一.什么是虚函数表,它有什么特点?
虚函数大家都知道是基本用于实现多态的,当父类指针指向子类对象的时候,如何确定调用的函数是父类里的还是子类里面的,这就要用到虚函数表。下面一点点表诉什么是虚函数表,和虚函数表的特点。如有说错的地方,欢迎指正:
1.编译器会为每个有虚函数的类创建一个虚函数表
如有类中没有虚函数,那么这个虚函数表就不存在,而不是表中无数据。同时,所有类都会有自己的虚函数表,一个类不会有另外一个类的虚函数表,包括两个类属于继承关系。
2.虚函数表会被一个类的所有对象所拥有
类的每个虚函数成员占据虚函数表的一行,所以说,如果类中有N个虚函数,那么该虚函数表将会有N*4的大小。并不是每个类对象都会有自己的表。
3.编译器会将虚函数表指针存放在类对象最前面的位置
对于类的每个对象,编译器都会为其生成一个透明不可见的指针,这个指针就是虚函数表指针,存放在该对象内存的最前位置。例如:一个类拥有虚函数表,类对象内存布局中前4个字节就是虚函数表的地址(32位)。这个接下来我们会进行测试。
4.延伸,由第一条可知,子类继承父类,其虚函数表和表函数地址是不一样的。
5.父类指针指向子类对象时,调用时实际上是根据子类对象的虚函数表进行查找
二、测试
测试内容:
虚函数表地址和虚函数地址存放位置?
多个类对象的虚函数表地址是否一样?
测试类中无虚函数,是否存在虚函数表?
子类继承父类虚函数表地址分别是什么位置?
子类重写父类中虚函数或子类重定义父类虚函数虚函数表是否发生改变?
子类指针指向父类虚函数表是什么样子?
1.测试虚函数表地址和虚函数地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
cout << "测试地址是否正确" << endl;
Fun fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&father;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 2);
fun();
system("pause");
}
上面说过类对象内存中前4个字节就是虚函数表的地址,那么我们获取类对象前4个字节,(int)&father就是虚函数表地址,我们再给他转换成地址指针为(int*)(int)&father。
然后我们在看一下输出结果:
类对象地址:003BF90C 虚函数表地址: 00867898 虚函数FatherFun1地址:00867898 虚函数FatherFun2地址:0086789C 虚函数FatherFun3地址:008678A0 测试地址是否正确 FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 请按任意键继续. . .
从这个输出我们可以看到,FatherFun1、FatherFun2、FatherFun3的地址只差了4个字节,且输出是正确的,那么第三点已确认!
2.多个类对象的虚函数表地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
cout << "第二个类对象" << endl;
Father father1;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father1 + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father1 + 2 << endl;
system("pause");
}
定义了两个对象,分别看两个对象的虚函数表地址是否正确,发现两个类对象虚函数表地址相同。
以下为输出:
类对象地址:0020F9C8 虚函数表地址: 00B37894 虚函数FatherFun1地址:00B37894 虚函数FatherFun2地址:00B37898 虚函数FatherFun3地址:00B3789C 第二个类对象 类对象地址:0020F9BC 虚函数表地址: 00B37894 虚函数FatherFun1地址:00B37894 虚函数FatherFun2地址:00B37898 虚函数FatherFun3地址:00B3789C 请按任意键继续. . .
由此可见,第二点现在已经确认!
3.测试类中无虚函数,是否存在虚函数表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
void TestFun1() {cout << "TestFun1" <<endl;}
void TestFun2() {cout << "TestFun2" <<endl;}
void TestFun3() {cout << "TestFun3" <<endl;}
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
Test test;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &test << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&test << endl;
cout << "虚函数TestFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&test << endl;
cout << "虚函数TestFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&test + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数TestFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&test + 2 << endl;
system("pause");
}
以下为输出:
类对象地址:0041FCEB 虚函数表地址: CCCCCCCC 虚函数TestFun1地址:CCCCCCCC 虚函数TestFun2地址:CCCCCCD0 虚函数TestFun3地址:CCCCCCD4 请按任意键继续. . .
由此可见虚函数表地址为错误,第一条确认!
