1)spring对bean进行实例化,默认bean是单例
2)spring对bean进行依赖注入
3)如果bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,spring将bean的id传给setBeanName()方法
4)如果bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,spring将调用setBeanFactory方法,将BeanFactory实例传进来
5)如果bean实现了ApplicationContextAware()接口,spring将调用setApplicationContext()方法将应用上下文的引用传入
6) 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization接口方法
7) 如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,spring将调用它们的afterPropertiesSet接口方法,类似的如果bean使用了init-method属性声明了初始化方法,改方法也会被调用
8)如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessAfterInitialization接口方法
9)此时bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁
10)若bean实现了DisposableBean接口,spring将调用它的distroy()接口方法。同样的,如果bean使用了destroy-method属性声明了销毁方法,则该方法被调用
其实很多时候我们并不会真的去实现上面说描述的那些接口,那么下面我们就除去那些接口针对bean的单例和非单例来描述下bean的生命周期:
一,单例管理的对象:
1.默认情况下,spring在读取xml文件的时候,就会创建对象。
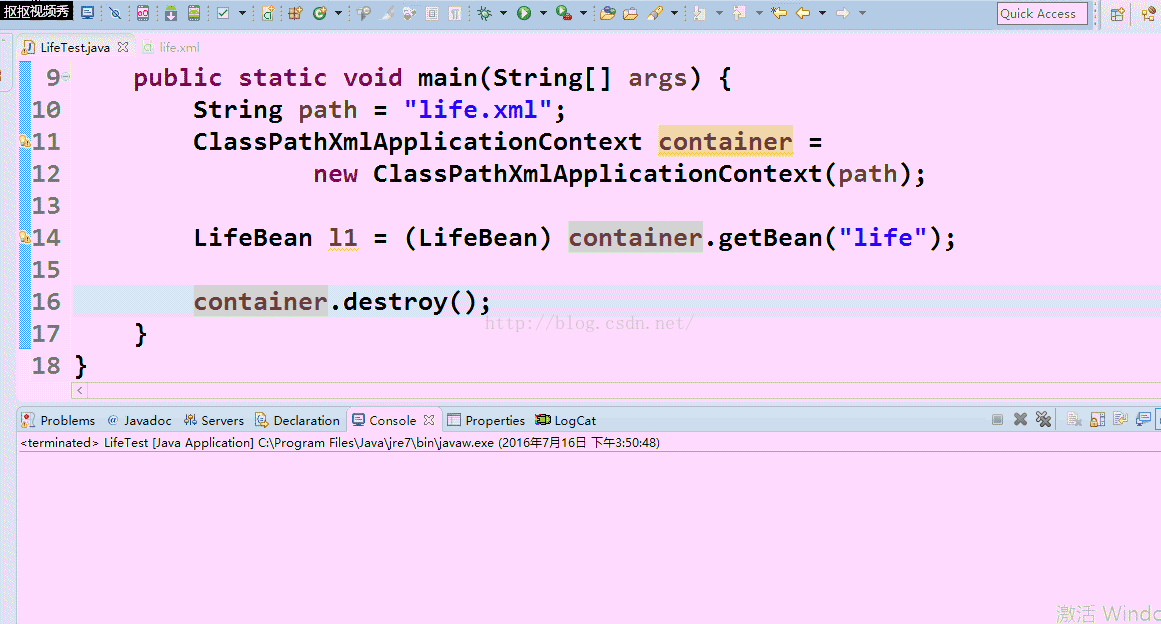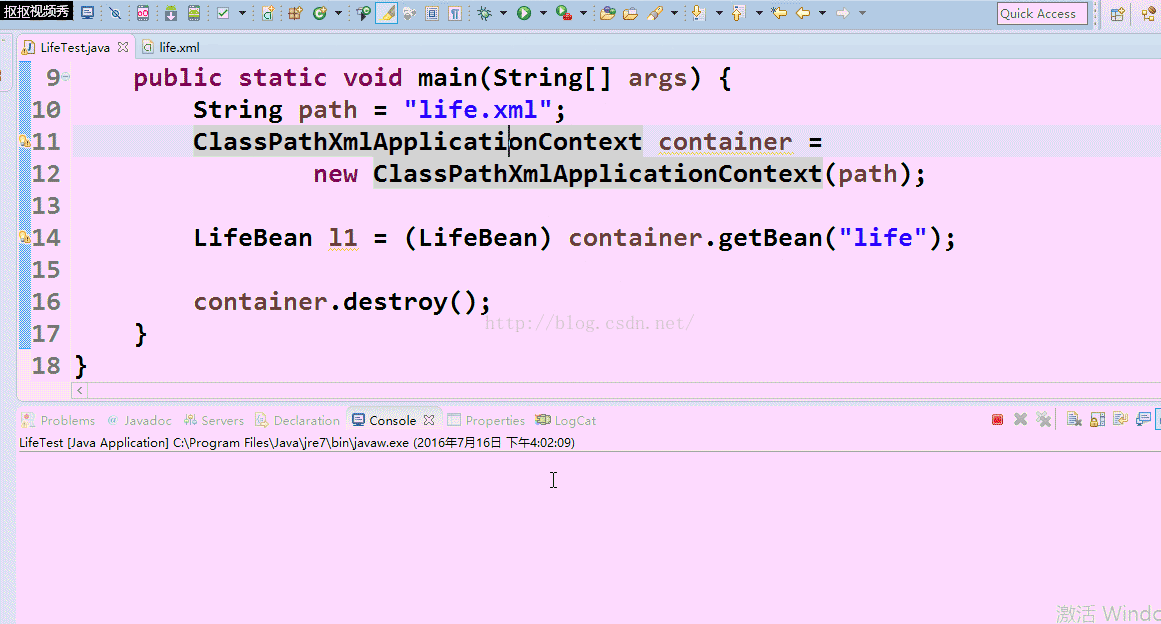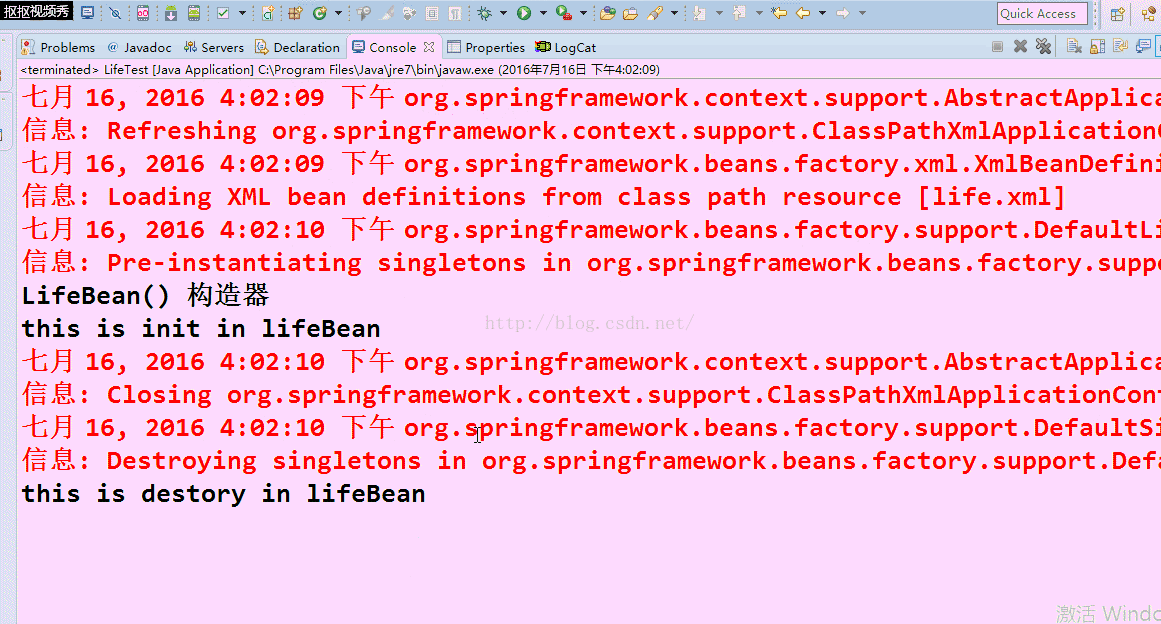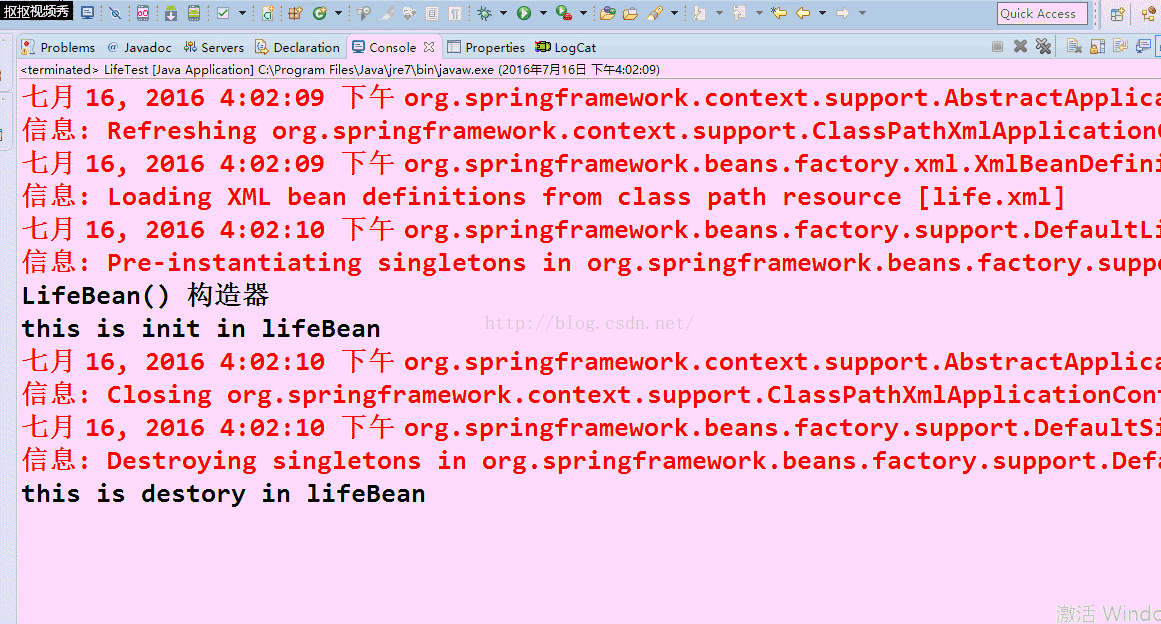
2.在创建的对象的时候(先调用构造器),会去调用init-method=".."属性值中所指定的方法.
3.对象在被销毁的时候,会调用destroy-method="..."属性值中所指定的方法.(例如调用container.destroy()方法的时候)
4.lazy-init="true",可以让这个对象在第一次被访问的时候创建
代码编写如下:
1.先写Bean类-LifeBean类:
- public class LifeBean{
- private String name;
- private LifeBean lb;
- public LifeBean getLb() {
- return lb;
- }
- public void setLb(LifeBean lb) {
- this.lb = lb;
- }
- public LifeBean(){
- System.out.println("LifeBean() 构造器");
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- System.out.println("setName() 方法");
- this.name = name;
- }
- public void init(){
- System.out.println("this is init in lifeBean");
- }
- public void destory(){
