1. 红黑树的特性
Red-Black Tree ( RBT)也是一种自平衡二叉树,其统计性能要好于 AVL树 。它是在1972年由 鲁道夫·贝尔 发明的,它现代的名字是在 Leo J. Guibas 和 Robert Sedgewick 于1978年写的一篇论文中获得的。它是复杂的,但它的操作有着良好的最坏情况运行时间,并且在实践中是高效的。[参考Wiki]
一般的,红黑树同时满足以下五大特性:
- 所有节点的颜色是红色或者黑色;
- 根节点是黑色;
- 所有的叶子节点是黑色(叶子节点包含NULL);
- 每个红色的节点都有两个黑色的子节点;
- 从任意节点出发,到其所有叶子节点的简单路径上都包含相同数目的黑色节点.
从上面的性质 4 和 5来看,红色节点和黑色节点基本上是交替的出现,所以红黑树从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长,这样的结果是这个树大致上是平衡的。因为操作比如插入、删除和查找某个值的最坏情况时间都要求与树的高度成比例,这个在高度上的理论上限允许红黑树在最坏情况下都是高效的。
2. 数据结构定义
RBT数据结构在基本二叉树数据结构之上增加一个color和parent,color用于保存节点颜色,parent指向父节点。
- #define COLOR_RED 0
- #define COLOR_BLACK 1
- typedef int keyType;
- // 定义而二叉树节点数据结构
- struct BinaryTreeNode {
- keyType key;
- int color;
- BinaryTreeNode* parent; // 保存父节点
- BinaryTreeNode* left; // left child
- BinaryTreeNode* right; // right child
- };
- // define red-black tree node
- typedef BinaryTreeNode rbnode;
- // define red-black tree
- typedef BinaryTreeNode rbtree;
#define COLOR_RED 0
#define COLOR_BLACK 1
typedef int keyType;
// 定义而二叉树节点数据结构
struct BinaryTreeNode {
keyType key;
int color;
BinaryTreeNode* parent; // 保存父节点
BinaryTreeNode* left; // left child
BinaryTreeNode* right; // right child
};
// define red-black tree node
typedef BinaryTreeNode rbnode;
// define red-black tree
typedef BinaryTreeNode rbtree;
3. 插入Key
无论怎么样操作,性质1和性质3是始终能够保持的。新插入节点的时候,新节点的初始颜色为红色,这样可以不直接破坏性质5,这个时候可能性质4受到威胁,需要调整节点颜色或这左一些旋转等操作。假设新插入的节点为N,其父节点为P,祖父节点为G,叔父节点为U,下面具体分析一下插入新节点的各种情况。
情形1 、空树
当树为空的时候,直接将N节点设为黑色作为树的根节点返回。
情形2 、P为黑色节点
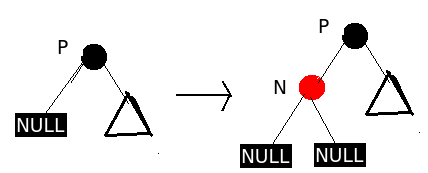
图中所示为N插入到P左孩子节点中,这个过程完全满足性质 1 - 5 的要求,并没有破坏 RBT 的规则,因此,此时即可停止检查,插入过程结束。
同理,若P为黑色节点,N插入后作为P的右孩子节点也不会破坏 RBT的规则。
(下面开始讨论 P 为红色 的情形,由 性质2 推导出 G 一定存在,根据性质 4,G一定是黑色)
情形3 、P为红色节点,U存在且为红色节点
 这种情况下,
将G变为红色,P和U变为黑色,这样维持了G为Root的子树内性质4和5,
然后以G作为新的插入节点,从情形1开始迭代。
这种情况下,
将G变为红色,P和U变为黑色,这样维持了G为Root的子树内性质4和5,
然后以G作为新的插入节点,从情形1开始迭代。
情形4 、P为红色节点,U不存在或者U为黑色
 | (a) 若P在G的左侧,插入点N也在P的左侧 ------ LL 型 假设G的右侧有 路径有 x个黑色节点,则c有x个黑色节点,G为root的子树路径有x+1个黑色节点。 此时, 只需要以P为中心右旋,将P变为黑色,G变为红色,G的左子树替换为c,这样就可以继续保证以P为root的子树有x+1个黑色节点,检查停止。 |
 | (b)若P在G的左侧,N在P的右侧 -----LR型 这时候先将节点P和节点N做调整,进行左旋,变化成(a)的形态,然后做一次右旋。到此,调整完毕。 |
| 图略 | (c)若P在G的右侧,N在P的右侧 ----------RR型 情形和(a)正好相反,做一次左旋即可。 |
| 图略 | (d)若P在G的右侧,N在P的左侧 ----------RL型 情形和(b)正好相反,先做做一次右旋,后进行一次左旋即可。 |
RBT插入算法过程代码如下:
- // 向右旋转
- void rb_right_rotate(rbnode* g) {
- rbnode * p = g->left;
- keyType k = g->key;
- g->key = p->key;
- p->key = k;
- g->left = p->left;
- if (NULL != p->left) {
- p->left->parent = g;
- }
- p->left = p->right;
- p->right = g->right;
- if (NULL != g->right) {
- g->right->parent = p;
- }
- g->right = p;
- }
- // 向左旋转
- void rb_left_rotate(rbnode* g) {
- rbnode* p = g->right;
- keyType k = g->key;
- g->key = p->key;
- p->key = k;
- g->right = p->right;
- if (NULL != p->right) {
- p->right->parent = g;
- }
- p->right = p->left;
- p->left = g->left;
- if (NULL != g->left) {
- g->left->parent = p;
- }
- g->left = p;
- }
- // check and adjust after insertion
- void rbt_insert_check(rbnode* node) {
- // CASE 1 : if the node equals the root
- // set the color of the node black and return.
