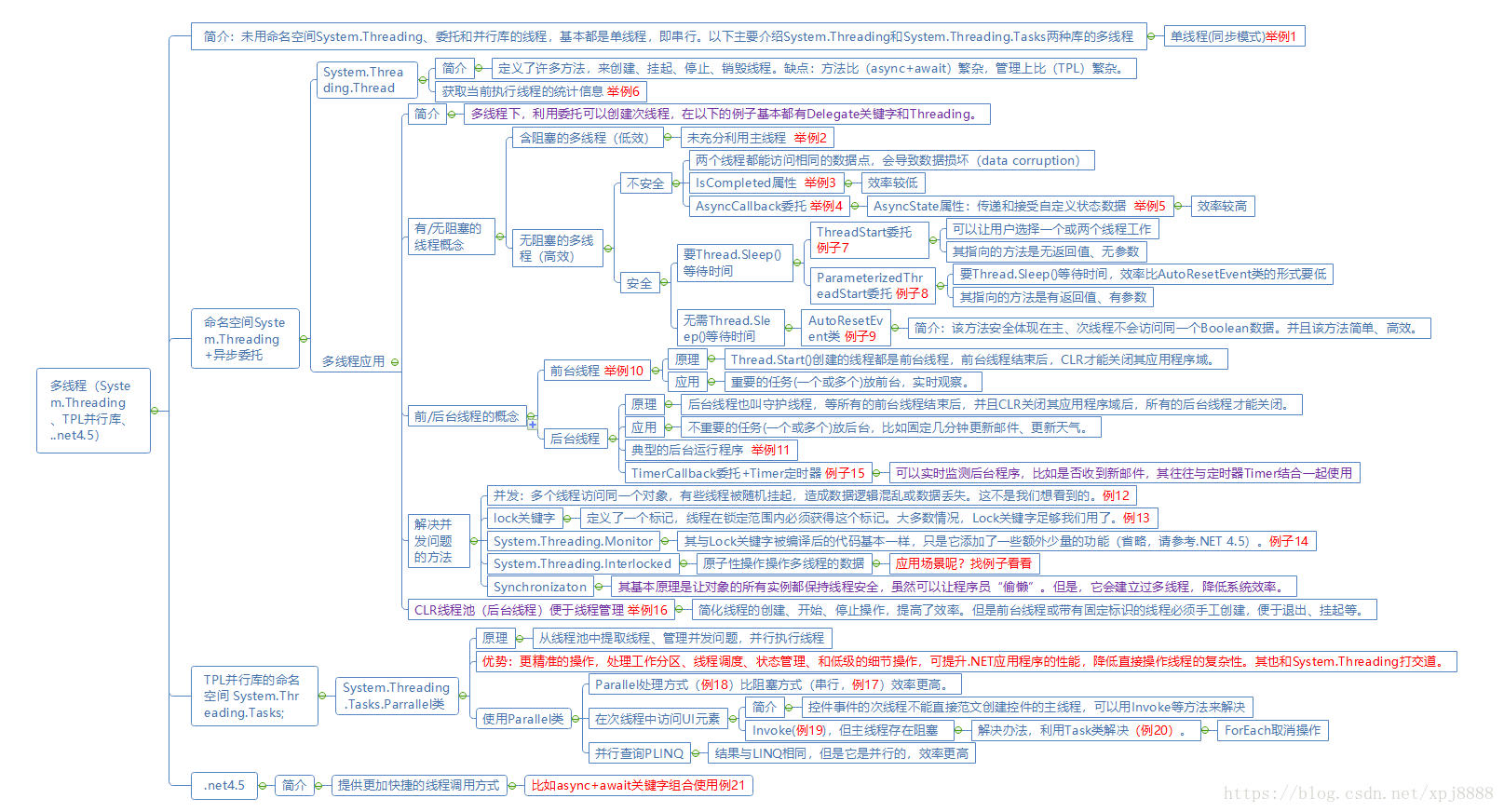
先看网上百度的几张图片:
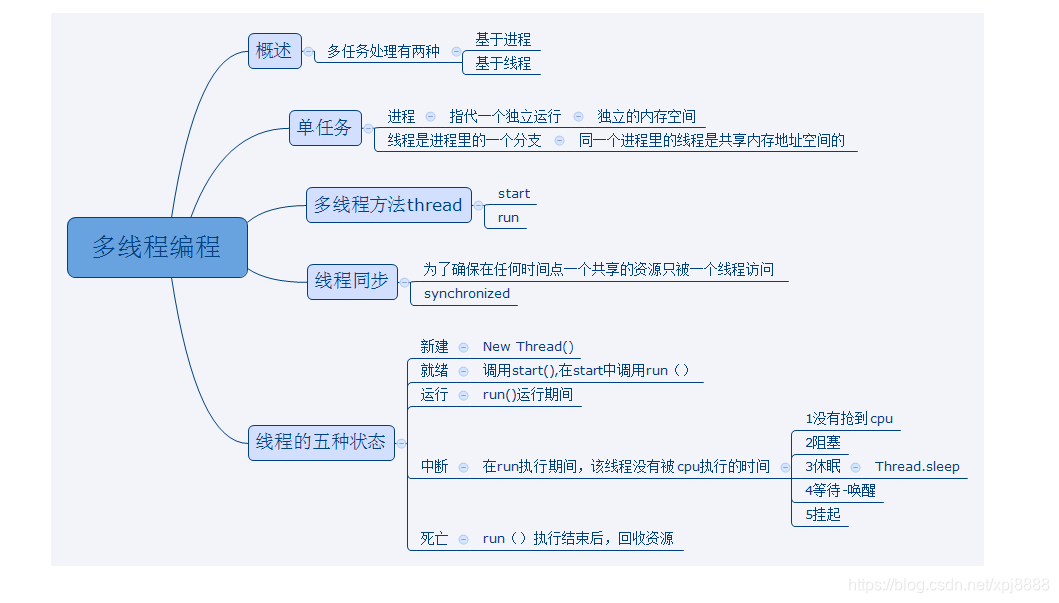
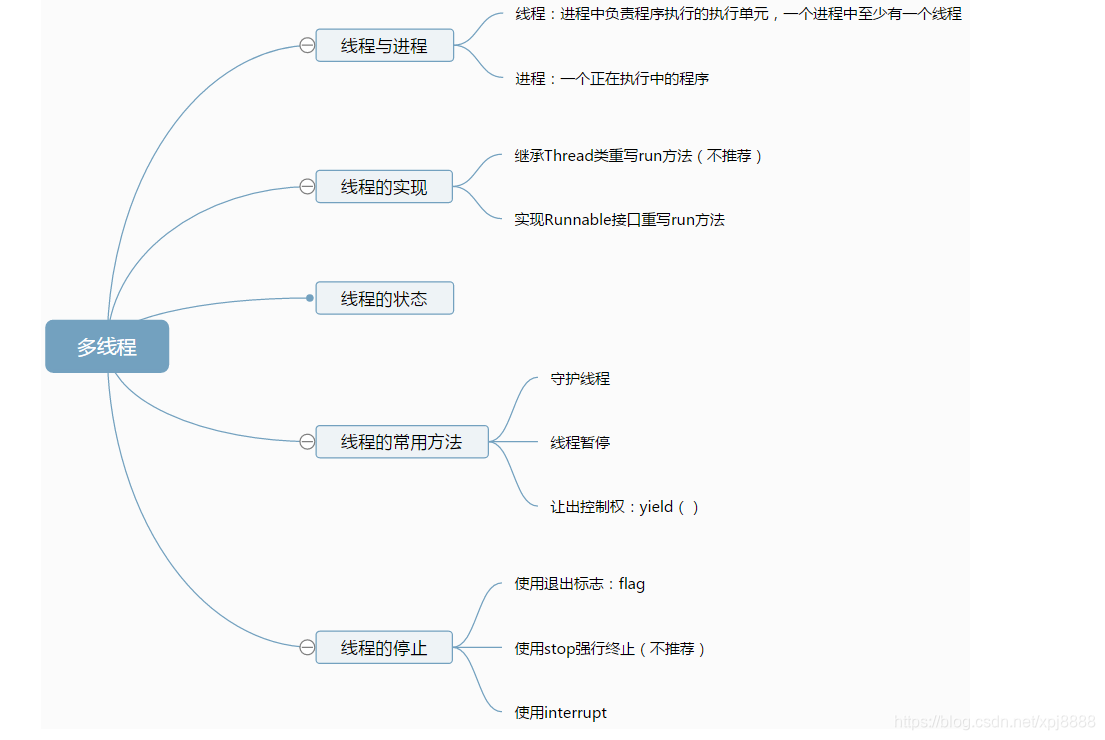

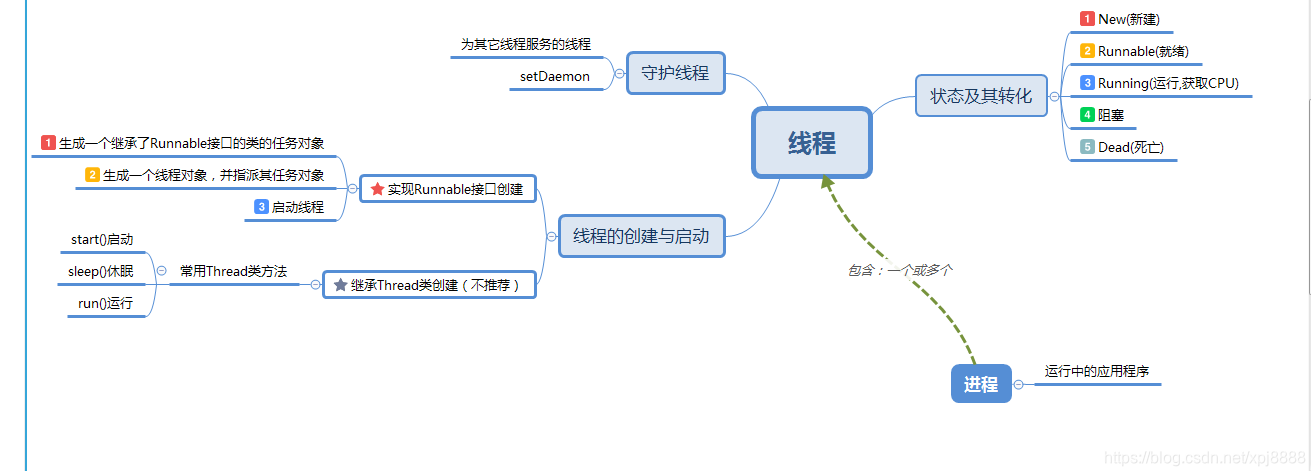
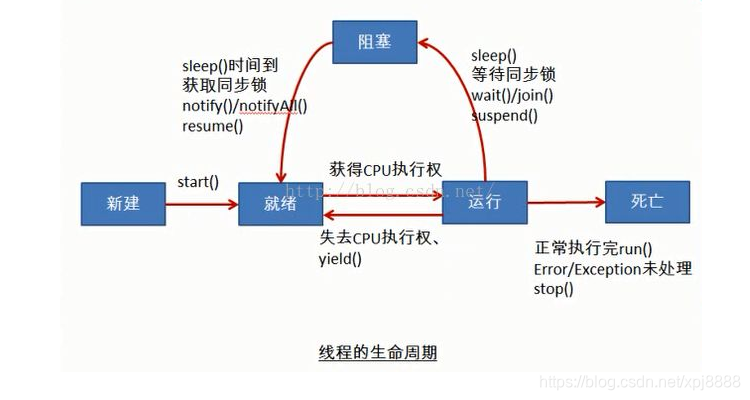
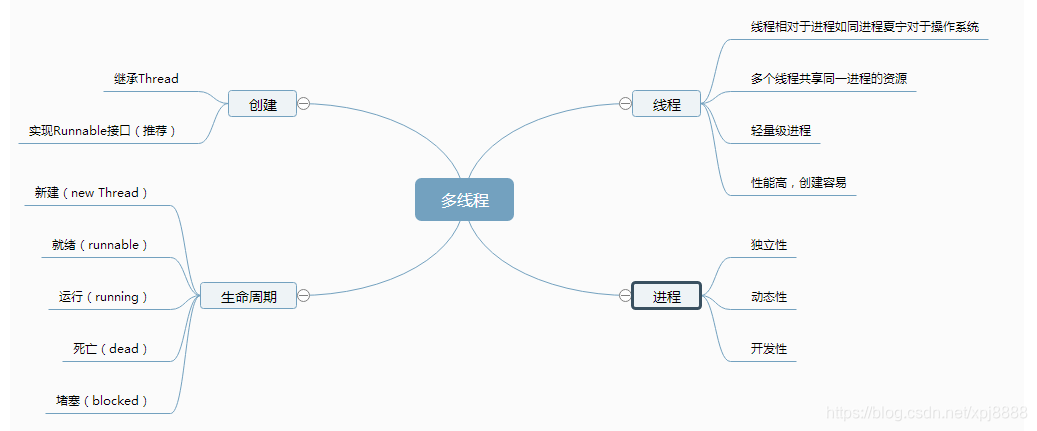
什么是单线程?单线程工作模式也成为同步模式。其就是在一定状态下只能做一件事情,比如我在18:00-18:30时间段可以做饭。
什么是多线程?多线程工作模式也成为异步模式。其就是在一定状态下可以做多件事情,比如我在18:00-18:30时间段既可以做饭,又可以在18:00-18:20时间段内玩游戏。这相对于,我在半小时内完成了两件事情。
举例1 单线程
功能描述:在单线程下,执行加法要9秒钟,执行减法要4秒钟,共需要13秒钟。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace SyncDelegateReview
{
public delegate int BinaryOp(int x, int y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//主线程正在做的事情
BinaryOp b1 = new BinaryOp(Add);
int answer1 = b1(11, 10);
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x + y = {0}", answer1);
BinaryOp b2 = new BinaryOp(Sub);
int answer2 = b2(11, 10);
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x - y = {0}", answer2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Add()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(9000);
return (x + y);
}
static int Sub(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Sub()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(4000);
return (x - y);
}
}
}
输出结果:
多线程
阻塞的定义:主线程执行完成之后,被停止工作,而次线程还在工作。相当浪费了5秒钟 = 执行加法要9秒钟 - 执行减法要4秒钟。从而降低了主线程的工作效率。
举例2、包含阻塞的多线程
功能描述:若是在单线程下,执行加法要9秒钟,执行减法要4秒钟。但是在多线程下,只需要9秒钟。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AsyncDelegateWithBlock
{
public delegate int BinaryOp(int x, int y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//异步模式下调用Add()(次线程正在做的事情)
