C# 程序在 Windows 7 中自我提升权限
Introduction
User Account Control (UAC) is a new security component inWindows Vista and newer operating systems. With UAC fully enabled,interactive administrators normally run with least user privileges.This article and the attached code samples demonstrate thesefrequently asked coding scenarios related to UAC.
- How to check if the current process is running asadministrator?
- How to know if the primary access token of the current processbelongs to user account that is a member of the localAdministrators group, even if it currently is not elevated?
- How to check if the current process is elevated? The elevationinformation is available to only Windows Vista and newer operatingsystems because there was no UAC and "elevation" before WindowsVista.
- How to get the integrity level of the current process(System/High/Medium/Low/Unknown)? The integrity level informationis available to only Windows Vista and newer operating systemsbecause there was no UAC and "integrity level" before WindowsVista.
- How to show a UAC shield icon on the UI for tasks that requireelevation?
- How to self-elevate the current process?
- How to automatically elevate the process when it's startedup?
We provide code samples to demonstrate the above how-toscenarios in three programming languages (native VC++, VC#, VB.NET)to meet the needs of different developers.
This is a quick demo of the attached UAC samples.
Step 1. After you successfully build the sampleproject in Visual Studio 2008, you will get an applicationdepending on the programming language that you are using:CppUACSelfElevation.exe / CSUACSelfElevation.exe/ VBUACSelfElevation.exe.
Step 2. Run the application as a protectedadministrator on a Windows Vista or Windows 7 system with UAC fullyenabled. The application should display the following content onthe main dialog. There is a UAC shield icon on the Self-elevatebutton.

Step 3. Click on the Self-elevate button. Youwill see a Consent UI.

Step 4. Click Yes to approve the elevation. Theoriginal application will then be started and display the followingcontent on the main dialog.
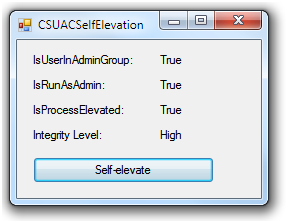
The Self-elevate button on the dialog does not have the UACshield icon this time. That is, the application is running aselevated administrator. The elevation succeeds. If you click on theSelf-elevate button again, the application will tell you that it isrunning as administrator.
Step 5. Click OK to close the application.
Using the Code
The code introduced in this section is for VC++ developers only.You can find the VC# and VB.NET implementations in theCSUACSelfElevation and VBUACSelfElevationsample packages.
- How to check if the current process is running asadministrator?
/// <summary>
/// The function checks whether the currentprocess is run as administrator.
/// Inother words, it dictates whether the primary access token ofthe
/// process belongs to user account that isa member of the local
/// Administrators group and it iselevated.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>
/// Returns true if the primary access tokenof the process belongs to user
/// accountthat is a member of the local Administrators group and itis
/// elevated. Returns false if the tokendoes not.
/// </returns>
internal bool IsRunAsAdmin()
{
WindowsIdentity id = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
WindowsPrincipal principal = newWindowsPrincipal(id);
returnprincipal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator);
} - How to know if the primary access token of the current processbelongs to user account that is a member of the localAdministrators group, even if it currently is not elevated?
