以下学习笔记记录于:2024.09.11-2024.09.17
文章目录
阶段二 JavaSE进阶
第三章 JDK8新特性、算法、正则表达式、异常
3-1 JDK8新特性
1)Lambda表达式
66 认识Lambda表达式

LambdaTest1.java:
public class LambdaTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Swimming s = new Swimming(){
// @Override
// public void swim() {
// System.out.println("学生快乐地游泳~~~");
// }
// };
// 用Lambda表达式来对函数式接口的匿名内部类进行简化
Swimming s = () -> {
System.out.println("学生快乐地游泳~~~");
};
s.swim();
}
}
interface Swimming{
void swim();
}
运行结果:
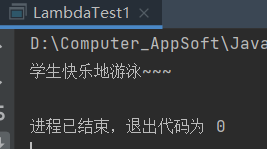
之前代码中可以用Lambda表达式简化的部分例子如下:
用“ctrl + 鼠标点击”即可进入具体的代码部分,若看到标志词“@FunctionalInterface”或仅有一个抽象方法的接口,则可以用Lambda表达式进行简化。
- 在第二章2-4的“63 基本使用”中,ArraysTest1有以下代码可以进行简化
// Arrays.setAll(prices, new IntToDoubleFunction() {
// @Override
// public double applyAsDouble(int value) {
// BigDecimal p = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
// double a = 0.8;
// BigDecimal p1 = p.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(a));
// return p1.doubleValue();
return prices[value] * 0.8; // 可以选择用BigDecimal计算(此处不会失真可直接return)
// }
// });
Arrays.setAll(prices, (int value) -> {
BigDecimal p = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
double a = 0.8;
BigDecimal p1 = p.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(a));
return p1.doubleValue();
});
- 在第二章2-4的“65 自定义排序规则的方式二”中,ArraysTest2有以下代码可以进行简化
// Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
// }
// });
Arrays.sort(students, (Student o1, Student o2) -> {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
});
67 Lambda表达式的省略规则

- 在第二章2-4的“63 基本使用”中,ArraysTest1的以下代码可以继续进行简化
// Arrays.setAll(prices, (int value) -> {
// BigDecimal p = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
// double a = 0.8;
// BigDecimal p1 = p.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(a));
// return p1.doubleValue();
// });
// Arrays.setAll(prices, (value) -> {
// BigDecimal p = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
// double a = 0.8;
// BigDecimal p1 = p.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(a));
// return p1.doubleValue();
// });
Arrays.setAll(prices, value -> {
BigDecimal p = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
double a = 0.8;
BigDecimal p1 = p.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(a));
return p1.doubleValue();
});
- 在第二章2-4的“65 自定义排序规则的方式二”中,ArraysTest2的以下代码可以进一步进行简化
// Arrays.sort(students, (Student o1, Student o2) -> {
// return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
// });
// Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2 ) -> {
// return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
// });
Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2 ) -> Double.compare( o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()) );
2)方法引用
方法引用简化Lambda表达式一共有4种常见的简化场景:静态方法的引用、实例方法的引用、特定类型方法的引用、构造器引用。方法引用的标志性符号"::",双冒号。
68 静态方法的引用、实例方法的引用


