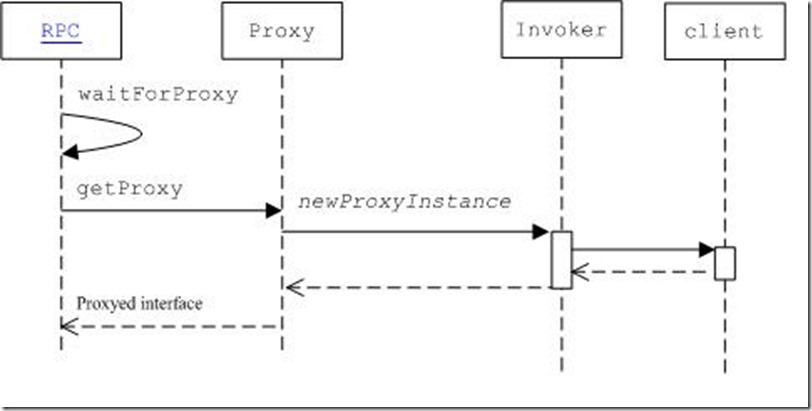
1.client运行的流程
1)创建代理对象;
2)代理对象调用相应方法(invoke());
3)invoke调用client对象的call方法,向服务器发送请求(参数、方法);
4)再等待call方法的完成;
5)返回请求结果。
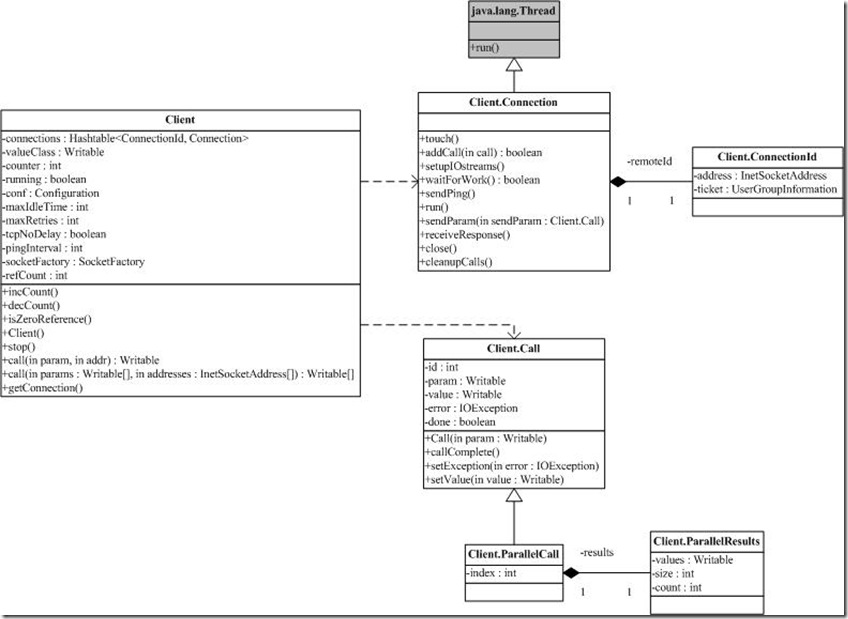
2.client主要的内部类
主要的几个类说明:
- 1. Call,表示一次rpc的调用请求
- 2. Connection,表示一个client与server之间的连接,一个连接一个线程启动
- 3. ConnectionId:连接的标记(包括server地址,协议,其他一些连接的配置项信息)
- 4. ParallelCall:实现并行调用的请求
- 5. ParallelResults:并行调用的执行结果
3.client调用过程
3.0一个实际的调用
在DFSclient中
return (ClientDatanodeProtocol)RPC.getProxy(ClientDatanodeProtocol.class, ClientDatanodeProtocol.versionID, addr, conf);
3.1生成代理
public static VersionedProtocol getProxy(Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol, long clientVersion, InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout) throws IOException { …… VersionedProtocol proxy = (VersionedProtocol) Proxy.newProxyInstance(protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { protocol }, new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout)); …… return proxy; }
其中Invoker是一个实现了InvocationHandler 接口的类
3.2代理对象调用相应方法(invoke())
getProxy调用者,使用这个proxy进行任何protocol声明的函数调用,比如还是上例中DFSclient的例子,如果调用proxy.getBlockInfo(…);都会转化成调用Invoker类的invoke函数
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { …… ObjectWritable value = (ObjectWritable) client.call(new Invocation(method, args), remoteId); …… return value.get(); }
Invocation 用于封装方法名和参数,作为数据传输层。远程调用的主要关键就是Invocation实现了Writable接口,Invocation在write(DataOutput out)函数中将调用的methodName写入到out,将调用方法的参数个数写入out ,同时逐个将参数的className写入out,最后将所有参数逐个写入out,这也就决定了通过RPC实现调用的方法中的参数要么是简单类型,要么是String,要么是实现了Writable接口的类(参数自己知道如何序列化到stream),要么是数组(数组的元素也必须为简单类型,String,实现了Writable接口的类)。
Invocation序列化参数的实现是通过如下函数实现的:org.apache.hadoop.io.ObjectWritable.writeObject
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { UTF8.writeString(out, methodName); out.writeInt(parameterClasses.length); for (int i = 0; i < parameterClasses.length; i++) { ObjectWritable.writeObject(out, parameters[i], parameterClasses[i], conf); } }
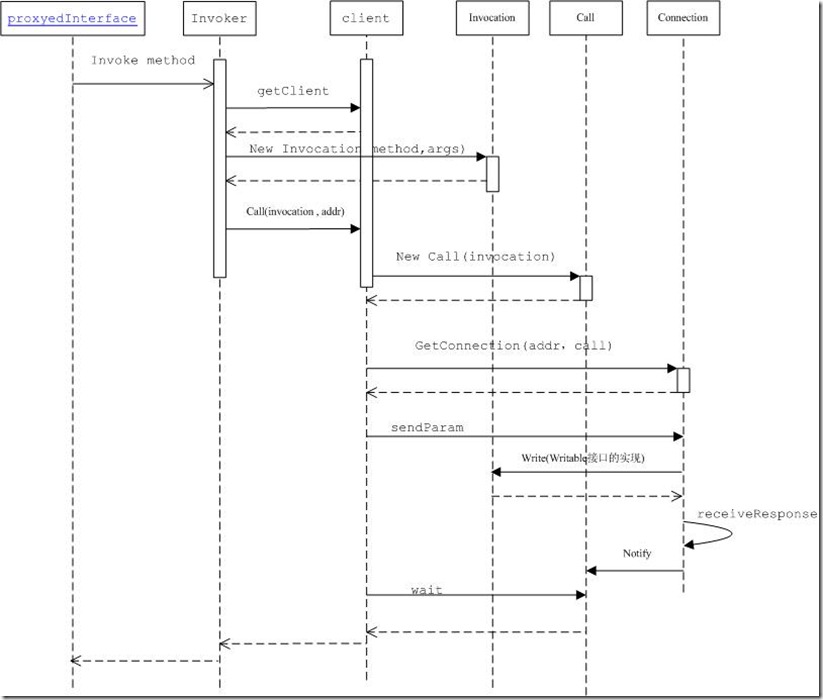
3.3invoke调用client对象的call方法,向服务器发送请求(参数、方法)