BinaryOp b = new BinaryOp(Add);
IAsyncResult iftAR = b.BeginInvoke(10, 10, null, null);
//主线程正在做的事情
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x - y = {0}", Sub(11, 10));
//输出次线程的结果
int answer = b.EndInvoke(iftAR);
Console.WriteLine("10 + 10 = {0}", answer);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Add()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(9000);
return (x + y);
}
static int Sub(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Sub()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(4000);
return (x - y);
}
}
}
输出结果:
举例3、无阻塞的多线程(IsCompleted属性)
功能描述:主线程执行减法要4秒钟,并一直采用IsCompleted属性,检验次线程(即减法)是否完成。若是未完成次线程,主线程可以做其他工作,而不会发生阻塞,也不会浪费主线程做事情的能力。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AsyncDelegateWithNoBlock
{
public delegate int BinaryOp(int x, int y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//异步模式下调用Add()(次线程正在做的事情)
BinaryOp b = new BinaryOp(Add);
IAsyncResult iftAR = b.BeginInvoke(10, 10, null, null);
//主线程正在做的事情
while(!iftAR.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x - y = {0}", Sub(11, 10));
}
//输出次线程的结果
int answer = b.EndInvoke(iftAR);
Console.WriteLine("10 + 10 = {0}", answer);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Add()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(9000);
return (x + y);
}
static int Sub(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Sub()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(4000);
return (x - y);
}
}
}
输出结果:
