原创 Springboot实战案例锦集 Spring全家桶实战案例源码 2024-01-29 08:10 发表于新疆

Spring全家桶实战案例源码
spring, springboot, springcloud 案例开发详解
419篇原创内容
公众号
环境:Spring5.3.23
1. 简介
在Spring框架中,事务管理是保障数据一致性和系统可靠性的重要手段。但在实际开发中,Spring事务失效的问题却时有发生。本文将总结并分析Spring事务失效的各种场景,帮助你全面了解事务失效的原因和解决方案,让你不再被事务问题困扰。。让我们一起揭开Spring事务失效的神秘面纱,迎接更稳健、高效的系统开发之旅!
2. 事务失效场景
2.1 非public方法
@Transactionalprotected void save() {Person person = new Person();person.setAge(36);person.setName("张三");int result = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_person (age, name) values (?, ?)", person.getAge(),person.getName());System.out.println("save Db Update " + result + " 次");System.out.println(1 / 0) ;}
以上方法是protected修饰的,事务将失效,默认Spring支持支public修饰的方法。如何让Spring支持非public方法呢?可以通过如下方法修改
@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {// 设置为false,这样protected及默认修饰的方法都将支持事务功能return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(false) ;}
该要想上面bean生效,你还需要开启如下功能
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();// 允许Bean覆盖,后面的BeanDefintion能覆盖前面的// 我们定义的transactionAttributeSource bena能够覆盖系统默认的context.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(true) ;
2.2 异常被吞
@Transactionalprotected void save() {try {// ...int result = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_person (age, name) values (?, ?)", person.getAge(),person.getName());System.out.println(1 / 0) ;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace() ;}}
上面代码将异常信息捕获了后并没有再进行抛出。Spring 事务的原理就是根据你代码执行时是否发生了异常来控制事务是否回滚。源码如下:
Spring事务的核心拦截器TransactionInterceptor
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport {protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(...) throws Throwable {TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);Object retVal;try {// 执行实际的业务代码调用retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();}catch (Throwable ex) {// 执行事务回滚completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);// 继续抛出,终止向下执行throw ex;}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}// 没有异常则进行事务的提交commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);}}
2.3 回滚异常类设置错误
Spring事务回滚策略是只会回滚RuntimeException与Error类型的异常和错误。
@Transactionalprotected void save() throws Exception {try {Person person = new Person();person.setAge(36);person.setName("张三");int result = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_person (age, name) values (?, ?)", person.getAge(),person.getName());System.out.println("save Db Update " + result + " 次");System.out.println(1 / 0) ;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace() ;throw new Exception(e) ;}}
这里并没有设置rollbackFor属性,所以这里事务不会被回滚。回滚逻辑处理如下:
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport {protected Object invokeWithinTransaction() {try {retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();}catch (Throwable ex) {// 回滚处理completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);throw ex;}}protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing() {// 检查异常if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {try {txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());}}}}public abstract class DelegatingTransactionAttribute {// 实现类是下面的RuleBasedTransactionAttributeprivate final TransactionAttribute targetAttribute;public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {return this.targetAttribute.rollbackOn(ex);}}public class RuleBasedTransactionAttribute {public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 遍历处理你配置的rollbackFor属性配置if (this.rollbackRules != null) {for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {deepest = depth;winner = rule;}}}// 如果上没有找到异常,则进行默认行为的处理,检查异常类型if (winner == null) {return super.rollbackOn(ex);}return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);}public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {// 回滚是运行时及Error类型的异常或错误return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);}}
2.4 同一类中方法互相调用
protected void save() {// ...this.updatePerson()}@Transactionalpublic void updatePerson() {// ...}
上面的事务将会失效,因为在save中通过this调用updatePerson,而这时的this是原始对象,并不是当前容器中生成的那个代理对象,通过如下方式解决:
方式1:
protected void save() {// 通过AopContext获取当前代理对象PersonService proxy = (PersonService)AopContext.currentProxy() ;proxy.save() ;}
这种方式,不推荐;这将你的代码与Spring AOP完全耦合,并使类本身意识到它正在AOP上下文中使用,这与AOP背道而驰。
方式2:
自己注入自己
@Resourceprivate PersonService personService ;public void save() {personService.save() ;}
2.5 方法被final修饰
@Transactionalprotected final void save() {// ...}
方法被final修饰,cglib是通过继承的方式实现代理,final修饰后将不能重写save方法。程序抛出NPE异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerExceptionat com.pack.main.transaction.TransactionNoPublicMethodMain2$PersonService.save(TransactionNoPublicMethodMain2.java:98)
因为无法重写save方法,首先是没法对方法进行增强处理,其次只能调用父类的save方法,而父类中的所有属性(需要注入的)都将是null。
2.6 传播类型设置错误
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)protected void save() {// ...}
或者是设置为Propagation.NEVER,这都将使得事务失效。部分源码:
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport {protected Object invokeWithinTransaction() {// 使用getTransaction和commit/rollback调用进行标准事务划分。TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);}protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary() {// 调用事务管理器获取事务对象status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);}}public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager {public final TransactionStatus getTransaction() {// 根据配置的事务传播属性进行相应的处理if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");}else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {} else {// 创建“空”事务:没有实际的事务,但可能是同步。boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);}}}
2.7 异步线程执行
在一个事务方法中开启新的线程执行事务方法
@Transactional()protected void save() {new Thread(() -> {Person person = new Person();person.setAge(36);person.setName("张三");int result = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_person (age, name) values (?, ?)", person.getAge(),person.getName());System.out.println("save Db Update " + result + " 次");System.out.println(1 / 0) ;}).start() ;try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3) ;} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}
上面的事务将不会生效,这是因为主线程与子线程使用的不是同一个Connection对象,Spring事务执行会为每一个执行线程绑定一个Connection对象。源码如下:
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager {// 开始新的事务private TransactionStatus startTransaction() {doBegin(transaction, definition);}}public class DataSourceTransactionManager {protected void doBegin(...) {DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;Connection con = null;try {if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {// 获取连接对象Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);}// 将连接对象绑定到当前线程上if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());}}}}
你新启动的线程是拿不到主线程中的Connection。
2.8 数据库不支持
在MySQL建表时指定了错误的引擎,比如使用了MyISAM。mysql支持哪些引擎及事务支持情况如下:
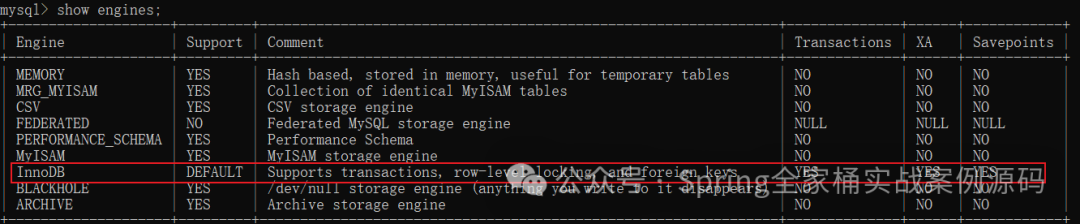
支持事务的只有InnoDB。在建表时明确指定引擎。
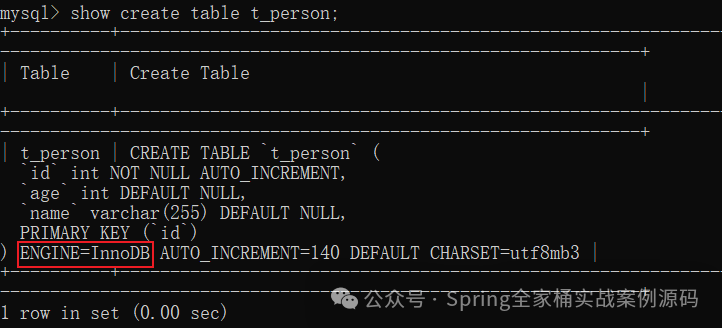
通过上面的方式制定ENGINE=InnoDB。
2.9 关于@Transactional注解使用错误的情况
有些人说使用了错误的@javax.transaction.Transactional注解。通过源码分析
Spring在定义事务的切面时,会使用TransactionAttributeSource来判断当前的类上或者是方法上是否有@Transactional注解
@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();}public class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource {private static final boolean jta12Present;private static final boolean ejb3Present;static {// 判断是否存在该注解类jta12Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", classLoader);}public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) {this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());if (jta12Present) {// 如果存在会加入专门解析@javax.transaction.Transactional注解的解析器类this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());}if (ejb3Present) {this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());}}else {this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());}}}
所以如果你类路径下只要存在,那么你的事务还是可以生效的。
总结:在本文中,深入探讨了Spring事务失效的各种情况。通过了解这些情况,我们可以更好地理解事务管理在Spring框架中的重要性,以及如何避免和解决事务失效的问题。
完毕!!!







 本文详细讨论了Spring框架中事务失效的多种场景,包括非public方法、异常处理策略、传播类型错误、异步线程、数据库引擎选择等,并提供了相应的解决策略,助你提升系统开发的稳健性。
本文详细讨论了Spring框架中事务失效的多种场景,包括非public方法、异常处理策略、传播类型错误、异步线程、数据库引擎选择等,并提供了相应的解决策略,助你提升系统开发的稳健性。














 1041
1041











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








