Java的内置锁一直都是备受争议的,在JDK 1.6之前,synchronized这个重量级锁其性能一直都是较为低下,虽然在1.6后,进行大量的锁优化策略,但是与Lock相比synchronized还是存在一些缺陷的:虽然synchronized提供了便捷性的隐式获取锁释放锁机制(基于JVM机制),但是它却缺少了获取锁与释放锁的可操作性,可中断、超时获取锁,且它为独占式在高并发场景下性能大打折扣。
多线程同步内部如何实现的
模拟一些同步的思路
- 自旋实现同步
volatile int status=0;//标识---是否有线程在同步块-----是否有线程上锁成功
void lock(){
while(!compareAndSet(0,1)){
}
//lock
//10 t1
}
void unlock(){
status=0;
}
boolean compareAndSet(int except,int newValue){
//cas操作,修改status成功则返回true
}
缺点:耗费cpu资源。没有竞争到锁的线程会一直占用cpu资源进行cas操作,假如一个线程获得锁后要花费Ns处理业务逻辑,那另外一个线程就会白白的花费Ns的cpu资源
- 让得不到锁的线程让出CPU:yield+自旋
volatile int status=0;
void lock(){
while(!compareAndSet(0,1)){
yield();//自己实现
}
//lock logic
}
void unlock(){
status=0;
}
要解决自旋锁的性能问题必须让竞争锁失败的线程不空转,而是在获取不到锁的时候能把cpu资源给让出来
yield()方法就能让出cpu资源,当线程竞争锁失败时,会调用yield方法让出cpu
自旋 + yield的方式并没有完全解决问题,当系统只有两个线程竞争锁时,yield是有效的。需要注意的是该方法只是当前让出cpu,有可能操作系统下次还是选择运行该线程,比如里面有2000个线程,想想会有什么问题?
- sleep + 自旋
volatile int status=0;
void lock(){
while(!compareAndSet(0,1)){
sleep(10);
}
//lock---10m
}
void unlock(){
status=0;
}
sleep的时间为什么是10?怎么控制呢?
就是你是调用者其实很多时候你也不知道这个时间是多少?
- park + 自旋 park相关资料: java 线程通信方式: suspend_resume、wait_notify、park_unpark 比较 - 四月謊言的个人空间 - OSCHINA Java的LockSupport.park()实现分析Java横云断岭的专栏-CSDN博客 LockSupport原理及应用- park_unpark park和unpark - 吼吼吼的吼 - 博客园
volatile int status=0;
Queue parkQueue;//集合 数组 list
void lock(){
while(!compareAndSet(0,1)){
//
park();----
}
//lock 10分钟
。。。。。。
unlock()
}
void unlock(){
lock_notify();
}
void park(){
//将当期线程加入到等待队列
parkQueue.add(currentThread);
//将当期线程释放cpu 阻塞 睡眠
releaseCpu();
}
void lock_notify(){
//status=0
//得到要唤醒的线程头部线程
Thread t=parkQueue.header();
//唤醒等待线程
unpark(t);
}
AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)
JUC同步器框架(AQS框架)原文翻译:
https://www.cnblogs.com/dennyzhangdd/p/7218510.html
AbstractQueuedSynchronizerde的底层实现是要是由下面三点实现的
- CAS以及自旋CAS:底层是lock cmpxchg
- park/unpark:底层是mutex(操作系统互斥量) park/unpark相关资料: java 线程通信方式: suspend_resume、wait_notify、park_unpark 比较 - 四月謊言的个人空间 - OSCHINA Java的LockSupport.park()实现分析Java横云断岭的专栏-CSDN博客 LockSupport原理及应用- park_unpark park和unpark - 吼吼吼的吼 - 博客园
- 队列:基于FIFO双向队列,队首的线程永远是null;对于队列的操作也是CAS的
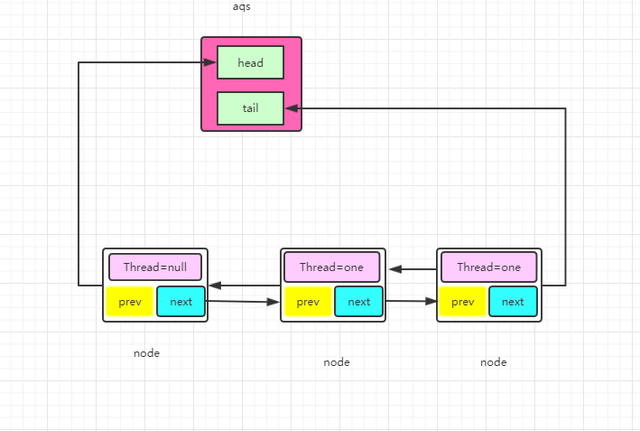
AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)类的主要成员变量
private transient volatile Node head; //队首
private transient volatile Node tail;//队尾
private volatile int state;//锁状态,加锁成功则为1,重入+1 解锁则为0
AQS当中的队列示意图
AQS.Node类的设计
public class Node{
volatile Node prev;//上一个节点
volatile Node next;//下一个节点
volatile Thread thread;//队列中的线程
volatile int waitStatus;;//线程等待状态
}
AQS.Node.waitStatus
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */
static final int CANCELLED = 1;//线程已取消
/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */
static final int SIGNAL = -1;//等待触发状态
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */
static final int CONDITION = -2;//线程在等待条件
/**
* waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should
* unconditionally propagate
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;//状态需要向后传播
上锁过程Demo
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Test {
private static int i ;
//锁对象,默认为非公平锁
final static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/*公平锁构造*/
//final static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
add();
}