public Writable call(Writable param, ConnectionId remoteId) throws InterruptedException, IOException { Call call = new Call(param);// new Invocation(method, args) Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call);// 获得连接对象 可见一个client可以有多个connection connection.sendParam(call); // 将Invocation(method, args)的函数名,参数序列化发送到server端 while (!call.done) { call.wait(); // wait for the result 调用client的线程在此阻塞 } return call.value;//返回调用结果 }
3.4获得连接对象getConnection
private Connection getConnection(ConnectionId remoteId, Call call) throws IOException, InterruptedException { Connection connection; do { synchronized (connections) { connection = connections.get(remoteId); if (connection == null) { connection = new Connection(remoteId); connections.put(remoteId, connection); } } } while (!connection.addCall(call));//可见 一个connection 可以有多个调用call connection.setupIOstreams();//实际进行连接 每个connection都新起一个线程 return connection; }
3.5 connection的线程等待接受结果
public void run() { try { while (waitForWork())//超时检测等条件 connection close {// wait here for work - read or close connection receiveResponse(); } } close(); } private void receiveResponse() { try { int id = in.readInt(); // try to read an id Call call = calls.get(id); int state = in.readInt(); // read call status if (state == Status.SUCCESS.state) { Writable value = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(valueClass, conf); value.readFields(in); // 将结果反序列化 call.setValue(value);//在这里 calls.remove(id); } } catch (IOException e) { markClosed(e); } }
3.6返回结果,通知client线程
public synchronized void setValue(Writable value) { this.value = value; callComplete(); } protected synchronized void callComplete() { this.done = true; notify(); // notify caller }
4. 异步/同步模型
Hadoop的RPC对外的接口其实是同步的,但是,RPC的内部实现其实是异步消息机制。hadoop用线程wait/notify机制实现异步转同步,发送请求(call)之后wait请求处理完毕,接收完响应(connection.receiveResponse())之后notify,notify()方法在call.setValue中。但现在有一个问题,一个connection有多个call。可能同时有多个call在等待接收消息,那么是当client接收到response后,怎样确认它到底是之前哪个request的response呢?这个就是依靠的connection中的一个HashTable<Integer, Call>了,其中的Integer是用来标识Call,这样就可以将request和response对应上了。
5.时序图
6.client类图
7.参考
http://weixiaolu.iteye.com/blog/1504898
http://www.wikieno.com/2012/02/hadoop-ipc-client/
http://caibinbupt.iteye.com/blog/280790
http://blog.csdn.net/sxf_824/article/details/4842153
http://blog.csdn.net/historyasamirror/article/details/6159248






















 970
970











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