显然,IsCompleted属性是由主线程发起的,并一直在检查次线程,当次线程刚好完成工作时,主线程会花费少量事件输出次线程的结果(这段时间内,相当于发生了阻塞)。因此,我们需要找到一种更加高效的方法。下面将讲到AsyncCallback委托。
举例4、无阻塞的多线程(AsyncCallback委托)。
功能描述:AsyncCallback委托是由次线程返回一个值,告诉主线程自己完成了工作,这时候主线程就直接输出次线程的结果即可。若是在其他时间段(即,次线程未返回一个值时),主线程自由处理其他事情。这种工作方式下,效率更高。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AsyncCallbackDelegate
{
public delegate int BinaryOp(int x, int y);
class Program
{
private static bool isDone = false;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//异步模式下调用AddComplete()(次线程正在做的事情)
BinaryOp b = new BinaryOp(Add);
IAsyncResult iftAR = b.BeginInvoke(10, 10, new AsyncCallback(AddComplete), null);
//主线程正在做的事情
while (!isDone)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
//Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x - y = {0}", Sub(11, 10));
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情.");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Add()方法正在执行的次线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(5000);
return (x + y);
}
//static int Sub(int x, int y)
//{
// //
// Console.WriteLine("输出Sub()方法正在执行的次线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// //时延5秒钟
// Thread.Sleep(5000);
// return (x - y);
//}
static void AddComplete(IAsyncResult itfAR)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出AddComplete()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("次线程已经工作完成");
isDone = true;
}
}
}
输出结果:
输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:10
输出Add()方法正在执行的次线程ID:6
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
输出AddComplete()方法正在执行的线程ID:6
次线程已经工作完成