- if (NULL == node->parent) {
- node->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- return;
- }
- // CASE 2 : when the parent of the node is black
- // All features have been met, stop check and return
- if (node->parent->color == COLOR_BLACK) {
- return;
- }
- // Otherwise, the the parent node is RED, and this means the grandfather node exists.
- rbnode* gf = node->parent->parent;
- rbnode* uf = (gf->left == node->parent) ? gf->right : gf->left;
- // CASE 3 : When the uncle node exists and it's RED
- if (NULL != uf && uf->color == COLOR_RED) {
- // set parent and uncle black, set grandfather red
- node->parent->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- uf->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- gf->color = COLOR_RED;
- // then re check the tree at grandfather node from CASE 1.
- rbt_insert_check(gf);
- return;
- }
- // CASE 4 : when the uncle is NULL or its color is Black.
- if (node->parent == gf->left) { // the node in the left of its grandfather
- // (a) LL model
- if (node == node->parent->left) { // the node in the left of its parent
- rb_right_rotate(gf);
- }
- // (b) LR model
- else if (node == node->parent->right) { //the node in the right of its parent.
- rb_left_rotate(node->parent);
- rb_right_rotate(gf);
- }
- } else if (node->parent == gf->right) { //the node in the right of its grandfather
- // (c) RR model
- if (node == node->parent->right) { //the node in the right of its parent.
- rb_left_rotate(gf);
- }
- // (d) RL model
- else if (node == node->parent->left) { //the node in the left of its parent.
- rb_right_rotate(node->parent);
- rb_left_rotate(gf);
- }
- }
- }
- // 插入新的关键字
- int rbt_insert(rbtree* &tree, keyType key) {
- if (NULL == tree) { // if the tree is NULL
- tree = (rbtree*) malloc((sizeof(rbnode)));
- tree->key = key;
- tree->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- tree->parent = tree->left = tree->right = NULL;
- return 1;
- }
- // find insert point
- rbnode *n = tree, *p = tree->parent;
- while (NULL != n) {
- if (key == n->key) {
- return 0;
- }
- p = n;
- n = (key > p->key) ? p->right : p->left;
- }
- // insert the node
- n = (rbtree*) malloc((sizeof(rbnode)));
- n->key = key;
- n->color = COLOR_RED;
- n->parent = p;
- n->right = n->left = NULL;
- ((key > p->key) ? p->right : p->left) = n;
- // adjust the tree
- rbt_insert_check(n);
- return 1;
- }
// 向右旋转
void rb_right_rotate(rbnode* g) {
rbnode * p = g->left;
keyType k = g->key;
g->key = p->key;
p->key = k;
g->left = p->left;
if (NULL != p->left) {
p->left->parent = g;
}
p->left = p->right;
p->right = g->right;
if (NULL != g->right) {
g->right->parent = p;
}
g->right = p;
}
// 向左旋转
void rb_left_rotate(rbnode* g) {
rbnode* p = g->right;
keyType k = g->key;
g->key = p->key;
p->key = k;
g->right = p->right;
if (NULL != p->right) {
p->right->parent = g;
}
p->right = p->left;
p->left = g->left;
if (NULL != g->left) {
g->left->parent = p;
}
g->left = p;
}
// check and adjust after insertion
void rbt_insert_check(rbnode* node) {
// CASE 1 : if the node equals the root
// set the color of the node black and return.
if (NULL == node->parent) {
node->color = COLOR_BLACK;
return;
}
// CASE 2 : when the parent of the node is black
// All features have been met, stop check and return
if (node->parent->color == COLOR_BLACK) {
return;
}
// Otherwise, the the parent node is RED, and this means the grandfather node exists.
