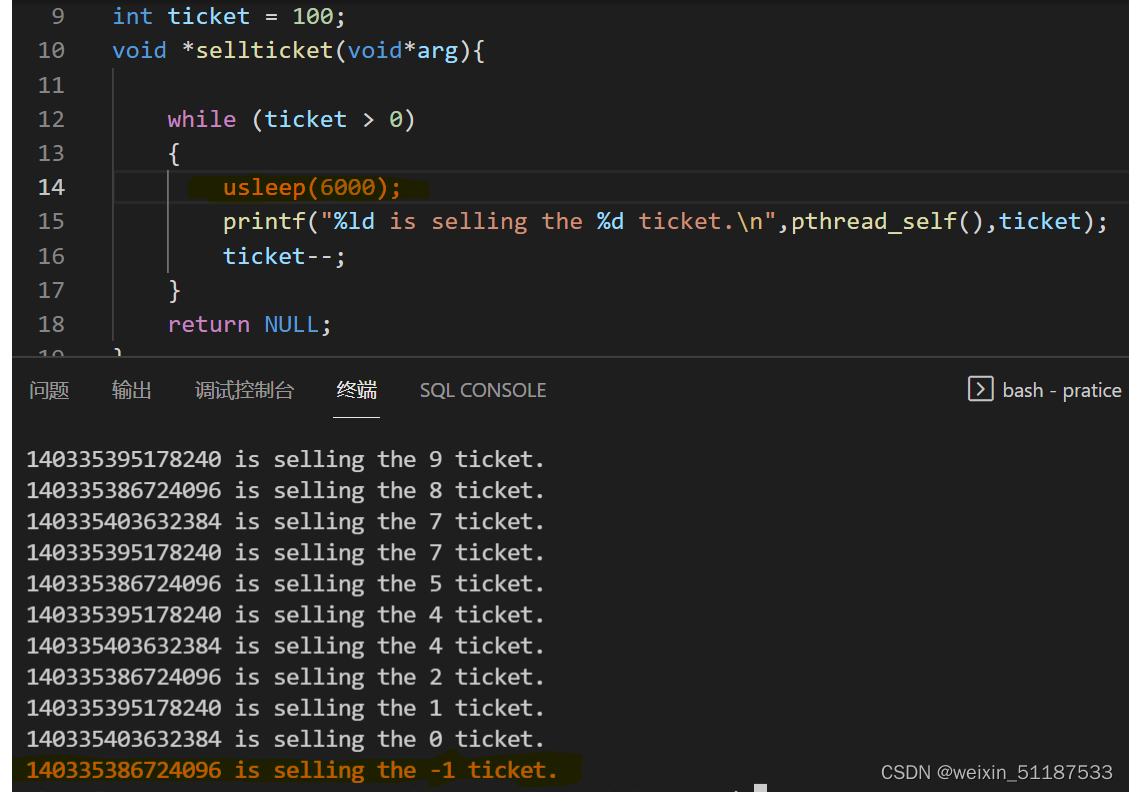
为什么会产生负数呢?
剩下最后一张票的时候,(i = = 1)
线程1、线程2、线程3 一起抢占 CPU,
当线程 1 进来的时候,符合条件(i= = 1 > 0),进入循环,线程 1 被迫休眠;
交给线程 2 ,线程 2 符合条件(i= = 1 > 0),进入循环,线程 2 也被迫休眠;
交给线程 3 ,线程 3 符合条件(i= = 1 > 0),进入循环,线程 3 也被迫休眠;
线程 1 醒来的时候 ,接着循环,–i ,最终 i = = 0;
线程 2 醒来的时候 ,接着循环,–i ,最终 i = = -1;
线程 3 醒来的时候 ,接着循环,–i ,最终 i == -2;
因为醒过来后再次执行就没有判断了
如何解决呢?