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
举例5 在例4的基础上,传递和接受自定义状态数据。
功能描述:利用AsyncResult参数的AsyncState属性,在方法BeginInvoke()中,来传递和输出输出消息。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AsyncCallbackDelegate
{
public delegate int BinaryOp(int x, int y);
class Program
{
private static bool isDone = false;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//异步模式下调用AddComplete()(次线程正在做的事情)
BinaryOp b = new BinaryOp(Add);
IAsyncResult iftAR = b.BeginInvoke(10, 10, new AsyncCallback(AddComplete), "可以在这里设置自定义消息");
//主线程正在做的事情
while (!isDone)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
//Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情:x - y = {0}", Sub(11, 10));
Console.WriteLine("当前主线程正在处理的事情.");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
//
Console.WriteLine("输出Add()方法正在执行的次线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//时延5秒钟
Thread.Sleep(5000);
return (x + y);
}
//static int Sub(int x, int y)
//{
// //
// Console.WriteLine("输出Sub()方法正在执行的次线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// //时延5秒钟
// Thread.Sleep(5000);
// return (x - y);
//}
static void AddComplete(IAsyncResult itfAR)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出AddComplete()方法正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("次线程已经工作完成");
string msg = (string)itfAR.AsyncState;
Console.WriteLine(msg);
isDone = true;
}
}
}
输出结果:
输出Main函数正在执行的线程ID:8
输出Add()方法正在执行的次线程ID:9
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
输出AddComplete()方法正在执行的线程ID:9
次线程已经工作完成
可以在这里设置自定义消息
当前主线程正在处理的事情.
