UI相关
ui相关的任务需要使用主线程来运行。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), {
print("Current thread = \(NSThread.currentThread())")
print("Main thread = \(NSThread.mainThread())")
})
print("hello")
}
}主线程在异步执行时会把需要执行的任务放在主队列队尾。
此程序将闭包内的程序放在队列末尾先打印“hello”,打印结束后开始执行闭包。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), {[weak self] in
let alertController = UIAlertController(title: "GCD",
message: "GCD is amazing!",
preferredStyle: .Alert)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "OK",
style: .Default,
handler: nil))
self!.presentViewController(alertController,
animated: true,
completion: nil)
})
}
}UI无关
UI无关的任务通常使用并发队列异步执行,这样不会阻塞主线程。
若使用并发队列同步执行,则还是不会开启新线程,依旧会使用当前线程(主线程)来执行。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
func printFrom1To1000(){
for counter in 0..<1000{
print("Counter = \(counter) - Thread = \(NSThread.currentThread())")
}
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0)
dispatch_sync(queue, printFrom1To1000)
dispatch_sync(queue, printFrom1To1000)
}
}结果如下:
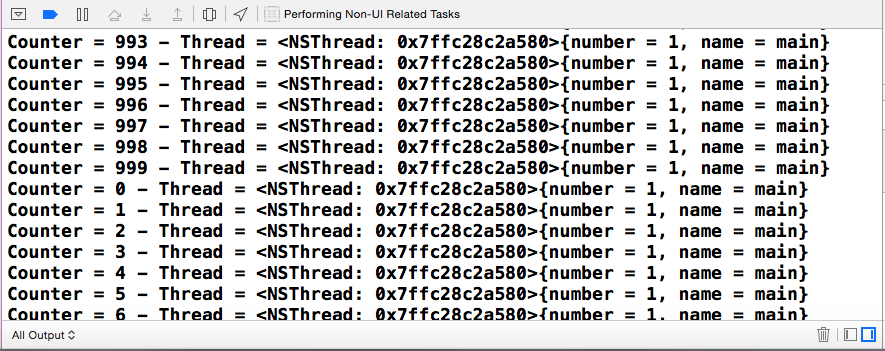
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidAppear(animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
let queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0)
dispatch_async(queue, {[weak self] in
var image: UIImage?
dispatch_sync(queue, {
/* Download the image here */
/* Put your own URL here */
let urlAsString = "http://pic.nipic.com/2007-11-09/2007119122519868_2.jpg"
let url = NSURL(string: urlAsString)
let urlRequest = NSURLRequest(URL: url!)
var downloadError: NSError?
let imageData: NSData?
do {
imageData = try NSURLConnection.sendSynchronousRequest(urlRequest,
returningResponse: nil)
} catch let error as NSError {
downloadError = error
imageData = nil
} catch {
fatalError()
}
if let error = downloadError{
print("Error happened = \(error)")
} else if let imageData = imageData{
if imageData.length > 0{
image = UIImage(data: imageData)
/* Now we have the image */
} else {
print("No data could get downloaded from the URL")
}
}
})
dispatch_sync(dispatch_get_main_queue(), {
/* Show the image to the user here on the main queue */
if let theImage = image{
let imageView = UIImageView(frame: self!.view.bounds)
imageView.contentMode = .ScaleAspectFit
imageView.image = theImage
self!.view.addSubview(imageView)
}
})
})
}
}
这个例子使用并发队列异步执行,不会阻塞主线程。
效果如下:

