一、使用Stream的三个操作步骤:创建Stream->中间操作->终止操作
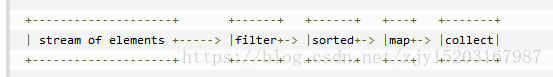
二、详情
①.创建Stream
1.可以通过collection系列集合提供的stream或parallelStream
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream1 = list.stream();
2.通过Arrays中的静态方法stream()获取数组流
Employee[] emps = new Employee[10];
Stream<Employee> stream2 = Arrays.stream(emps);
3.通过Stream类中的静态方法of()
Stream.of("a","b","c");
4.创建无限流
//迭代
Stream<Integer> stream4 = Stream.iterate(0, (x)->x+2);
stream4.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
//生成
Stream.generate(()->Math.random())
.limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);;
②.中间操作
排序:
sorted()-自然排序(Comparable)
sorted(Comparator com) - 定制排序(Comparator)
//年龄不一样按年龄排序,年龄一样按姓名排序
@Test
public void test7() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","bb","cc","dd");
list.stream()
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
emps.stream()
.sorted((e1,e2)->{
if (e1.getAge()==(e2.getAge())) {
return e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
}else {
return Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge());
}
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
映射:
map——接收Lambda,将元素转换成成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,改函数会被应用到每个元素 上,并将其映射成一个新的元素
flatMap——接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都转换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
@Test
public void test5() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","cc","dd","ff","tt");
list.stream()
.map((str)-> str.toUpperCase())
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
/* Stream<Stream<Character>> liStream = list.stream()
.map(TestaStreamAPI2::filterCharacter);
liStream.forEach((sm)->{sm.forEach(System.out::println);});
System.out.println("----------------------------------");*/
Stream<Character> stream= list.stream()
.flatMap(TestaStreamAPI2::filterCharacter);
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
public static Stream<Character> filterCharacter(String str ){
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Character ch: str.toCharArray()) {
list.add(ch);
}
return list.stream();
}筛选与切片 filter
——接受Lambda,从流中排除某些元素 limit——截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量
skip(n)——跳过元素,返回一个人扔掉了前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,则返回一个空流,与limit(n)互补
distinct——筛选,通过流锁生成元素的hashCode()和equals()去除重复元素
@Test
public void test4() {
emps.stream()
.filter((e)->e.getSalary()>5000)
.skip(2)
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
emps.stream().filter((e) ->{
System.out.println("短路!");
return e.getSalary() > 5000;})
//.limit(2)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}- 内部迭代:迭代操作由Stream API 完成
@Test
public void test1() {
// 中间操作:不会执行任何操作
Stream<Employee> stream = emps.stream().filter((e) -> {
System.out.println("Strean API 的中间操作");
return e.getAge() > 35;
});
// 终止操作:一次性执行全部内容,即“惰性求值”
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}- 外部迭代
@Test
public void test2() {
Iterator<Employee> iterable = emps.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterable.next());
}
}③.终止操作
实体Employee的属性有
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double salary;
private Status status;getter,setter等方法请自行创建
List<Employee> emps = Arrays.asList(
new Employee("1", 18, 9999.99,Status.FREE),
new Employee("2", 25, 6666.99,Status.BUSY),
new Employee("3", 12, 33333.99,Status.VOCATION),
new Employee("4", 68, 3333.99,Status.FREE),
new Employee("5", 8, 77777.99,Status.BUSY),
new Employee("3", 56, 33333.99,Status.VOCATION)
);- 收集
collect - 将流转换为其他形式。接收一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法
@Test
public void test10() {
String str = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("--","====","===="));
System.out.println(str);
}
@Test
public void test9() {
DoubleSummaryStatistics dds = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(dds.getSum());
System.out.println(dds.getAverage());
System.out.println(dds.getCount());
}
- 分组
@Test
public void test6() {
Map<Status, List<Employee>> map = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus));
System.out.println(map);
}输出结果:根据状态分组
{BUSY=[Employee [id=0, name=2, age=25, salary=6666.99, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=5, age=8, salary=77777.99, status=BUSY]], FREE=[Employee [id=0, name=1, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=FREE], Employee [id=0, name=4, age=68, salary=3333.99, status=FREE]], VOCATION=[Employee [id=0, name=3, age=12, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION], Employee [id=0, name=3, age=56, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION]]}
