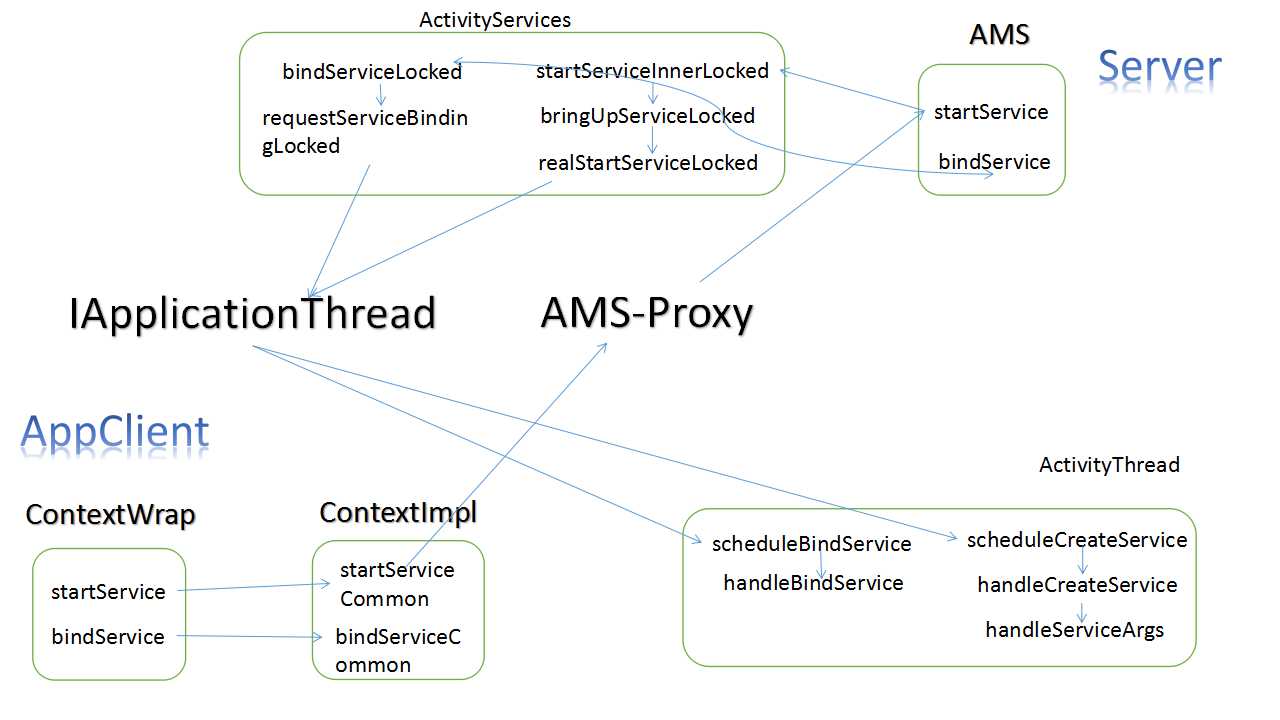
流程图
这几天抽出空又把主席的《Android开发艺术探索》的Service启动看了遍,用精简的语言总结下。
分析
- 当我们调用startService()方法的时候,其实就是调用了AMS的代理对象执行了次IPC操作,当AMS执行到realStartServiceLocked的时候,执行了
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);那么这个app.thread其实也是ApplicationThread的Proxy,至于AMS和他依附的时期是在ActivityThread的attach()方法里面
private void attach(boolean system) {
......
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
......
}那么,最终还是执行到ActivityThread中的ApplicationThread中scheduleCreateService()方法,
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}所以,我们要到H中去找标示识CREATE_SERVICE的分支,最终到handleCreateService方法内
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo







 本文详细介绍了Android中Service的启动和绑定流程。从startService()方法开始,涉及AMS的IPC操作,到ActivityThread的调度,再到Service的实例化。接着分析bindService的过程,包括ServiceDispatcher的作用,Binder的使用,以及onServiceConnected回调,确保服务已连接。
本文详细介绍了Android中Service的启动和绑定流程。从startService()方法开始,涉及AMS的IPC操作,到ActivityThread的调度,再到Service的实例化。接着分析bindService的过程,包括ServiceDispatcher的作用,Binder的使用,以及onServiceConnected回调,确保服务已连接。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1947
1947

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








