1.插入时id自增
<insert id="add" parameterType="com.xx.yy" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into sys_detail
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," >
<if test="key != null">key,</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," >
<if test="key != null">#{key},</if>
</trim>
</insert><insert id="insert" parameterType="Person">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="long">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into person(name,pswd) values(#{name},#{pswd})
</insert>2.批量插入
<insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="java.util.List">
INSERT INTO STUDENT (id,name,sex,tel,address)
VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator="," >
(#{item.id},#{item.name},#{item.sex},#{item.tel},#{item.address})
</foreach>
</insert> <update id="batchUpdate" parameterType="java.util.List">
UPDATE STUDENT SET name = "250" WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="(" separator="," close=")" >
#{item}
</foreach>
</update> 这种批量插入、修改、删除的方式比程序中for循环调用快原因如下:
(1)、网络间传递的数据量少,当然传递的时间就少了很多。
(2)、请求数据库服务的次数少,因为连接数据库服务是很耗时的(所以出了数据库连接池)。
(3)、mybatis 在执行的时候才会获取Connection ,statement 对象所以想不for循环少创建了很多对象。
(4)、mybatis 的 执行方式有三种即:SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH 三种方式,如果方便的话设置一下,如果使用SIMPLE每一次执行都创建Statement对象并执行,如果使用REUSE 则重复使用preparedStatement 对象来执行 而BATCH 就是批量执行了而mybatis默认就是使用 SIMPLE 方式来执行,所以我们要注意最起码是不是应该是REUSE 执行方式。
Mybatis有三种基本的Executor执行器,SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor。
SimpleExecutor:每执行一次update或select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象。
ReuseExecutor:执行update或select,以sql作为key查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭Statement对象,而是放置于Map<String, Statement>内,供下一次使用。简言之,就是重复使用Statement对象。
BatchExecutor:执行update(没有select,JDBC批处理不支持select),将所有sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理。与JDBC批处理相同。
作用范围:Executor的这些特点,都严格限制在SqlSession生命周期范围内。
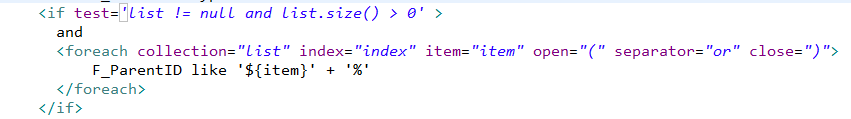
4、参数list时,先判断是否为空,否则会报错。
5、mybatis ${}与#{}的区别
简单来说#{} 解析的是占位符?可以防止SQL注入, 比如打印出来的语句 select * from table where id=?
然而${} 则是不能防止SQL注入打印出来的语句 select * from table where id=2 实实在在的参数。
最简单的区别就是${}解析穿过来的参数值不带单引号,#{}解析传过来参数带单引号。
最后总结一下必须使用$引用参数的情况,那就是参数的int型的时候,必须使用$引用。
6. 判断map
<select id="selectRule" parameterType="Map" resultType="com.ourangel.weixin.domain.Rule"> SELECT ruleId,msgType,event,respId,reqValue,firstRespId,createDate,yn FROM oal_tb_rule WHERE yn = 1 <if test="_parameter.containsKey('msgType')"> AND msgType = #{msgType,jdbcType=VARCHAR}) </if> <if test="_parameter.containsKey('event')"> AND event = #{event,jdbcType=VARCHAR}) </if> </select>
public interface CrawDao {
public void saveNewNews(@Param("params")Map<String, String> params);
} <insert id="saveNewNews" parameterType="java.util.Map">
insert ignore into tb_news
<foreach collection="params.keys" item="key" open="(" close=")" separator="," >
${key}
</foreach>
values
<foreach collection="params.keys" item="key" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{params[${key}]}
</foreach>
</insert> 7.mybatis 的if 比较标签在比较数值时可以这样写:
<if test="value=0">
</if>
8.在比较字符串时可以这么写:
<if test='str!=null and str!="" '>
</if>
9. 比较布尔值1、
<if test="boolvalue">
//boolvalue=true 时
</if>
2、
<if test="boolvalue==true">
//boolvalue=true 时
</if>






















 1423
1423

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