- 分区 满足条件的 一个区,不满足条件的一个区
@Test
public void test8() {
Map<Boolean, List<Employee>> map = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy((e)->e.getSalary()>8000));
System.out.println(map);
}输出结果:将对象分成了false和true两个区
{false=[Employee [id=0, name=2, age=25, salary=6666.99, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=4, age=68, salary=3333.99, status=FREE]],
true=[Employee [id=0, name=1, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=FREE], Employee [id=0, name=3, age=12, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION], Employee [id=0, name=5, age=8, salary=77777.99, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=3, age=56, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION]]}
- 多级分组
@Test
public void test7() {
Map<Status, Map<String, List<Employee>>> map = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus, Collectors.groupingBy((e)->{
if (((Employee) e).getAge()<35) {
return "青年";
}else if (((Employee) e).getAge()<50) {
return "中年";
}else {
return "老年";
}
})));
System.out.println(map);
}输出结果:根据FREE、BUSY、VOCATION分组后,又根据青年、中年、老年分组
{VOCATION={青年=[Employee [id=0, name=3, age=12, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION]], 老年=[Employee [id=0, name=3, age=56, salary=33333.99, status=VOCATION]]}, FREE={青年=[Employee [id=0, name=1, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=FREE]], 老年=[Employee [id=0, name=4, age=68, salary=3333.99, status=FREE]]}, BUSY={青年=[Employee [id=0, name=2, age=25, salary=6666.99, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=5, age=8, salary=77777.99, status=BUSY]]}}
- 求总数、平均数、总和、最大值、最小值
@Test
public void test5() {
//总数
Long count = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//平均值
Double avg = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(avg);
//总和
Double sum = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(sum);
//最大值
Optional<Employee> max = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy((e1,e2)->Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())));
System.out.println(max.get());
//最小值
Optional<Double> min = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compare));
System.out.println(min.get());
}
- 设置将结果以什么样的形式返回
@Test
public void test4() {
List<String> list = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Set<String> set = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
HashSet<String> hashSet = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
}- 归约
reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator)/reduce(BinaryOperator) 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值
@Test
public void test3() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6);
Integer sum = list.stream()
.reduce(0, (x,y)->x+y);
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Optional<Double> op = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.reduce(Double::sum);
System.out.println(op.get());
}查找与匹配
allMatch-检查是否匹配所有元素
anyMatch-检查是否只收匹配一个元素
noneMatch-检查是否没有匹配所有元素
findFirst-返回第一个元素
findany-返回当前流中的任意元素
count-返回流中元素的总个数
max-返回流中最大值
min-返回流中最小值
@Test
public void test2() {
long count = emps.stream()
.count();
System.out.println(count);
Optional<Employee> op1 = emps.stream()
.max((e1,e2)-> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(op1.get());
Optional<Double> op2= emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.min(Double::compare);
System.out.println(op2.get());
}
@Test
public void test1() {
boolean b1 = emps.stream()
.allMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b1);
boolean b2 = emps.stream()
.anyMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b1);
boolean b3 = emps.stream()
.noneMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b1);
Optional<Employee> op = emps.stream()
.sorted((e1,e2)-> -Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary()))
.findFirst();
System.out.println(op.get());
/*Optional<Employee> op2 = emps.stream()
.filter((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.FREE))
.findAny();
System.out.println(op2.get());*/
//emps.stream()串行,emps.parallelStream()并行(equals和findany同时进行,取出的值不固定)
Optional<Employee> op2 = emps.parallelStream()
.filter((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.FREE))
.findAny();
System.out.println(op2.get());
}

























 715
715











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








