LU分解是矩阵分解的一种,可以将一个矩阵分解为一个上三角矩阵和一个下三角矩阵的乘积。
LU分解可以用来求逆矩阵,解线性方程组等。本文将介绍LU分解求线性方程组的解。
1.定义
如果A是一个方阵,A的LU分解是将A分解成如下形式:
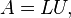
其中L,U分别为下三角矩阵和上三角矩阵。
2.例子
对于如下矩阵A,对A进行LU分解
首先将矩阵第一列对角线上元素A11下面的元素通过矩阵初等行变换变为0,
则得到的上三角矩阵就是U。这个时候,L也已经求出来了。通过将下三角形主对角线上的元素
都置为1,乘数因子放在下三角相应的位置(放在消元时将元素变为0的那个元素的位置),就
可以得到下三角矩阵L。如下:

对于L的构造,举个例子。如将第一列的元素2变为0时,第二行减去第一行乘以2,于是A21
就变成了0。这个乘数因子将元素A21变成了0,对应的,下三角矩阵L中对应位置的元素L21就为
乘数因子2。其它的与之类似。
3.LU分解程序实现(java实现)
通过上面举的例子,我们应该对LU分解的过程有了一个大致的了解。接下来可以看看程序
是怎么实现LU分解的,进一步加深对LU分解的了解。
/**
* Get matrix L and U. list.get(0) for L, list.get(1) for U
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @return matrix L and U, list.get(0) for L, list.get(1) for U
*/
private static List<double[][]> decomposition(double[][] a) {
final double esp = 0.000001;
double[][] U = a;
double[][] L = createIdentiyMatrix(a.length);
for(int j=0; j<a[0].length - 1; j++) {
if(Math.abs(a[j][j]) < esp) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("zero pivot encountered.");
}
for(int i=j+1; i<a.length; i++) {
double mult = a[i][j] / a[j][j];
for(int k=j; k<a[i].length; k++) {
U[i][k] = a[i][k] - a[j][k] * mult;
}
L[i][j] = mult;
}
}
return Arrays.asList(L, U);
}
而
Math.abs(a[j][i]) < esp
4.LU分解解线性方程组
通过上面的介绍,我们已经知道,一个方阵A可以分解成 A=LU的形式(这里假设矩阵A能够进行LU分解)。
对于一个线性方程组 Ax=b,则由 A=LU 有 LUx = b。
为了求出x,我们可以先将Ux看成一个整体V(V=UX),通过求解线性方程组 LV=b 得到V,即Ux,
再通过求解线性方程组 Ux=V 即可求出 x。
看到这里,你可能会觉得这样求解很麻烦。但是,别忘了L和U分别是下三角矩阵和上三角矩阵,
求解释很容易,不需要通过高斯消去法等求线性方程组的算法来求解。
首先来看一下 LV=b 求解V的程序代码:
/**
* Get U multiply X
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @param b - right-hand side of the equations
* @param L - L of LU Decomposition
* @return U multiply X
*/
private static double[] getUMultiX(double[][] a, double[] b, double[][] L) {
double[] UMultiX = new double[a.length];
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
double right_hand = b[i];
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {
right_hand -= L[i][j] * UMultiX[j];
}
UMultiX[i] = right_hand / L[i][i];
}
return UMultiX;
}/**
* Get solution of the equations
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @param U - U of LU Decomposition
* @param UMultiX - U multiply X
* @return Equations solution
*/
private static double[] getSolution(double[][] a, double[][] U,
double[] UMultiX) {
double[] solutions = new double[a[0].length];
for(int i=U.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
double right_hand = UMultiX[i];
for(int j=U.length-1; j>i; j--) {
right_hand -= U[i][j] * solutions[j];
}
solutions[i] = right_hand / U[i][i];
}
return solutions;
} 如果觉得整个LU分解求解方程组的解过程 还没有连接起来的话,可以看看下面整个程序的完整代码。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class LUDecomposition {
/**
* Get solutions of the equations
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @param b - right-hand side of the equations
* @return solution of the equations
*/
public static double[] solve(double[][] a, double[] b) {
List<double[][]> LAndU = decomposition(a); //LU decomposition
double[][] L = LAndU.get(0);
double[][] U = LAndU.get(1);
double[] UMultiX = getUMultiX(a, b, L);
return getSolution(a, U, UMultiX);
}
/**
* Get solution of the equations
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @param U - U of LU Decomposition
* @param UMultiX - U multiply X
* @return Equations solution
*/
private static double[] getSolution(double[][] a, double[][] U,
double[] UMultiX) {
double[] solutions = new double[a[0].length];
for(int i=U.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
double right_hand = UMultiX[i];
for(int j=U.length-1; j>i; j--) {
right_hand -= U[i][j] * solutions[j];
}
solutions[i] = right_hand / U[i][i];
}
return solutions;
}
/**
* Get U multiply X
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @param b - right-hand side of the equations
* @param L - L of LU Decomposition
* @return U multiply X
*/
private static double[] getUMultiX(double[][] a, double[] b, double[][] L) {
double[] UMultiX = new double[a.length];
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
double right_hand = b[i];
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {
right_hand -= L[i][j] * UMultiX[j];
}
UMultiX[i] = right_hand / L[i][i];
}
return UMultiX;
}
/**
* Get matrix L and U. list.get(0) for L, list.get(1) for U
* @param a - Coefficient matrix of the equations
* @return matrix L and U, list.get(0) for L, list.get(1) for U
*/
private static List<double[][]> decomposition(double[][] a) {
double[][] U = a;
double[][] L = createIdentityMatrix(a.length);
for(int j=0; j<a[0].length - 1; j++) {
if(a[j][j] == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("zero pivot encountered.");
}
for(int i=j+1; i<a.length; i++) {
double mult = a[i][j] / a[j][j];
for(int k=j; k<a[i].length; k++) {
U[i][k] = a[i][k] - a[j][k] * mult;
}
L[i][j] = mult;
}
}
return Arrays.asList(L, U);
}
private static double[][] createIdentityMatrix(int row) {
double[][] identityMatrix = new double[row][row];
for(int i=0; i<identityMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j=i; j<identityMatrix[i].length; j++) {
if(j == i) {
identityMatrix[i][j] = 1;
} else {
identityMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return identityMatrix;
}
}
5. LU分解的不足及改进
经典的LU分解算法当方阵中主元(主对角线上的元素) 出现0时,上面介绍的经典LU分解算法将失效,
上面的算法中也已经体现出来了。不过,我们可以在A=LU分解的基础上做出比较小的改动,就可以
使这个算法在上述情况下来能适用。随人 PA=LU 方法也可以解决这一问题,但是计算的耗费较大,
我们可以 将 decomposition 函数中的 对主元是否为0进行判断的 if 语句
if(a[j][j] == 0) {......}
改为
if(a[j][j] == 0) { a[j][j] = 1e-20; }
这样就可以方便的解决主元为0的问题,而且不需要额外的计算。
6.参考文献
1. 维基百科,http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/LU%E5%88%86%E8%A7%A3
2. Numerical Analysis, 2nd edition, Timothy Sauer.

























 7812
7812











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