1)对 变量 i 进行操作的时候,其他的线程不能对 i 进行操作;
2)线程进行一系列的操作的时候,那些操作必须是原子操作。不能做到一半其他的线程进入了循环
加上互斥量
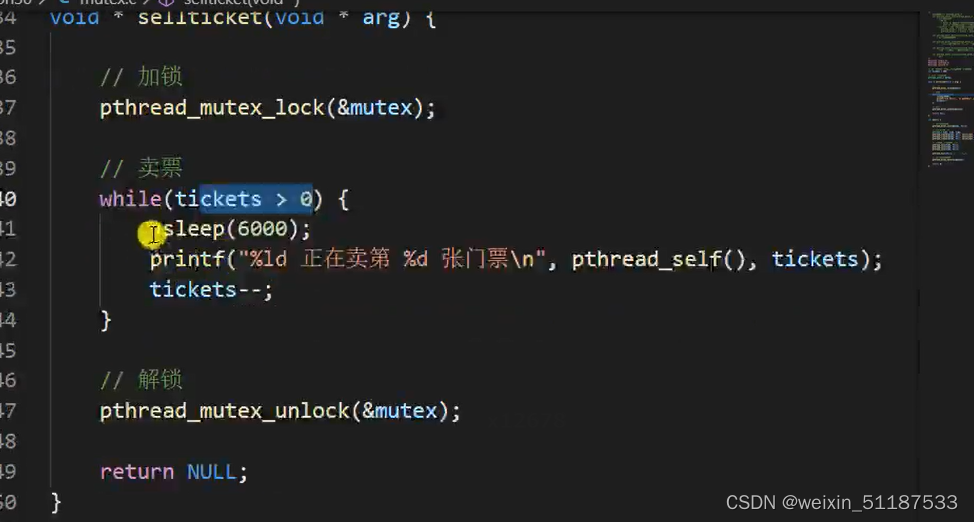
在进入临界区前加锁,但是这样会有一个问题:
最终的执行结果都是由同一个线程来执行的。
为什么会出现这种情况?
那样写的加锁的逻辑是:加锁进入循环,等到循环完了才会解锁,而循环结束的了票已经卖完了。
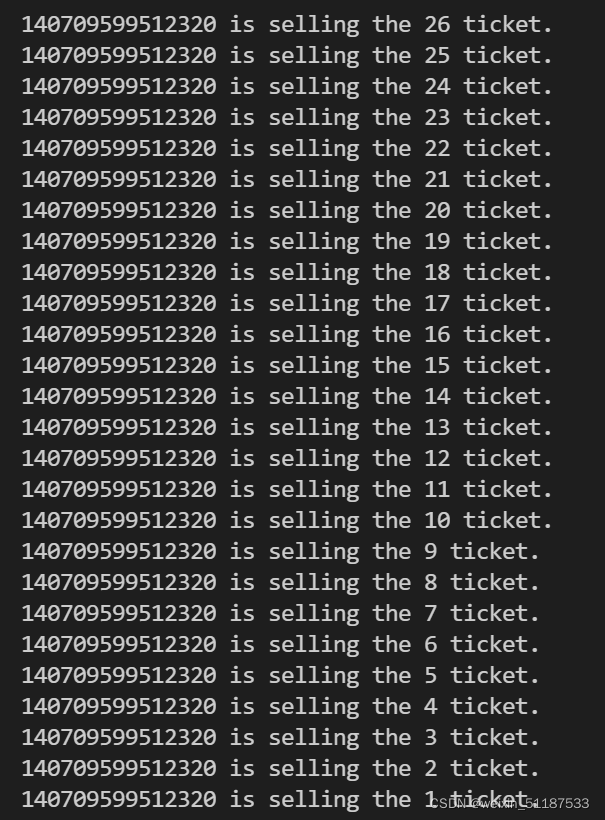
最后改成:循环可以随便进,对数据量进行修改的时候要加锁。
/*
互斥量的类型 pthread_mutex_t
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
- 初始化互斥量
- mutex 需要初始化的互斥量变量
- attr 互斥量相关的属性,传递 NULL 使用默认的属性
- restrict : C语言的修饰符,被修饰的指针不能由另外的指针进行操作
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex = xxx;
pthread_mutex_t * mutex1 = mutex;
(有了 restrict 的限制,mutex1 不能对 mutex 进行操作)
(这个操作符就是限定一个对象所享有的指针的操作权限。)
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 释放互斥量的资源
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 加锁,阻塞的,如果有一个线程加锁,其他的线程只能阻塞等待
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 尝试加锁,如果加锁失败,不会阻塞,会直接返回
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 解锁
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int ticket = 1000;
//创建一个互斥量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
// //第一版写法:最终只有一个线程在卖票
// void *sellticket(void*arg){
// //加锁
// pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
// //业务逻辑
// while (ticket > 0)
// {
// usleep(6000);
// printf("%ld is selling the %d ticket.\n",pthread_self(),ticket);
// ticket--;
// }
// //解锁
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
// return NULL;
// }
//第二版写法
void *sellticket(void*arg){
// //加锁
// pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//业务逻辑
while (1)
{
//加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(ticket > 0){
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld is selling the %d ticket.\n",pthread_self(),ticket);
ticket--;
}else{
//这里也需要解锁,否则跳出了循环不会释放锁造成线程无法结束
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void){
//初始化互斥量
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//创建3个子线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,sellticket,NULL);
//回收子线程的资源
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
//退出主线程
pthread_exit(NULL);
//释放互斥量资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
最终的运行结果:能够看到线程的切换





















 1751
1751











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