import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
func fileLocation() -> String?{
/* Get the document folder(s) */
let folders = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(.DocumentDirectory,
.UserDomainMask,
true) as [String]
/* Did we find anything? */
if folders.count == 0{
return nil
}
/* Get the first folder */
let documentsFolder = folders[0]
/* Append the filename to the end of the documents path */
return documentsFolder.stringByAppendingPathComponent("list.txt")
}
func hasFileAlreadyBeenCreated() -> Bool{
let fileManager = NSFileManager()
if let theLocation = fileLocation(){
return fileManager.fileExistsAtPath(theLocation)
}
return false
}
override func viewDidAppear(animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
let concurrentQueue =
dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0)
/* If we have not already saved an array of 10,000
random numbers to the disk before, generate these numbers now
and then save them to the disk in an array */
dispatch_async(concurrentQueue, {[weak self] in
let numberOfValuesRequired = 10000
if self!.hasFileAlreadyBeenCreated() == false{
dispatch_sync(concurrentQueue, {
var arrayOfRandomNumbers = [Int]()
for _ in 0..<numberOfValuesRequired{
let randomNumber = Int(arc4random())
arrayOfRandomNumbers.append(randomNumber)
}
/* Now let's write the array to disk */
let array = arrayOfRandomNumbers as NSArray
array.writeToFile(self!.fileLocation()!, atomically: true)
})
}
var randomNumbers: NSMutableArray?
/* Read the numbers from disk and sort them in an
ascending fashion */
dispatch_sync(concurrentQueue, {
/* If the file has now been created, we have to read it */
if self!.hasFileAlreadyBeenCreated(){
randomNumbers = NSMutableArray(
contentsOfFile: self!.fileLocation()!)
/* Now sort the numbers */
randomNumbers!.sortUsingComparator({
(obj1: AnyObject!, obj2: AnyObject!) -> NSComparisonResult in
let number1 = obj1 as! NSNumber
let number2 = obj2 as! NSNumber
return number1.compare(number2)
})
}
})
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), {
if let numbers = randomNumbers{
if numbers.count > 0{
/* Refresh the UI here using the numbers in the
randomNumbers array */
print("The sorted array was read back from disk = \(numbers)")
} else {
print("The numbers array is emtpy")
}
}
})
})
}
}延时一段时间
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let delayInSeconds = 2.0
let delayInNanoSeconds =
dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW,
Int64(delayInSeconds * Double(NSEC_PER_SEC)))
let concurrentQueue =
dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0)
dispatch_after(delayInNanoSeconds, concurrentQueue, {
print("hello")
})
}
}延时2秒后并发队列异步执行打印语句。
只执行一次
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
var token: dispatch_once_t = 0
var numberOfEntries = 0
func executedOnlyOnce(){
numberOfEntries++;
print("Executed \(numberOfEntries) time(s)")
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dispatch_once(&token, executedOnlyOnce)
dispatch_once(&token, executedOnlyOnce)
}
}效果如下:
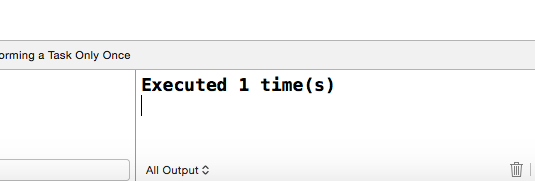
群组
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
func reloadTableView(){
/* Reload the table view here */
print(__FUNCTION__)
}
func reloadScrollView(){
/* Do the work here */
print(__FUNCTION__)
}
func reloadImageView(){
/* Reload the image view here */
print(__FUNCTION__)
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let taskGroup = dispatch_group_create()
let mainQueue = dispatch_get_main_queue()
/* Reload the table view on the main queue */
dispatch_group_async(taskGroup, mainQueue, {[weak self] in
self!.reloadTableView()
});
/* Reload the scroll view on the main queue */
dispatch_group_async(taskGroup, mainQueue, {[weak self] in
self!.reloadScrollView()
});
/* Reload the image view on the main queue */
dispatch_group_async(taskGroup, mainQueue, {[weak self] in
self!.reloadImageView()
});
/* At the end when we are done, dispatch the following block */
dispatch_group_notify(taskGroup, mainQueue, {[weak self] in
/* Do some processing here */
let controller = UIAlertController(title: "Finished",
message: "All tasks are finished",
preferredStyle: .Alert)
controller.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "OK",
style: .Default,
handler: nil))
self!.presentViewController(controller, animated: true, completion: nil)
});
}
}当所有群组的任务执行完之后执行group_notify任务。
小结:
1.主队列和全局队列
主队列
<1>串行队列,一次只执行一个任务
<2>队列所有任务都是在主线程执行
<3>所有UI更新的任务都需要放在主队列由主线程执行
全局队列
<1>并发队列,一次执行多个任务
<2>队列内任务可以由主线程完成也可以由其他线程完成,看具体的同步或异步执行方式。(在主线程执行区域内进行全局队列同步执行,则还是由当前线程(主线程)来执行)
2.同步执行和异步执行
同步执行
1.由当前线程执行(除了主队列的任务,需要主线程执行)
2.阻塞当前线程,必须等闭包执行完毕后在执行下面的任务(主线程执行区域内进行主队列的同步执行会造成死锁)
(串行队列的线程在执行过程中,遇到给该串行队列增加同步任务都会造成死锁)
异步执行
1.将任务放到队列尾就立刻返回,不会阻塞当前线程
2.交给其他线程进行任务
主线程外执行下载任务后更新界面的一般模式即为:
全局队列异步执行任务{ //不会阻塞主线程
//task 完成后
主队列异步执行更新UI任务{}
}
其中的主队列异步执行任务 也可以换成主队列同步执行任务,区别就是是否会阻塞当前执行下载任务的某线程。
若为同步执行,下载线程会等到改UI更新任务结束后才继续运行,若为异步任务,则会直接向下运行。
























 734
734

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








