题目:
poj3321
题意:
给你一棵以1为根的树,树上的结点不成规律(即pos结点的左子树不是pos<<1,右子树不是pos<<1|1),因此不能用线性数组来存数据。结点初始有1个apple,有如下操作:
C pos:把pos结点的apple取反(即1→0,0→1)
Q pos:查询pos结点以及它的子节点的apple总个数
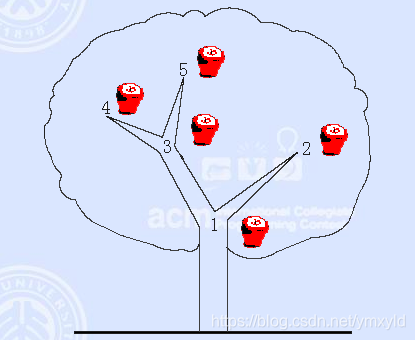
思路:先根据输入的数据建树(有可能是多叉树),再计算每个结点的有效范围(每个结点在树状数组的起点和终点,即这个有效范围包含了这个结点和它的子节点,as:一个结点的有效范围是 [2, 7],那么它的值(pos结点以及它的子节点的apple总个数)为sum(7) - sum(2-1)。)
ps:输入的结点数据具有向根性,即 fork u fork v 一定 u 是 v 的 parent 。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#define lowbit(a) ((a) & (-a))
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 10;
vector<vector<int> > son(MAXN); //这里如果是vector<int> son[MAXN]就会TLE
int tree[MAXN];
int s[MAXN], e[MAXN]; //结点的有效范围 s ~ e
int apple[MAXN];
int n, tot = 0; //tot:结点有效范围在树状数组的坐标
void build(int pos){
s[pos] = ++tot;
for (int i = 0; i < son[pos].size(); i++)
build(son[pos][i]);
e[pos] = tot;
}
void add(int x, int d){
while (x <= n){
tree[x] += d;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x){
int cnt = 0;
while (x > 0){
cnt += tree[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return cnt;
}
int main(){
// freopen("_in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("_out1.txt", "w", stdout);
int m, h, t, a;
char op;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d%d", &h, &t);
son[h].push_back(t);
}
build(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
tree[i] = lowbit(i); //因为一开始apple都是1,所有tree[i]=lowbit(i)
apple[i] = 1;
}
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--){
scanf(" %c", &op);
scanf("%d", &a);
if (op == 'C'){
if (apple[a] == 1)
add(s[a], -1);
else
add(s[a], 1);
apple[a] ^= 1;
}
else
printf("%d\n", sum(e[a]) - sum(s[a]-1));
}
return 0;
}





















 47
47











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