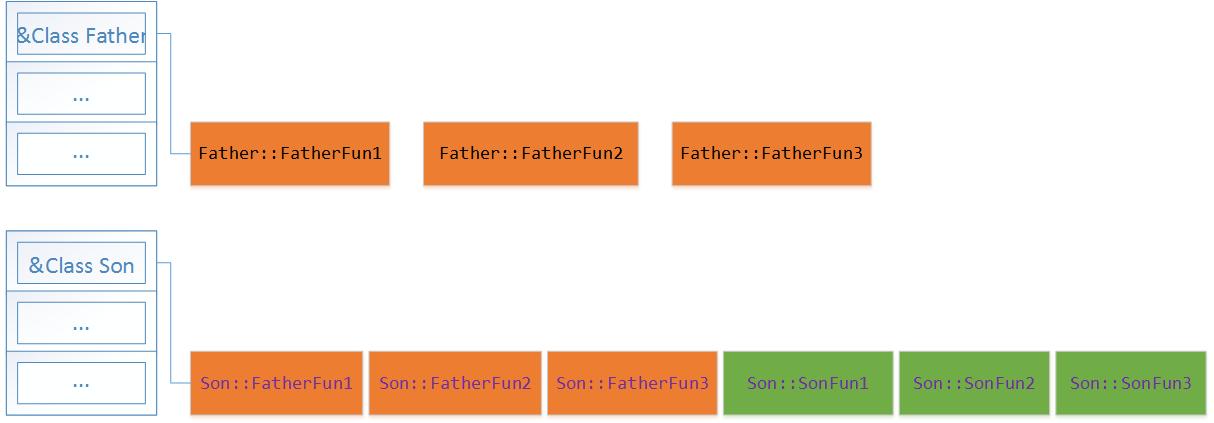
4.子类继承父类,但不继承虚函数表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
class Son : public Father
{
virtual void SonFun1() {cout << "SonFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun2() {cout << "SonFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun3() {cout << "SonFun3" <<endl;}
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
int main()
{
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
//cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 3 << endl;
//cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 4 << endl;
//cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 5 << endl;
Fun fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&father;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 2);
fun();
//fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 3);
//fun();
//fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 4);
//fun();
//fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 5);
//fun();
cout << "----------------测试子类------------------" << endl;
Son son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &son << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 5 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&son;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 5);
fun();
system("pause");
}
如果将代码中注释代码给恢复,会直接发生段错误。
以下为输出结果:
类对象地址:0027FCA8
虚函数表地址: 01317930
虚函数FatherFun1地址:01317930
虚函数FatherFun2地址:01317934
虚函数FatherFun3地址:01317938
FatherFun1
FatherFun2
FatherFun3
----------------测试子类------------------
类对象地址:0027FC90
虚函数表地址: 01317974
虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:01317974
虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:01317978
虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:0131797C
虚函数sonFun1地址:01317980
虚函数sonFun2地址:01317984
虚函数sonFun3地址:01317988
FatherFun1
FatherFun2
FatherFun3
SonFun1
SonFun2
SonFun3
请按任意键继续. . .
由输出结果我们可以看到,父类和子类中的虚函数表地址是不一样的,而且子类继承了父类的虚函数,但是其地址是和父类中不一样的!。第四点确认!
并且我们根据输出可以发现,子类虚函数表中虚函数地址排序为先是继承的父类的函数,再是子类中的虚函数。
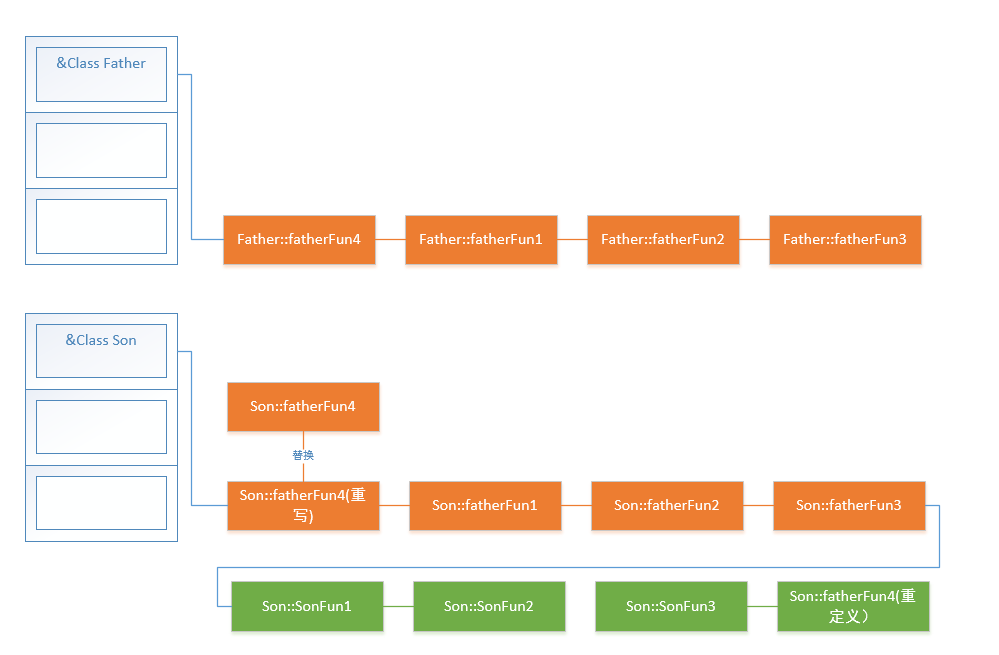
5.子类重写父类中虚函数,或子类重定义父类虚函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun4() {cout << "FatherFun4" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
class Son : public Father
{
virtual void SonFun1() {cout << "SonFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun2() {cout << "SonFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun3() {cout << "SonFun3" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun4() {cout << "SonGetFatherFun4" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun4(int a = 0) {cout << "SonGetFatherFun4 diffrent param" <<endl;}
};
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
typedef void (*FunParam)(int);
int main()
{
#if 1
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun4地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 3 << endl;
Fun fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&father;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 3);
fun();
cout << "----------------测试子类------------------" << endl;
Son son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &son << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承SonGetFatherFun4地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 5 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 6 << endl;
cout << "虚函数SonGetFatherFun4 diffrent param地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 7 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&son;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 5);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 6);