Student.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d5_arrays;
public class Student {
private String name;
private double height;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, double height, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
CompareByData.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d7_method_references;
import com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d5_arrays.Student;
public class CompareByData {
// 静态方法
public static int compareByAge(Student o1, Student o2){
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); // 升序
}
// 实例方法
public int compareByAgeDesc(Student o1, Student o2){
return o2.getAge() - o1.getAge(); // 降序
}
}
Test1.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d7_method_references;
import com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d5_arrays.Student;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = new Student[4];
students[0] = new Student("蜘蛛精",169.6, 890);
students[1] = new Student("紫霞",165.5, 18);
students[2] = new Student("至尊宝",183.0, 1000);
students[3] = new Student("兔精",158.9, 248);
// 原始写法:对数组中的学生对象按照年龄升序排序
// Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
// }
// });
// 使用Lambda简化后的形式
// Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge());
// Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> CompareByData.compareByAge(o1, o2));
// 静态方法的引用
Arrays.sort(students, CompareByData::compareByAge);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
// 使用Lambda简化后的形式(降序)
// Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge());
CompareByData compare = new CompareByData();
// Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> compare.compareByAgeDesc(o1, o2));
// 实例方法的引用
Arrays.sort(students, compare::compareByAgeDesc);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");
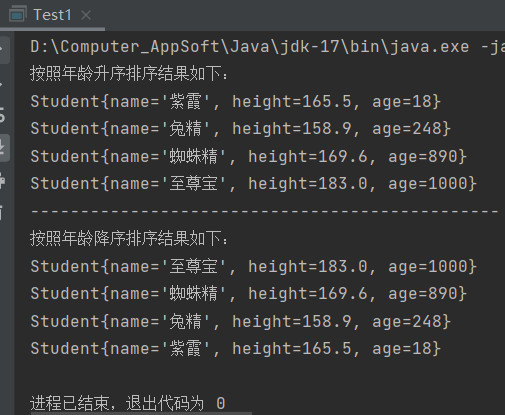
System.out.println("按照年龄降序排序结果如下:");
for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
System.out.println(students[i]);
}
}
}
运行结果:
69 特定类型方法的引用

Test2.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d7_method_references;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"boby", "angela", "Andy" ,"dlei", "caocao", "Babo", "jack", "cici"};
// 进行排序(默认是按照字符串的首字符编号(ASCII码)进行升序排序的)
// Arrays.sort(names);
// 要求忽路首字符大小写进行排序。
// Arrays.sort(names, new Comparator<String>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2); // Java提供的方法
// }
// });
// Lambda简化
// Arrays.sort(names, ( o1, o2) -> o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2));
// 特定类型的方法引用
Arrays.sort(names, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
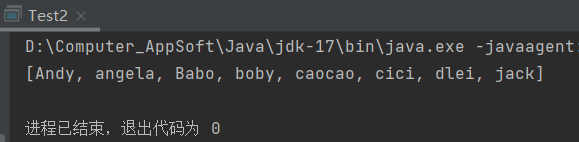
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
}
}
运行结果:
70 构造器引用(很少使用场景)

Car.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d7_method_references;
public class Car {
private String name;
private double price;
public Car() {
}
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
Test3.java:
package com.itheima.hello.ObjectDemo.d7_method_references;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、创建这个接口的匿名内部类对象
// CreateCar cc = new CreateCar() {
// @Override
// public Car create(String name, double price) {
// return new Car(name, price);
// }
// };
// CreateCar cc = ( name, price) -> new Car(name, price);
// 构造器引用
CreateCar cc = Car::new;
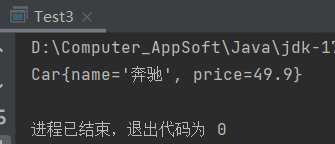
Car c = cc.create("奔驰", 49.9);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
interface CreateCar{
Car create(String name, double price);
}
运行结果:
3-2 算法
72 排序算法——冒泡排序