rbnode* gf = node->parent->parent;
rbnode* uf = (gf->left == node->parent) ? gf->right : gf->left;
// CASE 3 : When the uncle node exists and it's RED
if (NULL != uf && uf->color == COLOR_RED) {
// set parent and uncle black, set grandfather red
node->parent->color = COLOR_BLACK;
uf->color = COLOR_BLACK;
gf->color = COLOR_RED;
// then re check the tree at grandfather node from CASE 1.
rbt_insert_check(gf);
return;
}
// CASE 4 : when the uncle is NULL or its color is Black.
if (node->parent == gf->left) { // the node in the left of its grandfather
// (a) LL model
if (node == node->parent->left) { // the node in the left of its parent
rb_right_rotate(gf);
}
// (b) LR model
else if (node == node->parent->right) { //the node in the right of its parent.
rb_left_rotate(node->parent);
rb_right_rotate(gf);
}
} else if (node->parent == gf->right) { //the node in the right of its grandfather
// (c) RR model
if (node == node->parent->right) { //the node in the right of its parent.
rb_left_rotate(gf);
}
// (d) RL model
else if (node == node->parent->left) { //the node in the left of its parent.
rb_right_rotate(node->parent);
rb_left_rotate(gf);
}
}
}
// 插入新的关键字
int rbt_insert(rbtree* &tree, keyType key) {
if (NULL == tree) { // if the tree is NULL
tree = (rbtree*) malloc((sizeof(rbnode)));
tree->key = key;
tree->color = COLOR_BLACK;
tree->parent = tree->left = tree->right = NULL;
return 1;
}
// find insert point
rbnode *n = tree, *p = tree->parent;
while (NULL != n) {
if (key == n->key) {
return 0;
}
p = n;
n = (key > p->key) ? p->right : p->left;
}
// insert the node
n = (rbtree*) malloc((sizeof(rbnode)));
n->key = key;
n->color = COLOR_RED;
n->parent = p;
n->right = n->left = NULL;
((key > p->key) ? p->right : p->left) = n;
// adjust the tree
rbt_insert_check(n);
return 1;
}
4.删除Key
从RBT中删除指定的Key时,需要重新调整树的形态使之满足红黑树的特性。下面来具体分析一下删除Key的过程。
(1)根据key找到要删除的节点Node:如果没有找到,直接返回,否则,进行下一步操作;
(2)如果Node有两个孩子节点,那么删除Node之后该如何放置其孩子节点呢?
这个时候需要进行预处理,转化为删除只有一个孩子的节点的情形。
找到Node的中序前驱(后继)节点,将前驱(后继)节点的值复制到Node中,Node指向前驱(后继)节点;
(3)到此步骤,Node确切的指示为待删除的节点,且Node最多只有一个孩子节点。
删除Node节点,将Node的孩子节点顶替Node的位置.(注意Node为Root的情形)
(4)调整RBT树使其满足规定的5大特性。假设上一步中顶替上来的节点为 N ,其父节点为 P ,其兄弟节点为 S ,Sl 和 Sr 分别为 S 的左右孩子节点 ,假设 N 在 P 的左侧, 调整过程如下:
(右侧与左侧对称,这里分析一种即可)
情形1 、N节点为红色
 | 当N节点为红色的时候,由于左侧缺少一个黑色的节点,可以将N节点的颜色修改为黑色,这样即可从新满足性质5. 调整完毕。 |
情形2、S节点为红色
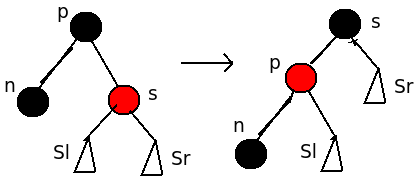 | 当S节点为红色节点时,则可以将P节点向左旋转,旋转之后P为红色,S为黑色,这个时候S-Sl这条简单路径黑色节点数目合法,S-P-Sl节点数目也合法,S-P-N路径黑色节点数目少一个。 相当于,P的左侧删除了一个黑色节点,应当重新调整 P,S,Sl,Sr所指向的节点,进行后续操作。 后续可能的情形为:3,5,6 |
情形3、P节点为红色,S,Sl,Sr为黑色
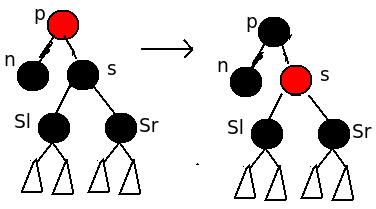 | 当P为红色,S为黑色,Sl和Sr均为黑色的时候,则可以简单的交换P节点和S节点的颜色,这样即可使各条简单路径的黑色节点数目和删除节点前相等。 调整完毕。 |
情形4、P,S,Sl,Sr均为黑色
 | 当P、S、Sl、Sr均为黑色节点的时候,只需要简单的将S节点标记为红色,这样以P节点为根的个简单路径黑色节点数目比删除之前少一个。 因此,P相当与N的位置,从P的父节点开始递归进行调整。 (如果此时P为树的根节点,即可停止调整) |
情形5、Sl为红色节点并且Sr为黑色
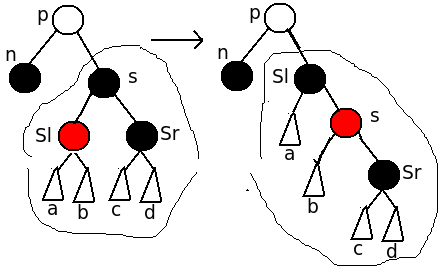 | 这种情况下,可以将Sl进行右旋操作,右旋之后,Sl为黑色,S为红色,Sr不变,这样保持P节点右子树中各简单路径黑色节点数目和旋转前一样。 这个时候,原来的S相当于Sl的位置,Sl相当与a,Sr相当与S。 更新S,Sl,Sr新指向的位置,进行下一步操作。 后续情形为:6. |
情形6、Sr为红色