例子6 用System.Threading.Thread类,来获得当前执行线程的信息
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace ThreadStats
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//给当前线程一个名字
Thread primaryThread = Thread.CurrentThread;
primaryThread.Name = "ThePrimaryThread";
//当前线程的应用程序域的FriendlyName和上下文的ContextID
Console.WriteLine("当前线程的应用程序域:{0}", Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
Console.WriteLine("当前线程的上下文:{0}",Thread.CurrentContext.ContextID);
//输出线程的友好名字、是否开始、优先级、线程状态
Console.WriteLine(primaryThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine(primaryThread.IsAlive);
Console.WriteLine(primaryThread.Priority);
Console.WriteLine(primaryThread.ThreadState);
Console.WriteLine("当前正在执行的线程ID:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.Read();
}
}
}
输出结果:
当前线程的应用程序域:ThreadStats.vshost.exe
当前线程的上下文:0
ThePrimaryThread
True
Normal
Running
当前正在执行的线程ID:9
例子7 ThreadStart委托
功能描述:可以让用户选择一个或两个线程进行打印工作。需要加载using System.Windows.Forms和using System.Windows.Forms.DLL。以下是两个类文件:
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace SimpleMultiThreadApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("你想要1个或2个线程来工作,请输入数字1或2:");
string threadCount = Console.ReadLine();
//给当前线程一个名字
Thread primaryThread = Thread.CurrentThread;
primaryThread.Name = "Primary";
//当前线程名字
Console.WriteLine("->线程 {0} 正在执行Main()函数工作", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
//打印类的实例化
Printer p = new Printer();
switch (threadCount)
{
case "2":
//ThreadStart()表示一个委托。p.PrintNumbers表示传递到委托的方法。backgroundThread表示一个线程的名字。
Thread backgroundThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.PrintNumbers));
backgroundThread.Name = "Secondary";
//Start()告诉CLR:线程已经准备好执行了。即要启动线程了。
backgroundThread.Start();
break;
case "1":
p.PrintNumbers();
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("你输入的数字不对,请输入数字1或2");
goto case "1";
}
MessageBox.Show("我在忙着打印工作","我工作在主函数的线程上");
Console.Read();
}
}
}
Printer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace SimpleMultiThreadApp
{
class Printer
{
public void PrintNumbers()
{
Console.WriteLine("->次线程 {0} 正在执行打印工作",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine("你要打印的数字为:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
例子8 ParameterizedThreadStart委托
功能描述:同例7,但是比之写法更加简单,值得推荐。例子8包含了Program.cs和AddParams.cs两个类文件。
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AddWithThreads_ParameterizedThreadStart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//主线程
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Main():{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//建立AddParams对象,并传递给次线程t
AddParams ap = new AddParams(10,20);
Thread t = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(Add));
t.Start(ap);//用ap作为参数传递。
//强制等待让其他线程结束,加法的结果才能显示出来:因为次线程消耗一定的时间。
Thread.Sleep(5);//自己单部到这里试试。
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Add(object data)
{
if (data is AddParams)
{
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Add():{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
AddParams ap = (AddParams)data;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}",ap.a, ap.b, ap.a + ap.b);
}
}
}
}
AddParams.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AddWithThreads_ParameterizedThreadStart
{
class AddParams
{
public int a;
public int b;
public AddParams(int numb1, int numb2)
{
a = numb1;
b = numb2;
}
}
}
例子9 AutoResetEvent类
功能描述:AutoResetEvent类实现高效的、安全的主/次线程工作方式。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace AddWithThreads_AutoResetEvent
{
class Program
{
//AutoResetEvent是系统自带的一个类
private static AutoResetEvent waitHandle = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Main():{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//建立AddParams对象,并传递给次线程t
AddParams ap = new AddParams(10, 20);
Thread t = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(Add));
t.Start(ap);//用ap作为参数传递。
//等待,知道收到次线程的通知,才执行主线程
waitHandle.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine("其他线程已经结束,从这继续执行主线程");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Add(object data)
{
if (data is AddParams)
{
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Add():{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
AddParams ap = (AddParams)data;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", ap.a, ap.b, ap.a + ap.b);
//通知其他线程,该线程已经结束。
waitHandle.Set();
}
}
}
}
举例10 前台线程
功能描述:
program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace ForegroundThread
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("->主线程ID: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Printer p = new Printer();
Thread gg = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.PrintNumbers));
//前台线程,即使没有Console.ReadLine(),也可以看到控制台打印数字后,关系控制台。
gg.IsBackground = false;
gg.Start();
//Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Printer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace ForegroundThread
{
class Printer
{
public void PrintNumbers()
{
Console.WriteLine("->次线程ID: {0} 正在执行打印工作", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("->次线程 {0} 正在执行打印工作",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine("你要打印的数字为:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
举例11 后台线程
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace BackgroundThread
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("->主线程ID: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Printer p = new Printer();
Thread gg = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.PrintNumbers));
//使用任务管理器,可以查看后台程序。
gg.IsBackground = true;
gg.Start();
//Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
举例12 并发问题
功能描述:10个线程访问同一个对象,导致输出混合。
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace MultiThreadedPrinting