/// <summary> /// The function checks whether the primary access token of the process belongs /// to user account that is a member of the local Administrators group, even if /// it currently is not elevated. /// </summary> /// <returns> /// Returns true if the primary access token of the process belongs to user /// account that is a member of the local Administrators group. Returns false /// if the token does not. /// </returns> /// <exception cref="System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception"> /// When any native Windows API call fails, the function throws a Win32Exception /// with the last error code. /// </exception> internal bool IsUserInAdminGroup() {
bool fInAdminGroup = false; SafeTokenHandle hToken = null; SafeTokenHandle hTokenToCheck = null; IntPtr pElevationType = IntPtr.Zero; IntPtr pLinkedToken = IntPtr.Zero; int cbSize = 0; try { // Open the access token of the current process for query and duplicate. if (!NativeMethod.OpenProcessToken(Process.GetCurrentProcess().Handle, NativeMethod.TOKEN_QUERY | NativeMethod.TOKEN_DUPLICATE, out hToken)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Determine whether system is running Windows Vista or later operating // systems (major version >= 6) because they support linked tokens, but // previous versions (major version < 6) do not. if (Environment.OSVersion.Version.Major >= 6) { // Running Windows Vista or later (major version >= 6). // Determine token type: limited, elevated, or default. // Allocate a buffer for the elevation type information. cbSize = sizeof(TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE); pElevationType = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(cbSize); if (pElevationType == IntPtr.Zero) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Retrieve token elevation type information. if (!NativeMethod.GetTokenInformation(hToken, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS.TokenElevationType, pElevationType, cbSize, out cbSize)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Marshal the TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE enum from native to .NET. TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE elevType = (TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE) Marshal.ReadInt32(pElevationType); // If limited, get the linked elevated token for further check. if (elevType == TOKEN_ELEVATION_TYPE.TokenElevationTypeLimite d) { // Allocate a buffer for the linked token. cbSize = IntPtr.Size; pLinkedToken = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(cbSize); if (pLinkedToken == IntPtr.Zero) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Get the linked token. if (!NativeMethod.GetTokenInformation(hToken, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS.TokenLinkedToken, pLinkedToken, cbSize, out cbSize)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Marshal the linked token value from native to .NET. IntPtr hLinkedToken = Marshal.ReadIntPtr(pLinkedToken); hTokenToCheck = new SafeTokenHandle(hLinkedToken); } } // CheckTokenMembership requires an impersonation token. If we just got // a linked token, it already is an impersonation token. If we did not // get a linked token, duplicate the original into an impersonation // token for CheckTokenMembership. if (hTokenToCheck == null) { if (!NativeMethod.DuplicateToken(hToken, SECURITY_IMPERSONATION_LEVEL.SecurityIdentification, out hTokenToCheck)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } } // Check if the token to be checked contains admin SID. WindowsIdentity id = new WindowsIdentity(hTokenToCheck.DangerousGetHandle()); WindowsPrincipal principal = new WindowsPrincipal(id); fInAdminGroup = principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator); } finally { // Centralized cleanup for all allocated resources. if (hToken != null) { hToken.Close(); hToken = null; } if (hTokenToCheck != null) { hTokenToCheck.Close(); hTokenToCheck = null; } if (pElevationType != IntPtr.Zero) { Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pElevationType); pElevationType = IntPtr.Zero; } if (pLinkedToken != IntPtr.Zero) { Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pLinkedToken); pLinkedToken = IntPtr.Zero; } } return fInAdminGroup; } - How to check if the current process is elevated? The elevationinformation is available to only Windows Vista and newer operatingsystems because there was no UAC and "elevation" before WindowsVista.
/// <summary> /// The function gets the elevation information of the current process. It /// dictates whether the process is elevated or not. Token elevation is only /// available on Windows Vista and newer operating systems, thus /// IsProcessElevated throws a C++ exception if it is called on systems prior /// to Windows Vista. It is not appropriate to use this function to determine /// whether a process is run as administrator. /// </summary> /// <returns> /// Returns true if the process is elevated. Returns false if it is not. /// </returns> /// <exception cref="System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception"> /// When any native Windows API call fails, the function throws a Win32Exception /// with the last error code. /// </exception> /// <remarks> /// TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS provides TokenElevationType to check the elevation /// type (TokenElevationTypeDefaul
