1. 铺垫基础知识:
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp4
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("1. 创建");
Create();
Console.WriteLine("2. 线程池");
ThreadPoolTest();
Console.WriteLine("3. 传入参数");
ParaTest();
Console.WriteLine("4. 返回值");
ReturnTest();
Console.WriteLine("5. Semaphore 信号量(锁很好理解,忽视)");
SemaphoreSlimTest();
Console.WriteLine("6. 异常");
//ThreadExceptionTest();
//TaskExceptionTest();
Console.Read();
}
public static void TaskExceptionTest()
{
try
{
var task = Task.Run(() => { GoException(); });
task.Wait(); // 在调用了这句话之后,主线程才能捕获task里面的异常
// 对于有返回值的Task, 我们接收了它的返回值就不需要再调用Wait方法了
// GetName 里面的异常我们也可以捕获到
var task2 = Task.Run(() => { GetNameExeception(); });
task2.Wait();
//var name = task2.Result;
}
catch (AggregateException ex)
{
foreach(Exception ex2 in ex.InnerExceptions)
Console.WriteLine("Exception!{0}", ex2.Message);
}
}
private static void GetNameExeception()
{
throw new Exception("Task Exeception.");
}
public static void ThreadExceptionTest()
{
try
{
new Thread(GoException).Start();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 其它线程里面的异常,我们这里面是捕获不到的。
Console.WriteLine("Thread Exception!");
}
}
static void GoException() { throw new Exception("Go Exception"); }
static SemaphoreSlim _sem = new SemaphoreSlim(3); // 我们限制能同时访问的线程数量是3
static void SemaphoreSlimTest()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
new Thread(Enter).Start(i);
}
}
static void Enter(object id)
{
Console.WriteLine(id + " 开始排队...");
_sem.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("{0} 开始执行!, 将允许进入 SemaphoreSlim 线程数: {1}", id, _sem.CurrentCount);
Thread.Sleep(1000 * (int)id);
Console.WriteLine(id + " 执行完毕,离开!");
_sem.Release();
}
static void ReturnTest()
{
// GetDayOfThisWeek 运行在另外一个线程中
var dayName = Task.Run<string>(() => { return GetDayOfThisWeek(); });
Console.WriteLine("今天是:{0}", dayName.Result);
}
private static string GetDayOfThisWeek()
{
return DateTime.Now.DayOfWeek.ToString();
}
private static void ParaTest()
{
new Thread(Go2).Start("arg1"); // 没有匿名委托之前,我们只能这样传入一个object的参数
new Thread(delegate ()
{ // 有了匿名委托之后...
GoGoGo("arg1", "arg2", "arg3");
}).Start();
new Thread(() =>
{ // 当然,还有 Lambada
GoGoGo("arg1", "arg2", "arg3");
}).Start();
Task.Run(() =>
{ // Task能这么灵活,也是因为有了Lambda呀。
GoGoGo("arg1", "arg2", "arg3");
});
}
public static void GoGoGo(string arg1, string arg2, string arg3)
{
Console.WriteLine("1.{0}; 2.{1}; 3.{2}",arg1,arg2,arg3);
}
private static void ThreadPoolTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是主线程:Thread Id {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Go2);
}
public static void Go2(object data)
{
Console.WriteLine("我是另一个线程:Thread Id {0}, 参数值:{1}"
, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId
, data
);
}
private static void Create()
{
new Thread(Go).Start(); // .NET 1.0开始就有的
Task.Factory.StartNew(Go); // .NET 4.0 引入了 TPL
Task.Run(new Action(Go)); // .NET 4.5 新增了一个Run的方法
}
public static void Go()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是另一个线程");
}
}
}
2. 一个小例子认识async & await
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test(); // 这个方法其实是多余的, 本来可以直接写下面的方法
// await GetName()
// 但是由于控制台的入口方法不支持async,所有我们在入口方法里面不能 用 await
Console.WriteLine("Current Thread Id :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.Read();
}
static async Task Test()
{
// 方法打上async关键字,就可以用await调用同样打上async的方法