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Printer p = new Printer();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
threads[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.PrintNumbers));
threads[i].Name = string.Format("Worker thread #{0}", i);
}
//十个线程都访问Printer
foreach (Thread t in threads)
{
t.Start();
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Printer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace MultiThreadedPrinting
{
class Printer
{
public void PrintNumbers()
{
//lock (threadLock)
//{
Console.WriteLine("->次线程ID: {0} 正在执行打印工作", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("->次线程 {0} 正在执行打印工作",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine("你要打印的数字为:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Random r = new Random();
int a = r.Next(5);
int b = 1000 * a;
Thread.Sleep(b);
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine();
//}
}
}
}
输出结果(由于输出结果太长,将用代码段表述输出结果):
->次线程ID: 10 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #0 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 11 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #1 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 12 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #2 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 13 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #3 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 14 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #4 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 15 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #5 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 16 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #6 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
->次线程ID: 17 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #7 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 18 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #8 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 19 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #9 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
3
4
3
3
2
2
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
3
5
6
7
8
4
5
6
7
8
9
9
4
3
3
4
5
4
5
6
7
8
9
5
6
7
8
9
6
4
5
6
7
7
8
9
8
9
举例13 Lock关键字
功能描述:10个线程访问同一个对象,但是采用Lock关键字,不会导致输出混合。
Program.cs 同 例12的Program.cs
Printer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace MultiThreadedPrinting
{
class Printer
{
private object threadLock = new object();
public void PrintNumbers()
{
lock (threadLock)
{
Console.WriteLine("->次线程ID: {0} 正在执行打印工作", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("->次线程 {0} 正在执行打印工作",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine("你要打印的数字为:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Random r = new Random();
int a = r.Next(5);
int b = 1000 * a;
Thread.Sleep(b);
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
输出结果(由于输出结果太长,将用代码段表述输出结果):
->次线程ID: 10 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #0 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 11 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #1 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 12 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #2 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 13 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #3 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 14 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #4 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 15 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #5 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 16 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #6 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 17 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #7 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 18 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #8 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
->次线程ID: 19 正在执行打印工作
->次线程 Worker thread #9 正在执行打印工作
你要打印的数字为:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
举例14 Monitor关键字
功能描述:10个线程访问同一个对象,但是采用Monitor关键字,不会导致输出混合。
Program.cs 同 例12的Program.cs
Printer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace MultiThreadedPrinting_Monitor
{
class Printer
{
private object threadLock = new object();
public void PrintNumbers()
{
//lock (threadLock)
Monitor.Enter(threadLock);
try
{
Console.WriteLine("->次线程ID: {0} 正在执行打印工作", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("->次线程 {0} 正在执行打印工作", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.WriteLine("你要打印的数字为:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Random r = new Random();
int a = r.Next(5);
int b = 1000 * a;
Thread.Sleep(b);
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
finally
{
Monitor.Exit(threadLock);
}
}
}
}
输出结果:同例13
例子15:TimerCallback委托+Timer定时器
功能描述:每隔一秒打印出系统的时间。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace TimerApp
{
class Program
{
static void PrintTime(object state)
{
Console.WriteLine("Time is: {0}", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("***** Working with Timer type *****\n");
// Create the delegate for the Timer type.
TimerCallback timeCB = new TimerCallback(PrintTime);
// Establish timer settings.
Timer t = new Timer(
timeCB, // The TimerCallback delegate type.
"Hello From Main", // Any info to pass into the called method (null for no info).
0, // Amount of time to wait before starting.
1000); // Interval of time between calls (in milliseconds).
Console.WriteLine("Hit key to terminate...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
输出结果:
***** Working with Timer type *****
Hit key to terminate...