},"线程1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
add();
}
},"线程2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(i);//i一定是200000,如果不加锁,则i可能小于200000
}
private static void add(){
//上锁
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " 获得锁!");
i++;
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
锁对象:其实就是ReentrantLock的实例对象,上述代码lock对象就是所谓的锁自由状态,自由状态表示锁对象没有被别的线程持有,计数器为0。
计数器:再lock对象中有一个字段state用来记录上锁次数,比如lock对象是自由状态则state为0,如果大于零则表示被线程持有了,当然也有重入那么state>1
waitStatus:仅仅是一个状态而已;ws是一个过渡状态,在不同方法里面判断ws的状态做不同的处理,所以ws=0有其存在的必要性
公平锁非公平锁的区别
[图片上传失败…(image-71ea0f-1612603525615)]
AQS.acquire方法
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//tryAcquire(arg)尝试加锁,如果加锁失败则会调用acquireQueued方法加入队列去排队,如果加锁成功则不会调用
//加入队列之后线程会立马park,等到解锁之后会被unpark,醒来之后判断自己是否被打断了,如果被打断了则执行selfInterrupt方法
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
/**
* Convenience method to interrupt current thread.
*/
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
AQS.addWaiter方法
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
//mode 为Node.EXCLUSIVE表示独占锁
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
//看看队列是否初始化,初始化了就直接CAS将当前线程设置为队尾,如果多线程环境下加入失败
//调用enq自旋加入队列
//没有初始化则调用enq入队
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) { //队尾不是空,说明队列已经初始化
node.prev = pred;//当前要加入节点的前驱节点设置为之前的队尾
//CAS设置当前节点为队尾(多线程环境下可能设置失败)
//设置失败直接走下面的enq自旋设置队尾
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;//之前的队尾后驱节点设置为当前节点,当前节点成了真正队尾
return node;//返回node
}
}
enq(node);//队列没有初始化时或者加入队尾失败事调用enq入队
return node;
}
AQS.enq方法
注意此处有自旋!也就是说node一定会被添加到队列中去,一次不行再循环,直到添加进去为止!
/**
* 将节点插入队列,必要时进行初始化
* Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.
* @param node the node to insert 要插入的节点(线程)
* @return node's predecessor 节点的前驱节点
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
//for (;;) 死循环即为自旋
//如果队列没有初始化。第一次进入循环时初始化队列并设置一个空节点,第二次进入循环的时候把节点设置为尾
//如果队列已经初始化则直接把节点设置为尾
for (;;) {//自旋
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize,此处进行初始化,初始化的node线程为null
//CAS初始化队头,无论有多少线程并发初始化,最终只有一个线程初始化成功
//其他线程自旋加入队尾
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;//当前节点的前驱节点为队尾
//CAS设置队尾,设置失败自旋再次设置,直到设置成功为止
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;//队尾的后驱节点设置为当前节点,当前节点是真正的队尾
return t;//返回当前节点
}
}
}
}
AQS.acquireQueued方法
注意此处有自旋!
/**
*
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
//for (;;)自旋
//对于第一个即将被park的线程,再次尝试获取一下锁(此时上一次获取锁的线程也可能执行完了),
//如果获取到锁了,则直接拿到锁开始执行,如果没获取到锁,说明上一个获取到锁的线程还没执行完
//如果不是第一个即将被park的线程,那么立即调用park阻塞,对于公平锁而言
//队列前面都还有线程在等待锁,你有啥资格一上来就要tryAcquire尝试获取锁??
//排在别人后面就安心的排队
boolean failed = true;//是否没获取到锁
try {
boolean interrupted = false;//是否被打断
for (;;) {//自旋
final Node p = node.predecessor();//前驱节点
//重点来了 p == head说明此时队列中只有当前线程处于等待状态,此时可以获取一下锁
//如果获取到了则直接拿到锁开始执行
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//尝试获取锁
setHead(node);//设置为队头,线程置为null
p.next = null; // help GC,把之前的队首的后驱节点设置为null,gc才能回收
failed = false;//成功获取到了锁
//注意!!此方法只有这一句返回语句,也就是说
//没有排在第二个的线程要等前面线程执行完后
//等自己变成了排在第二个线程才能返回
return interrupted;//没有被打断,直接返回
}
//自旋两次才能进入,第一次自旋shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire将前驱节点
//的ws改成-1(CAS操作),表示上一个线程正在休眠,第二次自旋返回true
//让当前线程休眠
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) //告诉当前线程是否应该休眠
&&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())//休眠操作,注意,此时当前线程在此阻塞住!!!