Test1.java:
package com.itheima.hello.d1_algorithm;
import java.util.Arrays;
// 冒泡排序
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备一个数组
int[] arr = {5, 2, 3, 1};
// 2、定义一个循环控制排几轮
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
// i = 0 1 2 [5, 2, 3, 1] 比较次数
// i = 0 第一轮 0 1 2 3
// i = 1 第二轮 0 1 2
// i = 2 第三轮 0 1
// 3、定义一个循环控制每轮比较几次
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
// 判断当前位置的元素值是否大于后一个位置处的元素值,如果是则交换
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "轮排序结果:" +Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
运行结果:
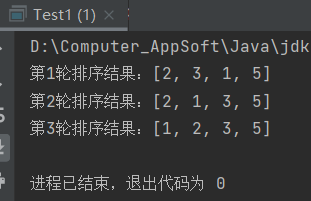
73 排序算法——选择排序
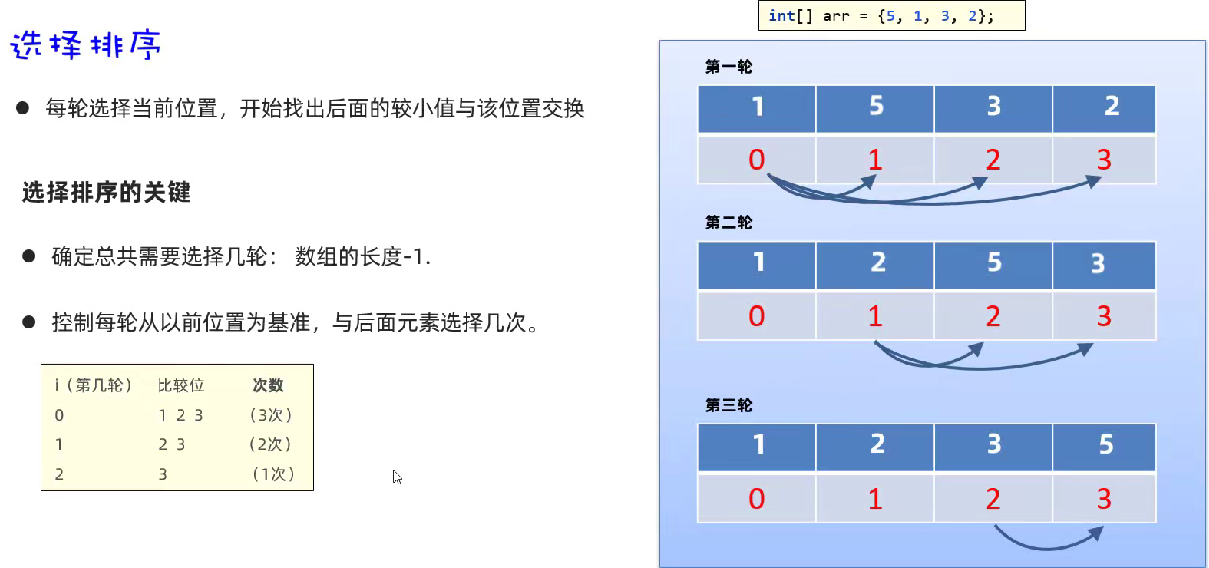
Test2.java:
package com.itheima.hello.d1_algorithm;
import java.util.Arrays;
// 选择排序
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备一个数组
int[] arr = {5, 1, 3, 2};
// 2、控制选择几轮
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
// i = 0 第一轮 j = 1 2 3
// i = 1 第二轮 j = 2 3
// i = 2 第三轮 j = 3
// 3、控制每轮选择几次
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
// 判断当前位置的元素值是否大于后面位置处的元素值,如果是则交换
if (arr[i] > arr[j]){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "轮排序结果:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
运行结果:
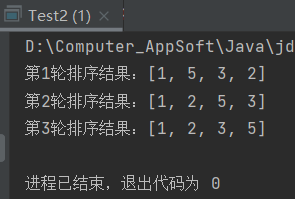
74 查找算法——二分查找
前提条件:数组中的数据必须是有序的
核心思想:每次排除一半的数据,查询数据的性能明显提高极多
Test3.java:
package com.itheima.hello.d1_algorithm;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 二分查找(折半查找)
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、准备好一个数组
int[] arr = {7, 23, 79, 81, 103, 127, 131, 147};
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入想要查找的数据值(int):");
int data = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(data + "在数组中的索引位置为:" + binarySearch(arr, data));
// System.out.println(data + "在数组中的索引位置为:" + Arrays.binarySearch(arr, data));
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int data){
// 1、定义两个变量,一个在左边,一个在右边
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
// 2、定义一个循环控制折半
while(left <= right){
// 3、每次折半,都算出中间位置处的索引
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
// 4、判断当前要找的元素值与中间位置处的元素值的大小情况
if (data < arr[middle]){
right = middle - 1;
}else if (data > arr[middle]){
left = right + 1;
}else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1; // 代表没有找到该数据
}
}
运行结果:
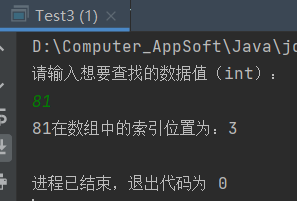






















 819
819

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