Time is: 9:27:17
Time is: 9:27:18
Time is: 9:27:19
Time is: 9:27:20
Time is: 9:27:21
Time is: 9:27:22
Time is: 9:27:23
Time is: 9:27:24
Time is: 9:27:25
Time is: 9:27:26
Time is: 9:27:27
Time is: 9:27:29
Time is: 9:27:31
............................
例子16:CLR线程池
功能描述:直接调用系统的十个线程来打印数字。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace ThreadPoolApp
{
#region Helper class
public class Printer
{
private object lockToken = new object();
public void PrintNumbers()
{
lock (lockToken)
{
// Display Thread info.
Console.WriteLine("-> {0} is executing PrintNumbers()",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// Print out numbers.
Console.Write("Your numbers: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0}, ", i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("***** Fun with the CLR Thread Pool *****\n");
Console.WriteLine("Main thread started. ThreadID = {0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Printer p = new Printer();
WaitCallback workItem = new WaitCallback(PrintTheNumbers);
// Queue the method 10 times
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(workItem, p);
}
Console.WriteLine("All tasks queued");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void PrintTheNumbers(object state)
{
Printer task = (Printer)state;
task.PrintNumbers();
}
}
}
输出结果:
***** Fun with the CLR Thread Pool *****
Main thread started. ThreadID = 9
-> 6 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, All tasks queued
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 10 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 11 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 12 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 13 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 14 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 15 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 16 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 17 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
-> 18 is executing PrintNumbers()
Your numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
例子17:拷贝并旋转图片(缺点,阻塞方式,效率低下。你只有在运行的过程中,才会发现其加载图片的效率比Parralel方式慢)
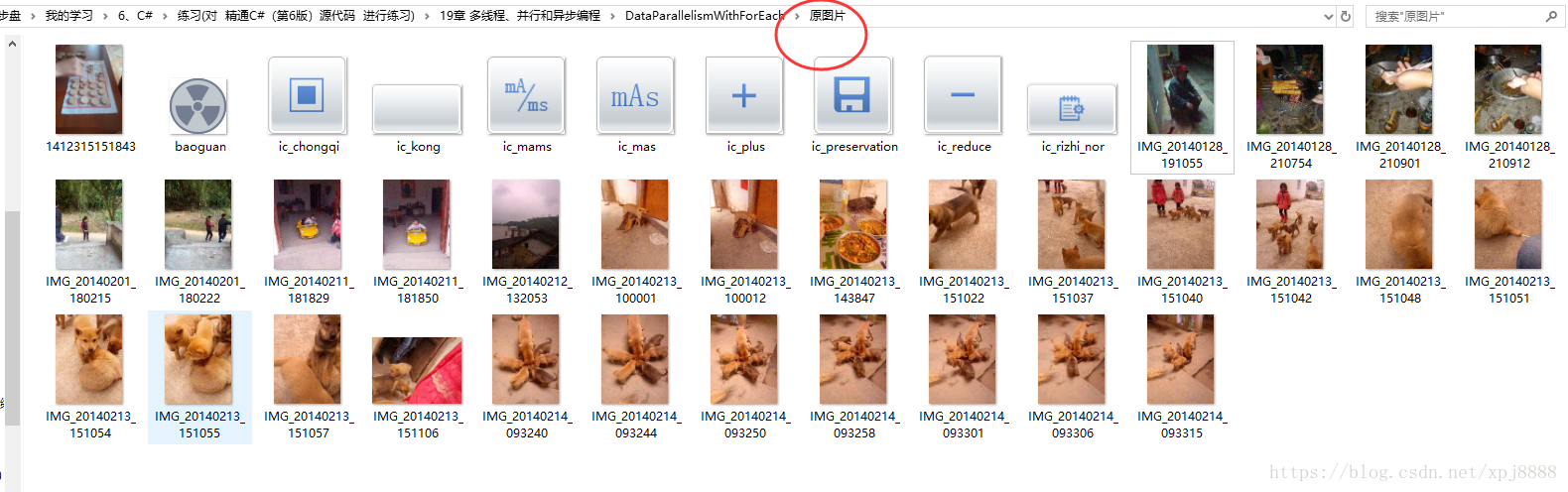
功能描述:构造WinFrom应用桌面程序,放置一个Textbox+一个Button,点击Button,在电脑本机用阻塞方式拷贝并旋转图片。
原图
WinForm界面图:
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
using System.IO;
namespace DataParallelismWithForEach
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnProcessImages_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ProcessFilse();
}
private void ProcessFilse()
{
//j加载所有的*.jpg文件,并未修改后的数据创建一个新的文件夹。
string[] files = Directory.GetFiles(@"F:\百度云同步盘\我的学习\6、C#\练习(对 精通C#(第6版)源代码 进行练习)\19章 多线程、并行和异步编程\DataParallelismWithForEach\原图片", "*.*",
SearchOption.AllDirectories);
string newDir = @"F:\百度云同步盘\我的学习\6、C#\练习(对 精通C#(第6版)源代码 进行练习)\19章 多线程、并行和异步编程\DataParallelismWithForEach\新图片";
Directory.CreateDirectory(newDir);
//以阻塞方式处理图像数据
foreach (string currentFile in files)
{
string filename = Path.GetFileName(currentFile);
using (Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(currentFile))
{
bitmap.RotateFlip(RotateFlipType.Rotate180FlipNone);
bitmap.Save(Path.Combine(newDir, filename));
//打印处理当前图像的线程ID
this.Text = string.Format("进程 {0} 使用的线程是;{1}", filename, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
}
//以并行方式处理图像数据
//Parallel.ForEach(files, currentFile =>
// {
// string filename = Path.GetFileName(currentFile);
// using (Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(currentFile))
// {
// bitmap.RotateFlip(RotateFlipType.Rotate180FlipNone);
// bitmap.Save(Path.Combine(newDir, filename));
// //打印处理当前图像的线程ID
// //this.Text = string.Format("进程 {0} 使用的线程是;{1}", filename, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// }
// }
//);
//try
//{
// // Process the image data in a parallel manner!