 | 这时,将P节点做一次左旋操作,将Sr的颜色设置为黑色,P和S交换颜色,调整之后,各简单路径的黑色节点数目和删除节点之前一样。 此时调整结束。 |
- int is_black(rbnode * node) {
- if (node == NULL) return 1;
- if (node->color == COLOR_BLACK) return 1;
- return 0;
- }
- // check and adjust after deletion
- void rbt_delete_check(rbnode* p, bool delLeft) {
- rbnode * n = delLeft ? p->left : p->right;
- // case 1: n is red
- if (NULL != n && n->color == COLOR_RED) {
- n->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- return;
- }
- // else the other subtree of p at least has one more node.
- rbnode * s = delLeft ? p->right : p->left;
- rbnode * sl = s->left;
- rbnode * sr = s->right;
- // case 2 : S is red , p left rotate
- if (s->color == COLOR_RED) {
- if (delLeft) {
- rb_left_rotate(p);
- } else {
- rb_right_rotate(p);
- }
- p = s;
- s = delLeft ? sl : sr;
- sl = s->left;
- sr = s->right;
- }
- // Other cases : S is black
- // when SL and SR are black
- if (is_black(sl) && is_black(sr)) {
- // case 3 : P is red, S SL and SR are black
- if (!is_black(p)) {
- p->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- s->color = COLOR_RED;
- }
- // case 4: P ,S, SL and SR are black
- else {
- s->color = COLOR_RED;
- if (NULL == p->parent) {
- return;
- }
- delLeft = (p == p->parent->left);
- rbt_delete_check(p->parent, delLeft);
- }
- return;
- }
- // when SL and SR has red node
- if (delLeft) {
- if (is_black(sr)) { // case 5(a) : delLeft is true and SR is black
- rb_right_rotate(s);
- sr = s->right;
- }
- rb_left_rotate(p); // case 6(a) : rotate the p node
- sr->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- } else {
- if (is_black(sl)) { // case 5(b) : delLeft is false and SL is black
- rb_left_rotate(s);
- sl = s->left;
- }
- rb_right_rotate(p); // case 6(b) : rotate the p node
- sl->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- }
- }
- // delete a key from the RBT
- int rbt_delete(rbtree* &tree, keyType key) {
- if (NULL == tree) {
- return 0;
- }
- // find the node
- rbnode *curr, *temp;
- for (curr = tree;;) {
- if (key == curr->key) {
- break;
- }
- curr = (key > curr->key) ? curr->right : curr->left;
- if (NULL == curr) {
- return 0;
- }
- }
- // if the node to delete has two children
- if (NULL != curr->left && NULL != curr->right) {
- for (temp = curr->left; NULL != temp->right; temp = temp->right) {
- }
- curr->key = temp->key;
- curr = temp;
- }
- if (NULL == curr->parent) { // it is the tree root
- tree = (NULL == curr->left) ? curr->right : curr->left;
- if (tree != NULL) {
- tree->color = COLOR_BLACK;
- tree->parent = NULL;
- }
- free(curr);
- return 1;
- }
- // delete the node
- rbnode* fa = curr->parent;
- temp = (NULL == curr->left) ? curr->right : curr->left;
- bool delLeft = (fa->left == curr);
- if (NULL != temp) {
- temp->parent = fa;
- }
- delLeft ? fa->left = temp : fa->right = temp;
- if (curr->color != COLOR_RED) { // adjust after deletion
- rbt_delete_check(fa, delLeft);
- }
- free(curr);
- return 1;
- }

























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