// await 之后不会开启新的线程(await 从来不会开启新的线程)
await GetName();
}
static async Task GetName()
{
// Delay 方法来自于.net 4.5
await Task.Delay(1000); // 返回值前面加 async 之后,方法里面就可以用await了
Console.WriteLine("Current Thread Id :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine("In antoher thread.....");
}
}
}
3. 看清什么时候才创建线程:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp6
{
class Program
{
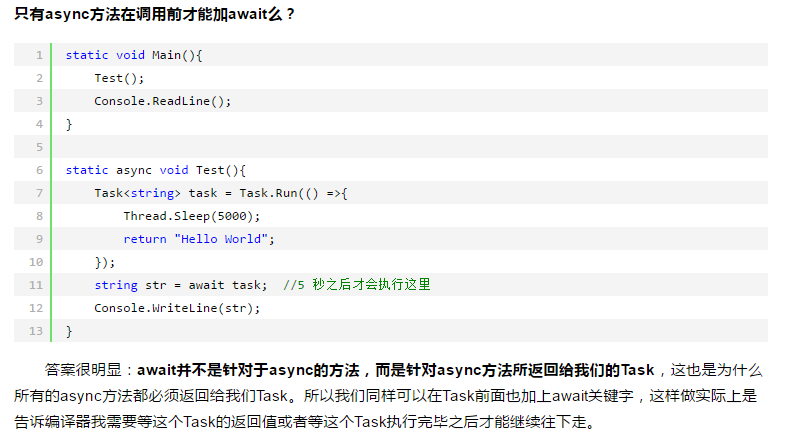
static void Main(string[] args)
{
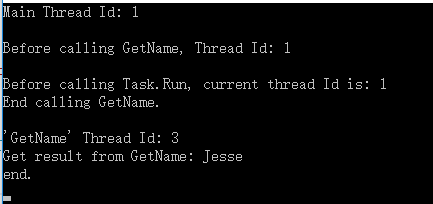
Console.WriteLine("Main Thread Id: {0}\r\n", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Test();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static async Task Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Before calling GetName, Thread Id: {0}\r\n", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
var name = GetName(); //我们这里没有用 await,所以下面的代码可以继续执行
// 但是如果上面是 await GetName(),下面的代码就不会立即执行,输出结果就不一样了。
Console.WriteLine("End calling GetName.\r\n");
Console.WriteLine("Get result from GetName: {0}", await name);
Console.WriteLine("end.");
}
static async Task<string> GetName()
{
// 这里还是主线程
Console.WriteLine("Before calling Task.Run, current thread Id is: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
return await Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("'GetName' Thread Id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
return "Jesse";
});
}
}
}
不用 await 关键字, 如何确认Task已执行完?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp6
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var task = Task.Run(() => {
return GetName();
});
task.GetAwaiter().OnCompleted(() => {
// 2 秒之后才会执行这里
var name = task.Result;
Console.WriteLine("My name is: " + name);
});
Console.WriteLine("主线程执行完毕");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static string GetName()
{
Console.WriteLine("另外一个线程在获取名称");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Jesse";
}
}
}
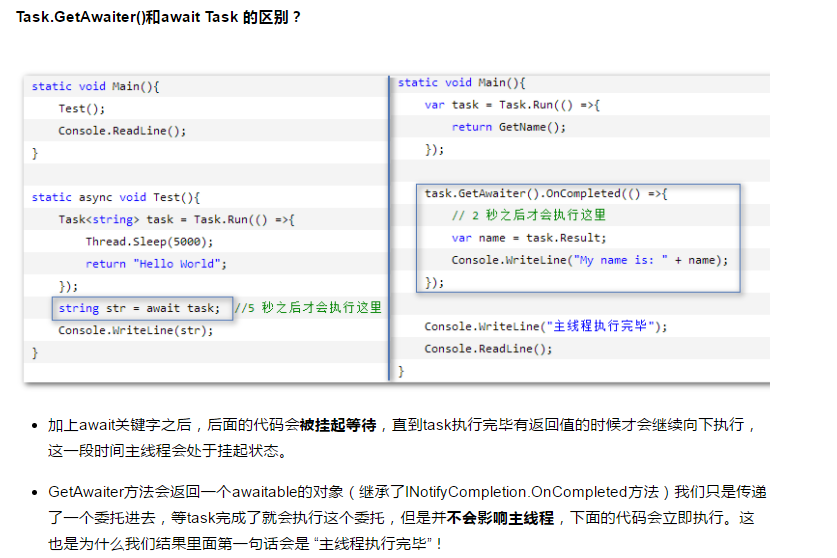
Task 如何让线程挂起?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp6
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var task = Task.Run(() => {
return GetName();
});
var name = task.GetAwaiter().GetResult();
Console.WriteLine("My name is:{0}", name);
Console.WriteLine("主线程执行完毕");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static string GetName()
{
Console.WriteLine("另外一个线程在获取名称");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Jesse";
}
}
}

Task.GetAwait()方法会给我们返回一个awaitable的对象,通过调用这个对象的GetResult方法就会挂起主线程,当然也不是所有的情况都会挂起。还记得我们Task的特性么? 在一开始的时候就启动了另一个线程去执行这个Task,当我们调用它的结果的时候如果这个Task已经执行完毕,主线程是不用等待可以直接拿其结果的,如果没有执行完毕那主线程就得挂起等待了。
await 实质是在调用awaitable对象的GetResult方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp6
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Test();
Console.ReadLine();
}
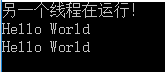
static async Task Test()
{
Task<string> task = Task.Run(() => {
Console.WriteLine("另一个线程在运行!"); // 这句话只会被执行一次
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return "Hello World";
});
// 这里主线程会挂起等待,直到task执行完毕我们拿到返回结果
var result = task.GetAwaiter().GetResult();
Console.WriteLine(result);
// 这里不会挂起等待,因为task已经执行完了,我们可以直接拿到结果
var result2 = await task;
Console.WriteLine(result2);
}
}
}






















 62
62

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