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
//如果拿锁失败,需要取消
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* Sets head of queue to be node, thus dequeuing. Called only by
* acquire methods. Also nulls out unused fields for sake of GC
* and to suppress unnecessary signals and traversals.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void setHead(Node node) {
//将节点设置为头
head = node;
//重点:设置为头的节点线程都被设置成了null
//符合队首为null的原则
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev.
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status 前驱节点
* @param node the node 当前节点
* @return {@code true} if thread should block 线程是否应该被阻塞
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
//检查线程是否需要被阻塞(调用park)
//如果队列里面上一个线程的ws为Node.SIGNAL,返回true,说明当前线程可以被park
//如果队列里面上一个线程的ws不为Node.SIGNAL。则通过CAS操作将上一个线程的ws改为
//Node.SIGNAL,再通过acquireQueued的自旋再次进入本方法返回true
//也就是说要不要让让当前线程park,得看上一个线程是否在等待状态
//一个线程休眠了,它自己不知道自己正在休眠,需要下一个线程来改ws状态值表明他休眠了
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)//Node.SIGNAL 为 -1
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);//休眠当前线程,线程在此阻塞住
return Thread.interrupted();
}
AQS.hasQueuedPredecessors方法(重点,判断是否需要进行排队)
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
// h != t 队列不是空 h == t 队列是空
//队列不是空并且队列第二个节点所在的线程不是当前正在执行的线程就需要排队
//反之队列不是空并且队列第二个节点所在的线程是当前正在执行的线程就不需要排队
//为啥第二个线程不需要排队? 我前面都没有线程排队了我还排队干嘛,直接执行就完了
//h != t && (s = h.next) == null 这种条件不成立,
//h != t 表示队列不是空,h.next = null表示第二个节点为null
//只有在队列为空的时候h.next = null才成立,所以相矛盾
//队列是空直接返回false,队列里面线程都没有,排什么队
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
AQS.release方法
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//如果尝试释放锁成功,tryRelease具体类有具体的实现
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;//拿到头
//判断头不是null并奇瑞ws不为0
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒头的后继节点
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 唤醒头的后继节点,如果存在的话
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;//队首的下一个节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
//如果队首的下一个节点为null或者ws大于0(线程已被取消)
//就从队尾开始遍历,为什么要从队尾开始遍历参考
//https://www.zhihu.com/question/50724462
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
//唤醒该线程
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
ReentrantLock.lock调用链(公平锁与非公平锁)
基础点:
- ReentrantLock.Sync继承自AQS
- ReentrantLock.FairSync继承自Sync
- ReentrantLock.NonfairSync也继承自Sync
- 公平锁(FairSync)ReentrantLock.lock() -> Sync.lock() -> FairSync.lock() -> AQS.acquire(1)
-> FairSync.tryAcquire(1) - 非公平锁(NonfairSync)ReentrantLock.lock() -> Sync.lock() -> NonfairSync.lock() -> AQS.acquire(1)
-> NonfairSync.tryAcquire(1)
ReentrantLock.FairSync(公平锁)
FairSync.tryAcquire
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
//拿到当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
//如果当前锁是自由状态
if (c == 0) {
//判断不需要排队并且CAS设置锁为占有状态成功则将活动线程设置为当前线程
//并返回true表明尝试获取锁成功
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
/*下面表示锁重入的时候*/
//如果当前锁不是自由状态(就是说有线程已经获取到了锁正在运行)
//并且活动线程为当前正在尝试获取锁的线程,即为锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
//锁状态累加
int nextc = c + acquires;
//累加的锁如果超过Integer.MAX_VALUE则抛出异常
//也就是说一直重入超过了int能表示的最大值
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
//直接将状态设置为累加的数值
//思考这里为什么不是CAS操作:因为此时活动线程只有一个,不会发生线程安全问题,所以不需要CAS
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
公平锁首先会调用tryAcquire去尝试加锁,当然这里的尝试加锁并不是直接加锁,事实上tryAcquire当中其实第一步便是判断锁是不是自由状态,如果是则判断直接是否需要排队(hasQueuedPredecessors方法判断队列是否被初始化(如果没有初始化显然不需要排队),和是否需要排队(队列如果被初始化了,则自己有可能需要排队,记住一朝排队,永远排队))
如果hasQueuedPredecessors返回false,由于取反了故而不需要排队则进行Cas操作去上锁,如果需要排队则不会进入if分支当中,也不会进else if,会直接返回false表示加锁失败
第二步如果不是自由状态再判断是不是重入,如果不是重入则直接返回false加锁失败,如果是重入则把计数器+1
ReentrantLock.NonfairSync(非公平锁)
NonfairSync.lock
final void lock() {
//直接去尝试加锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
//加锁成功设置为活动线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
//加锁失败进入等待队列
acquire(1);
}
NonfairSync.tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in
* subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
//拿出当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
//如果锁是自由状态
if (c == 0) {
//CAS尝试获取锁,获取成功则设置为活动线程
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
//锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
//没拿到锁返回flase
return false;
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