fun();
FunParam funParam= (FunParam)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 7);
funParam(0);
#endif
system("pause");
}
我们故意将父类中FatherFun4放在最前,而子类中的重写和重定义的FatherFun4 函数放在最后,看一下虚函数表中虚函数排放顺序是否有发生改变。
以下为输出结果:
类对象地址:0021FD4C 虚函数表地址: 011479B8 虚函数FatherFun4地址:011479B8 虚函数FatherFun1地址:011479BC 虚函数FatherFun2地址:011479C0 虚函数FatherFun3地址:011479C4 FatherFun4 FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 ----------------测试子类------------------ 类对象地址:0021FD34 虚函数表地址: 01147A10 虚函数继承SonGetFatherFun4地址:01147A10 虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:01147A14 虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:01147A18 虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:01147A1C 虚函数sonFun1地址:01147A20 虚函数sonFun2地址:01147A24 虚函数sonFun3地址:01147A28 虚函数SonGetFatherFun4 diffrent param地址:01147A2C **SonGetFatherFun4** FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 SonFun1 SonFun2 SonFun3 SonGetFatherFun4 diffrent param
我们可以清楚的看到,位于子类最后函数重写的FatherFun4被放在了本该继承的父类FatherFun4位置上(先输出的是SonGetFatherFun4),而函数重定义则没有发生改变。
由此可以得出结论:
(1)覆盖的FatherFun4函数被放到了虚函数表中原父类虚函数的位置
(2)没有被覆盖的函数没有变化
6.子类指针指向父类
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
class Son : public Father
{
virtual void SonFun1() {cout << "SonFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun2() {cout << "SonFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun3() {cout << "SonFun3" <<endl;}
};
#if 0
class Test
{
void TestFun1() {cout << "TestFun1" <<endl;}
void TestFun2() {cout << "TestFun2" <<endl;}
void TestFun3() {cout << "TestFun3" <<endl;}
};
#endif
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
typedef void (*FunParam)(int);
int main()
{
cout << "----------------测试父类------------------" << endl;
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
Fun fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&father;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 2);
fun();
cout << "----------------测试子类------------------" << endl;
Son son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &son << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 5 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&son;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 5);
fun();
cout << "----------------测试父类指针指向子类------------------" << endl;
Father* pointSon = new Son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 5 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)pointSon;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 5);
fun();
system("pause");
}
实际上父类指针指向子类,调用的是子类的虚函数表。
以下为输出:
----------------测试父类------------------
类对象地址:0029FDD0
虚函数表地址: 000F89BC
虚函数FatherFun1地址:000F89BC
虚函数FatherFun1地址:000F89C0
虚函数FatherFun2地址:000F89C4
FatherFun1
FatherFun2
FatherFun3
----------------测试子类------------------
类对象地址:0029FDB8
虚函数表地址: 000F8A00
虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:000F8A00
虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:000F8A04
虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:000F8A08
虚函数sonFun1地址:000F8A0C
虚函数sonFun2地址:000F8A10
虚函数sonFun3地址:000F8A14
FatherFun1
FatherFun2
FatherFun3
SonFun1
SonFun2
SonFun3
----------------测试父类指针指向子类------------------
类对象地址:003B55D8
虚函数表地址: 000F8A00
虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:000F8A00
虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:000F8A04
虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:000F8A08
虚函数sonFun1地址:000F8A0C
虚函数sonFun2地址:000F8A10
虚函数sonFun3地址:000F8A14
FatherFun1
FatherFun2
FatherFun3
SonFun1
SonFun2
SonFun3
请按任意键继续. . .