// Parallel.ForEach(files, parOpts, currentFile =>
// {
// parOpts.CancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
// string filename = Path.GetFileName(currentFile);
// using (Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(currentFile))
// {
// bitmap.RotateFlip(RotateFlipType.Rotate180FlipNone);
// bitmap.Save(Path.Combine(newDir, filename));
// //this.Text = string.Format("Processing {0} on thread {1}", filename,
// // Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// // We need to ensure that the secondary threads access controls
// // created on primary thread in a safe manner.
// this.Invoke((Action)delegate
// {
// this.Text = string.Format("Processing {0} on thread {1}", filename, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
// });
// }
// }
// );
//}
//catch (OperationCanceledException ex)
//{
// this.Invoke((Action)delegate
// {
// this.Text = ex.Message;
// });
//}
}
}
}
效果图:
例子18:拷贝并旋转图片(Parralel,效率比例17高。你只有在运行的过程中,才会发现其加载图片的效率比17方式快)
功能描述:与例17同
效果图:与例17同
代码片段:在例17注释中。
例19 允许次线程以线程安全的方式访问控件(即主线程)
功能描述:与18相同,但是主线程存在阻塞。
Parallel.ForEach(files, currentFile =>
{
string filename = Path.GetFileName(currentFile);
using (Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(currentFile))
{
bitmap.RotateFlip(RotateFlipType.Rotate180FlipNone);
bitmap.Save(Path.Combine(newDir, filename));
//次线性不能直接访问主线的线程ID
//this.Text = string.Format("进程 {0} 使用的线程是;{1}", filename, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//允许次线程以线程安全的方式访问控件(即主线程),但是主线程存在阻塞。this.Invoke在Windows Form API中调用,this.Diepatcher.Invoke在Windows WPF API中调用。
this.Invoke((Action)delegate
{
this.Text = string.Format("进程 {0} 使用的线程是;{1}", filename, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
);
}
}例20 Task类
Task类解决了例19主线程阻塞问题(阻塞问题表现在文本框不能输入文本,只有等待次线程Parralel运行完成后,才能输入)。但是现在,即可输入文本(主线程),也能执行点击事件(次线程)
private void btnProcessImages_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//ProcessFilse();
Task.Factory.StartNew(()=>
{
ProcessFilse();
}
);
}其他行的程序和例19相同。
例21 async+await
功能描述:async+await简化代码,快速实现加法操作。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AddWithThreads
{
#region The AddParams class
class AddParams
{
public int a, b;
public AddParams(int numb1, int numb2)
{
a = numb1;
b = numb2;
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AddAsync();
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static async Task AddAsync()
{
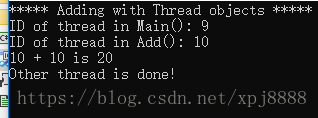
Console.WriteLine("***** Adding with Thread objects *****");
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Main(): {0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
AddParams ap = new AddParams(10, 10);
await Sum(ap);
Console.WriteLine("Other thread is done!");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static async Task Sum(object data)
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
if (data is AddParams)
{
Console.WriteLine("ID of thread in Add(): {0}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
AddParams ap = (AddParams)data;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} is {2}",
ap.a, ap.b, ap.a + ap.b);
}
});
}
}
}
效果图:
总结:
1、转载本博客请注明出处,谢谢。
2、本文QQ联系方式479166938,请多多指教

























 431
431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