t / TokenElevationTypeLimite d / /// TokenElevationTypeFull) of the process. It is different from TokenElevation /// in that, when UAC is turned off, elevation type always returns /// TokenElevationTypeDefaul t even though the process is elevated (Integrity /// Level == High). In other words, it is not safe to say if the process is /// elevated based on elevation type. Instead, we should use TokenElevation. /// </remarks> internal bool IsProcessElevated() { bool fIsElevated = false; SafeTokenHandle hToken = null; int cbTokenElevation = 0; IntPtr pTokenElevation = IntPtr.Zero; try { // Open the access token of the current process with TOKEN_QUERY. if (!NativeMethod.OpenProcessToken(Process.GetCurrentProcess().Handle, NativeMethod.TOKEN_QUERY, out hToken)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Allocate a buffer for the elevation information. cbTokenElevation = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(TOKEN_ELEVATION)); pTokenElevation = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(cbTokenElevation); if (pTokenElevation == IntPtr.Zero) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Retrieve token elevation information. if (!NativeMethod.GetTokenInformation(hToken, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS.TokenElevation, pTokenElevation, cbTokenElevation, out cbTokenElevation)) { // When the process is run on operating systems prior to Windows // Vista, GetTokenInformation returns false with the error code // ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER because TokenElevation is not supported // on those operating systems. throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Marshal the TOKEN_ELEVATION struct from native to .NET object. TOKEN_ELEVATION elevation = (TOKEN_ELEVATION)Marshal.PtrToStructure( pTokenElevation, typeof(TOKEN_ELEVATION)); // TOKEN_ELEVATION.TokenIsElevated is a non-zero value if the token // has elevated privileges; otherwise, a zero value. fIsElevated = (elevation.TokenIsElevated != 0); } finally { // Centralized cleanup for all allocated resources. if (hToken != null) { hToken.Close(); hToken = null; } if (pTokenElevation != IntPtr.Zero) { Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pTokenElevation); pTokenElevation = IntPtr.Zero; cbTokenElevation = 0; } } return fIsElevated; } - How to get the integrity level of the current process(System/High/Medium/Low/Unknown)? The integrity level informationis available to only Windows Vista and newer operating systemsbecause there was no UAC and "integrity level" before WindowsVista.
/// <summary> /// The function gets the integrity level of the current process. Integrity /// level is only available on Windows Vista and newer operating systems, thus /// GetProcessIntegrityLevel
throws a C++ exception if it is called on systems /// prior to Windows Vista. /// </summary> /// <returns> /// Returns the integrity level of the current process. It is usually one of /// these values: /// /// SECURITY_MANDATORY_UNTRUSTED_RID - means untrusted level. It is used /// by processes started by the Anonymous group. Blocks most write access. /// (SID: S-1-16-0x0) /// /// SECURITY_MANDATORY_LOW_RID - means low integrity level. It is used by /// Protected Mode Internet Explorer. Blocks write access to most objects /// (such as files and registry keys) on the system. (SID: S-1-16-0x1000) /// /// SECURITY_MANDATORY_MEDIUM_RID - means medium integrity level. It is /// used by normal applications being launched while UAC is enabled. /// (SID: S-1-16-0x2000) /// /// SECURITY_MANDATORY_HIGH_RID - means high integrity level. It is used /// by administrative applications launched through elevation when UAC is /// enabled, or normal applications if UAC is disabled and the user is an /// administrator. (SID: S-1-16-0x3000) /// /// SECURITY_MANDATORY_SYSTEM_RID - means system integrity level. It is /// used by services and other system-level applications (such as Wininit, /// Winlogon, Smss, etc.) (SID: S-1-16-0x4000) /// /// </returns> /// <exception cref="System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception"> /// When any native Windows API call fails, the function throws a Win32Exception /// with the last error code. /// </exception> internal int GetProcessIntegrityLevel () { int IL = -1; SafeTokenHandle hToken = null; int cbTokenIL = 0; IntPtr pTokenIL = IntPtr.Zero; try { // Open the access token of the current process with TOKEN_QUERY. if (!NativeMethod.OpenProcessToken(Process.GetCurrentProcess().Handle, NativeMethod.TOKEN_QUERY, out hToken)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Then we must query the size of the integrity level information // associated with the token. Note that we expect GetTokenInformation // to return false with the ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER error code // because we've given it a null buffer. On exit cbTokenIL will tell // the size of the group information. if (!NativeMethod.GetTokenInformation(hToken, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS.TokenIntegrityLevel, IntPtr.Zero, 0, out cbTokenIL)) { int error = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); if (error != NativeMethod.ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER) { // When the process is run on operating systems prior to // Windows Vista, GetTokenInformation returns false with the // ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER error code because // TokenIntegrityLevel is not supported on those OS's. throw new Win32Exception(error); } } // Now we allocate a buffer for the integrity level information. pTokenIL = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(cbTokenIL); if (pTokenIL == IntPtr.Zero) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Now we ask for the integrity level information again. This may fail // if an administrator has added this account to an additional group // between our first call to GetTokenInformation and this one. if (!NativeMethod.GetTokenInformation(hToken, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS.TokenIntegrityLevel, pTokenIL, cbTokenIL, out cbTokenIL)) { throw new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()); } // Marshal the TOKEN_MANDATORY_LABEL struct from native to .NET object. TOKEN_MANDATORY_LABEL tokenIL = (TOKEN_MANDATORY_LABEL) Marshal.PtrToStructure(pTokenIL, typeof(TOKEN_MANDATORY_LABEL)); // Integrity Level SIDs are in the form of S-1-16-0xXXXX. (e.g. // S-1-16-0x1000 stands for low integrity level SID). There is one // and only one subauthority. IntPtr pIL = NativeMethod.GetSidSubAuthority(tokenIL.Label.Sid, 0); IL = Marshal.ReadInt32(pIL); } finally { // Centralized cleanup for all allocated resources. if (hToken != null) { hToken.Close(); hToken = null; } if (pTokenIL != IntPtr.Zero) { Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pTokenIL); pTokenIL = IntPtr.Zero; cbTokenIL = 0; } } return IL; } - How to show an UAC shield icon on the UI for tasks that requireelevation?
// Get the process elevation information. bool fIsElevated = IsProcessElevated(); // Update the Self-elevate button to show the UAC shield icon on // the UI if the process is not elevated. this.btnElevate.FlatStyle = FlatStyle.System; NativeMethod.SendMessage(btnElevate.Handle, NativeMethod.BCM_SETSHIELD,
0, fIsElevated ? IntPtr.Zero : (IntPtr)1); - How to self-elevate the current process?
// Launch itself as administrator ProcessStartInfo proc = new ProcessStartInfo(); proc.UseShellExecute = true; proc.WorkingDirectory = Environment.CurrentDirectory; proc.FileName = Application.ExecutablePath; proc.Verb = "runas"; try {
Process.Start(proc); } catch { // The user refused the elevation. // Do nothing and return directly ... return; } Application.Exit(); // Quit itself - How to automatically elevate the process when it's started up?
If your application always requires administrative privileges,such as during an installation step, the operating system canautomatically prompt the user for privileges elevation each timeyour application is invoked.
If a specific kind of resource (
RT_MANIFEST) isfound embedded within the application executable, the system looksfor the<trustInfo>section andparses its contents. Here is an example of this section in themanifest file:<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2"><security> <requestedPrivileges> <requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" /> </requestedPrivileges> </security> </trustInfo>
Three different values are possible for the level attribute:
requireAdministrator
The application must be started with Administrator privileges; itwon't run otherwise.highestAvailable
The application is started with the highest possibleprivileges.If the user is logged on with anAdministrator account, an elevation prompt appears. If the user isa Standard User, the application is started (without any elevationprompt) with these standard privileges. asInvoker
The application is started with the same privileges as the callingapplication.
To configure the elevation level in this Visual C# Windows Formsproject, open the project's properties, turn to the Security tab,check the checkbox "Enable ClickOnce Security Settings", check"This is a fulltrust application" and close the applicationProperties page. This creates an app.manifest file andconfigures the project to embed the manifest. You can open the"app.manifest" file from Solution Explorer by expandingthe Properties folder. The file has the following contentby default.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<asmv1:assembly manifestVersion="1.0" xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"
xmlns:asmv1="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"
xmlns:asmv2="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
Here we are focusing on the line:
<requestedexecutionlevel uiaccess="false" level="asInvoker" />
You can change it to be:
<requestedexecutionlevel level="requireAdministrator" uiaccess="false" />
to require the application always be started with Administratorprivileges.






















 7879
7879

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