由虚函数表地址我们就可以看到,父类指针指向子类的时候,其虚函数表地址和子类虚函数表地址是一样的。由此,第五点确认
7.子类重写父类虚函数,并子类指针指向父类
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
virtual void FatherFun4() {cout << "FatherFun4" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun1() {cout << "FatherFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun2() {cout << "FatherFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun3() {cout << "FatherFun3" <<endl;}
};
class Son : public Father
{
virtual void SonFun1() {cout << "SonFun1" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun2() {cout << "SonFun2" <<endl;}
virtual void SonFun3() {cout << "SonFun3" <<endl;}
virtual void FatherFun4() {cout << "SonGetFatherFun4" <<endl;}
};
#if 0
class Test
{
void TestFun1() {cout << "TestFun1" <<endl;}
void TestFun2() {cout << "TestFun2" <<endl;}
void TestFun3() {cout << "TestFun3" <<endl;}
};
#endif
typedef void (*Fun)(void);
typedef void (*FunParam)(int);
int main()
{
cout << "----------------测试父类------------------" << endl;
Father father;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &father << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun4地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&father + 3 << endl;
Fun fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&father;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&father) + 3);
fun();
cout << "----------------测试子类------------------" << endl;
Son son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << &son << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun4地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 5 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)&son + 6 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)&son;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 5);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(&son) + 6);
fun();
cout << "----------------测试父类指针指向子类------------------" << endl;
Father* pointSon = new Son;
cout << "类对象地址:" << pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数表地址: " << (int*)*(int*)pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 1 << endl;
cout << "虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 2 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun1地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 3 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun2地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 4 << endl;
cout << "虚函数sonFun3地址:" <<(int*)*(int*)pointSon + 5 << endl;
fun = (Fun)*(int*)*(int*)pointSon;
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 1);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 2);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 3);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 4);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 5);
fun();
fun = (Fun)*((int*)*(int*)(pointSon) + 6);
fun();
system("pause");
}
直接看输出结果:
----------------测试父类------------------ 类对象地址:0034F788 虚函数表地址: 000B8A14 虚函数FatherFun4地址:000B8A14 虚函数FatherFun1地址:000B8A18 虚函数FatherFun2地址:000B8A1C 虚函数FatherFun3地址:000B8A20 FatherFun4 FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 ----------------测试子类------------------ 类对象地址:0034F770 虚函数表地址: 000B8A6C 虚函数继承FatherFun4地址:000B8A6C 虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:000B8A70 虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:000B8A74 虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:000B8A78 虚函数sonFun1地址:000B8A7C 虚函数sonFun2地址:000B8A80 虚函数sonFun3地址:000B8A84 SonGetFatherFun4 FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 SonFun1 SonFun2 SonFun3 ----------------测试父类指针指向子类------------------ 类对象地址:005855D8 虚函数表地址: 000B8A6C 虚函数继承FatherFun1地址:000B8A6C 虚函数继承FatherFun2地址:000B8A70 虚函数继承FatherFun3地址:000B8A74 虚函数sonFun1地址:000B8A78 虚函数sonFun2地址:000B8A7C 虚函数sonFun3地址:000B8A80 SonGetFatherFun4 FatherFun1 FatherFun2 FatherFun3 SonFun1 SonFun2 SonFun3 请按任意键继续. . .
实际上和第六点结果是一样的





















 466
466











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