- System.out.println("this is destory in lifeBean");
- }
- }

2.写配置文件life.xnl:(注:配置文件时随便命名的,只要是xml文件就行~)
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
- <bean name="life" class="com.x.spring.bean.LifeBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>
- </beans>

3.编写测试类LifeTest:
- public class LifeTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String path = "life.xml";
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext container =
- new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
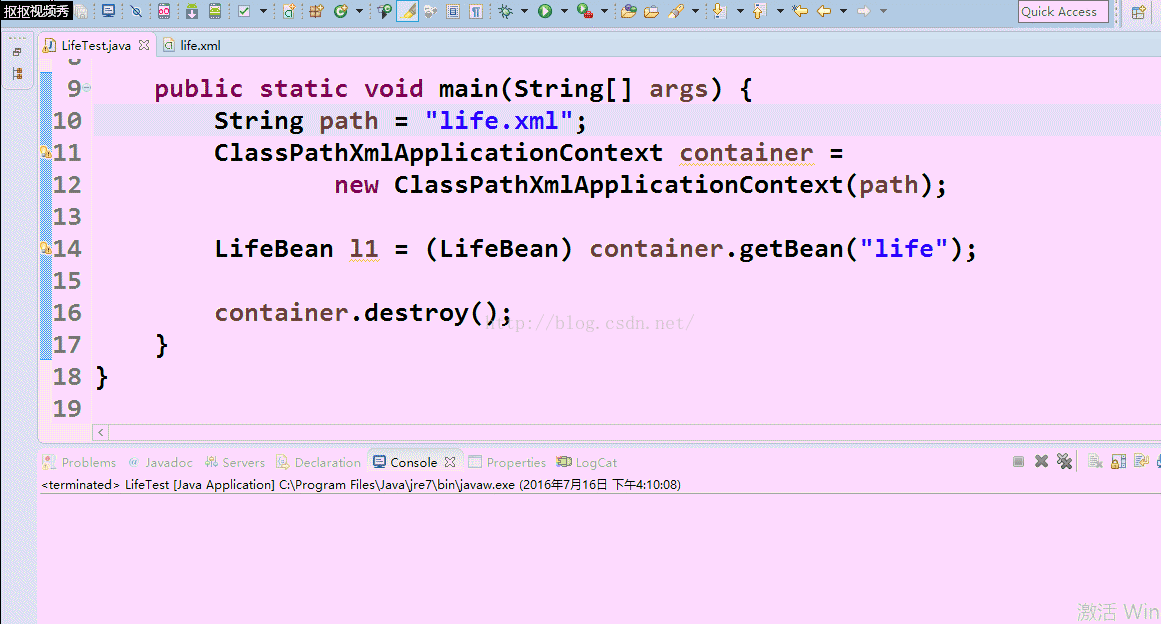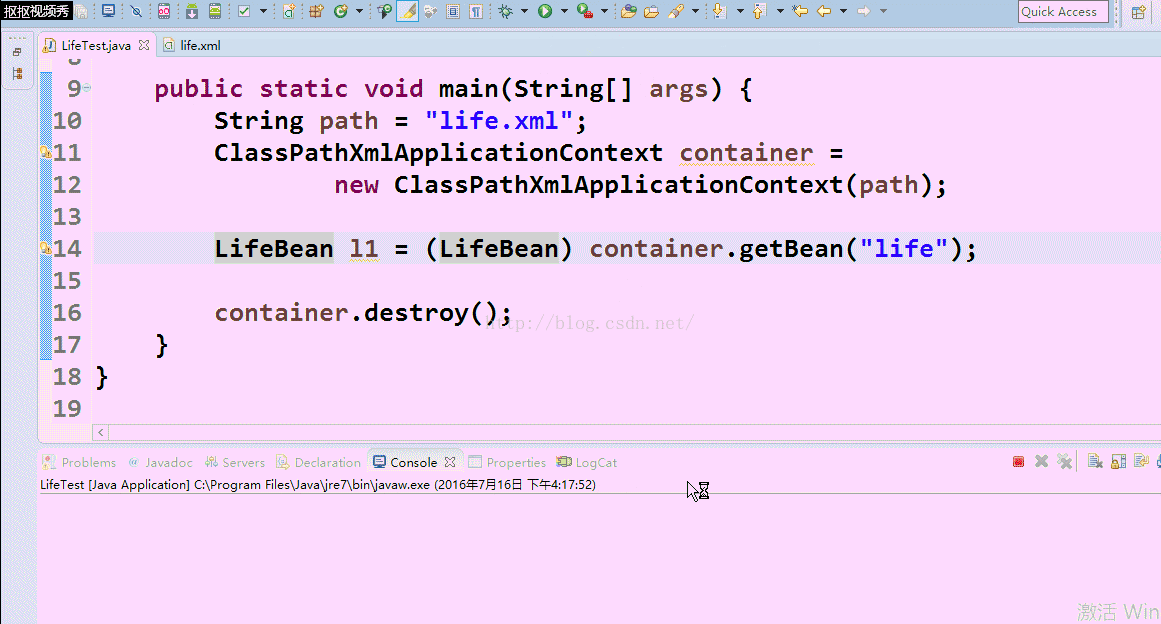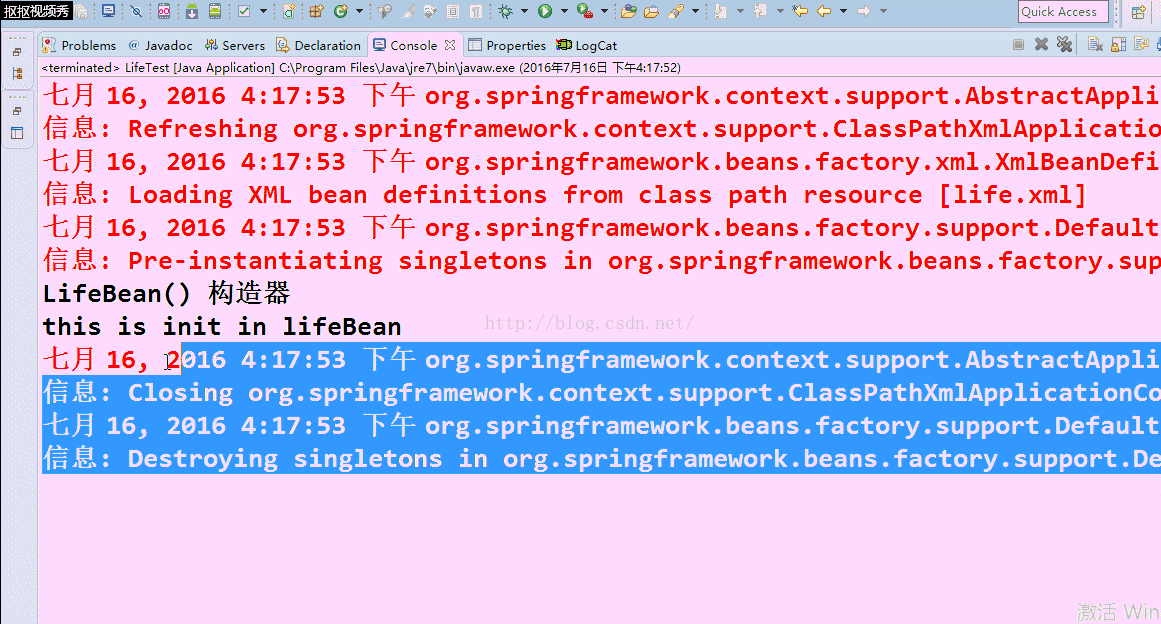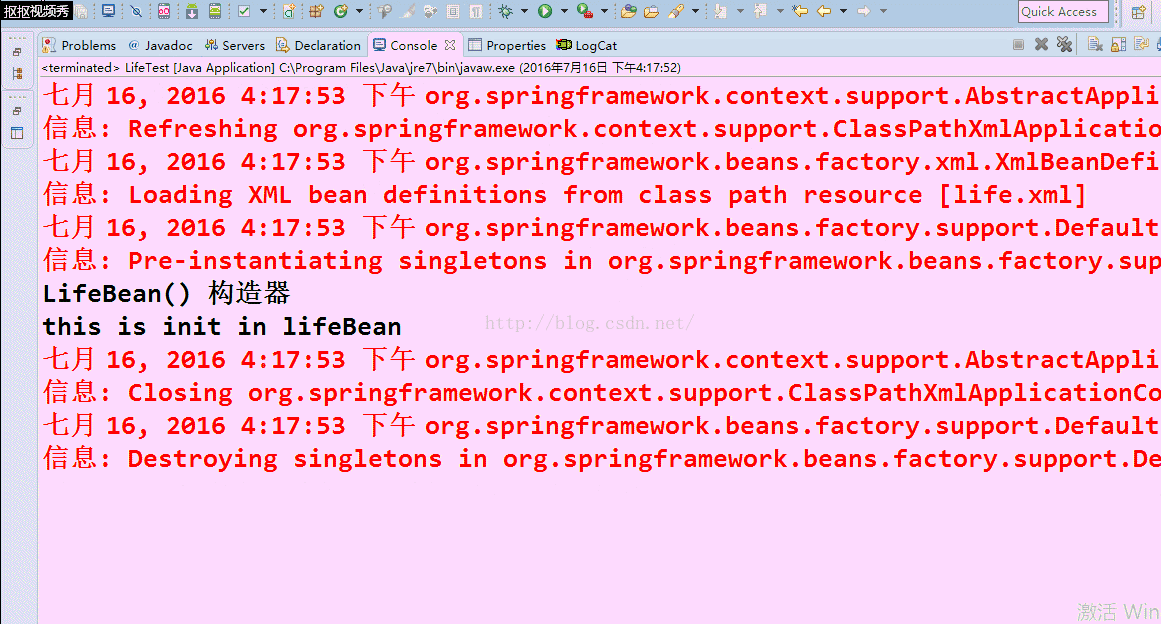
- LifeBean l1 = (LifeBean) container.getBean("life");
- //container.destroy();
- }
- }
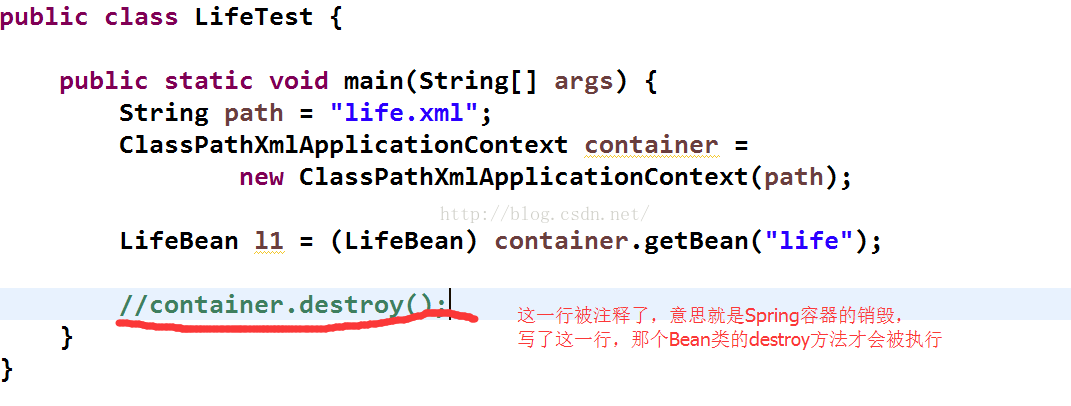
看看注释掉了这一行的效果图:
在看看没注释掉的效果图:
这个就算写完了~
二,非单例管理的对象:
1.spring读取xml文件的时候,不会创建对象.
2.在每一次访问这个对象的时候,spring容器都会创建这个对象,并且调用init-method=".."属性值中所指定的方法.
3.对象销毁的时候,spring容器不会帮我们调用任何方法,因为是非单例,这个类型的对象有很多个,spring容器一旦把这个对象交给你之后,就不再管理这个对象了.
代码编写:
只需要改一点配置文件的代码:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
- <bean name="life" class="com.x.spring.bean.LifeBean" scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>
- </beans>

效果图如下:
好了,这个生命周期到这里就写完了~
补充测试:
package com.java1234.entity;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class LifeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "life.xml";
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext container =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
LifeBean l1 = (LifeBean) container.getBean("life");
LifeBean l2 = (LifeBean) container.getBean("life");
System.out.println(l1);
System.out.println(l2);//打印内存地址 ,当scope="prototype"不一致说明不是同一个bean
//去除后打印内存地址相同,说明是同一个bean
container.destroy();
}
} 输出结果:
[main] INFO org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@d8355a8: startup date [Wed Mar 21 22:19:22 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
[main] INFO org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [life.xml]
LifeBean() 构造器
this is init in lifeBean
LifeBean() 构造器
this is init in lifeBean
com.java1234.entity.LifeBean@305b7c14
com.java1234.entity.LifeBean@6913c1fb
[main] INFO org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@d8355a8: startup date [Wed Mar 21 22:19:22 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy加上 scope="prototype"后,可以观察内存地址不同,说明是不同对象;且destro也不执行,说明非单例模式spring创建对象之后不再管理了。
[main] INFO org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [life.xml]
LifeBean() 构造器
this is init in lifeBean
com.java1234.entity.LifeBean@192b07fd
com.java1234.entity.LifeBean@192b07fd
[main] INFO org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@73a8dfcc: startup date [Wed Mar 21 22:17:48 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
this is destory in lifeBean而去除scope="prototype"后,打印地址相同说明是相同对象。
另附:
lazy-init 延迟加载:
Spring配置默认default-lazy-init为false,当属性default-lazy-init设置为true时,Spring启动时不会再去加载整个对象实例图,不过这样做可以大大减小Spring的启动时间。所谓的加载整个对象实例图就是从初始化action配置、到service配置、到dao配置以及数据库连接等等。
注意:default-lazy-init该属性是配置在beans里面
同时我们可以针对具体的模块在相应的bean里面使用lazy-init 属性,lazy-init 比default-lazy-init的优先级高。
ref:
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_33642117/article/details/51924653























 587
587











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








