一、判断两个二叉树是否相同
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
如果当前节点都为null,返回true;
如果有一个为null,另外一个不为null,返回false;
如果对应位置的val不同,返回fasle;
递归遍历左子树和右子树。
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null)return true;
if(p==null||q==null)return false;
if(p.val!=q.val)return false;
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&&isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}二、判断一个树是不是另外一个树的子树
572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
变相的判断两个树是否相同,
如果一个树是另外一个树的子树,那么这个树要么和他的左子树相同,要么和他的右子树相同,要么就是完全相同
那么只需要递归判断他的每一个子树是否和他相同就ok
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root==null)return false;
return isSametree(root,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);
}
public boolean isSametree(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null)return true;
if(p==null||q==null)return false;
if(p.val!=q.val)return false;
return isSametree(p.left,q.left)&&isSametree(p.right,q.right);
}三、求二叉树的最大深度
104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}四、判断一个二叉树是否为平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
①自底向上进行判断,如果当前节点不是平衡的,返回-1,否则,返回当前节点的高度
判断条件:只要当前节点的左子树或者右子树有一个不平衡或者左子树减去右子树的高度的绝对值>1,那么这个节点就不是平衡的,返回值为-1
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(height(root)==-1){
return false;
}
return true;
}
public int height(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int left=height(root.left);
int right=height(root.right);
if(left==-1||right==-1||Math.abs(left-right)>1){
return -1;
}else{
return Math.max(left,right)+1;
}
}②自顶向下进行判断:
从根节点开始,求左子树的深度和右子树的深度,进行判断
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int leftHight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHight = maxDepth(root.right);
return leftHight > rightHight ?leftHight+1:rightHight+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
//根节点为空,平衡二叉树
if(root==null) return true;
//求左子树和右子树的深度
int leftHight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHight = maxDepth(root.right);
//如果左子树-右子树的深度绝对值大于1,不是平衡二叉树
if(Math.abs(leftHight-rightHight)>1)return false;
//递归判断左子树和右子树是不是平衡二叉树
return isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right);
}五、对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
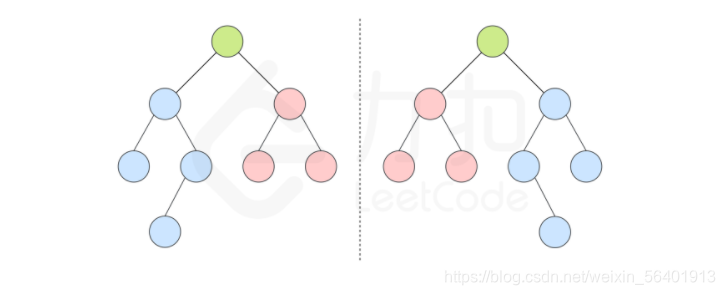
①递归写法
只要能找到对应位置,对当前位置的两个节点进行简单判断就可以
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return true;
return same(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean same(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null){
return true;
}
if(p==null||q==null||p.val!=q.val){
return false;
}
return same(p.left,q.right)&&same(p.right,q.left);
}②迭代写法
使用队列按照要比较的顺序存储节点
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return same(root);
}
public boolean same(TreeNode root){
Queue<TreeNode>queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode a=queue.poll();
TreeNode b=queue.poll();
if(a==null&&b==null){
continue;
}
if(a==null||b==null||a.val!=b.val){
return false;
}
queue.offer(a.left);
queue.offer(b.right);
queue.offer(a.right);
queue.offer(b.left);
}
return true;
}六、二叉树的层序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:用队列存储节点
一层一层的处理结点,保证该层结点处理完成后,队列中只有下一层的所有结点
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode>queue=new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)return lists;
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int ret=queue.size();
List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
while(ret!=0){
ret--;
TreeNode cur=queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
lists.add(list);
}
return lists;
}七、二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
递归查找,以root为根查找p和q,如果root==null || root==q || root==p,走到头,或者找到了都要返回,表示对当前的树已经查找完了,,然后对他的左右子树进行查找
如果在左右子树查找的值都不为null,说明此时的root就是祖先
如果其中一个为null,那么说明p或者q存在于一边,最先找到的就是祖先
返回都是null,说明不在当前的树里,返回null
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null){
return root;
}
if(root==p||root==q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null&&right!=null){
return root;
}else if(left!=null){
return left;
}else if(right!=null){
return right;
}
return null;
}八、二叉搜索树构建双向链表
二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
直接中序遍历即可,用pre指向前序结点,head指向当前结点,在中序遍历的过程过建立连接
public class Solution {
public TreeNode pre;
public TreeNode head;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null)return null;
pre=null;
ino(pRootOfTree);
return head;
}
public void ino(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return;
ino(root.left);
if(pre==null){
pre=root;
head=pre;
}else{
pre.right=root;
root.left=pre;
pre=root;
}
ino(root.right);
九、根据中序遍历和前序遍历构建二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:递归+区间分治,通过当前节点的值找到左子树和右子树的范围,在确定范围内建立左子树和右子树
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return creat(preorder,0,preorder.length-1,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode creat(int[]pre,int ps,int pe,int[]ino,int is,int ie){
if(ps>pe||is>ie){
return null;
}
int rootval=pre[ps];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootval);
int index=0;
for(int i=is;i<=ie;i++){
if(rootval==ino[i]){
index=i;
break;
}
}
int mid=index-is;
root.left=creat(pre,ps+1,ps+mid,ino,is,index-1);
root.right=creat(pre,ps+mid+1,pe,ino,index+1,ie);
return root;
}
}十、从中序和后序遍历构建二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
因此根据上文所述,我们可以发现后序遍历的数组最后一个元素代表的即为根节点。知道这个性质后,我们可以利用已知的根节点信息在中序遍历的数组中找到根节点所在的下标,然后根据其将中序遍历的数组分成左右两部分,左边部分即左子树,右边部分为右子树,针对每个部分可以用同样的方法继续递归下去构造。。
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return creat(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode creat(int[]ino,int is,int ie,int[]pos,int ps,int pe){
if(is>=ie){
return null;
}
if(ie-is==1){
return new TreeNode(ino[is]);
}
int rootval=pos[pe-1];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootval);
int index=0;
for(int i=is;i<ie;i++){
if(ino[i]==rootval){
index=i;
break;
}
}
root.left=creat(ino,is,index,pos,ps,ps+index-is);
root.right=creat(ino,index+1,ie,pos,ps+index-is,pe-1);
return root;
}




















 670
670










