1. 图形用户界面
概念及特点
1. GUI:
• Graphical User Interface(图形用户接口)。
•用图形的方式,来显示计算机操作的界面,这样更方便更直观。
Java为GUI提供的对象都存在java.Awt和javax.Swing两个包中。
java.Awt: Abstract Window ToolKit (抽象窗口工具包),需要调用本地系统方法实现功能。属
重量级控件。
javax.Swing:在AWT的基础上,建立的一套图形界面系统,其中提供了更多的组件,而且完全由Java实现。增强了移植性,属轻量级控件。
2. CLI
• Command line User Interface (命令行用户接口)
•就是常见的Dos命令行操作。
•需要记忆一些常用的命令,操作不直观。
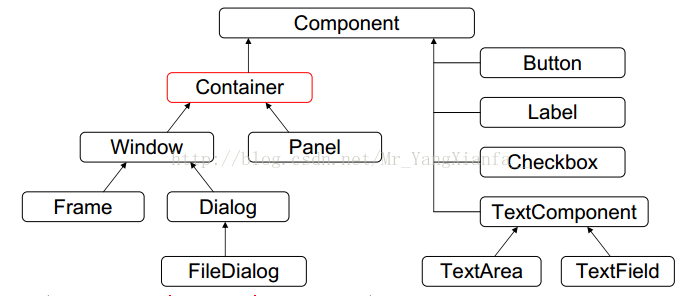
3. 继承关系图
1) Component:一个能以图形化方式显示出来,并可与用户交互的对象。
常用方法:
setLocation(int x, int y):将组件移到新位置。
void setSize(int width, int height):调整组件的大小,使其宽度为 width,高度为 height。
setBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height):移动组件并调整其大小。
setVisible(boolean b):根据参数 b 的值显示或隐藏此组件。
void validate() :确保组件具有有效的布局。
2) Container:为容器,是一个特殊的组件,该组件中可以通过add方法添加其他组件进来。
常用方法:
3) Windom: 对象是一个没有边界和菜单栏的顶层窗口。
4) Panel:是最简单的容器类。应用程序可以将其他组件放在面板提供的空间内,这些组件包括其他面板。不能单独存在,必须放置到其他容器中。
5) Frame: 是带有标题和边框的顶层窗口。
允许通过拖拉来改变窗口的位置,大小。
初始化时不可见,可用setVisible(true)使其显示出来。
6) Dialog:是一个带标题和边界的顶层窗口。默认布局为BorderLayout。
7) FileDialog :显示一个对话框窗口,用户可以从中选择文件。
由于它是一个模式对话框,当应用程序调用其 show方法来显示对话框时,它将阻塞其余应用程序,直到用户选择一个文件。
FileDialog(Frame parent, String title, int mode)
parent - 对话框的所有者
title - 对话框的标题
mode - 对话框的模式,可以是 FileDialog.LOAD或 FileDialog.SAVE
如果 mode 的值为 LOAD,那么文件对话框将查找要读取的文件,所显示的文件是当前目录中的文件。如果 mode的值为 SAVE,则文件对话框将查找要写入文件的位置。
FileDialog方法:
String getDirectory()
获取此文件对话框的目录。
String getFile()
获取此文件对话框的选定文件。
8) TextArea:文本域,可以将它设置为允许编辑或只读。
void append(String str) : 将给定文本追加到文本区的当前文本。
9) TextField: 是允许编辑单行文本的文本组件。
void setText(String t):将此文本组件显示的文本设置为指定文本。
4. 布局管理器
容器中的组件的排放方式,就是布局。
常见的布局管理器:
1) FlowLayout(流式布局管理器)
•从左到右的顺序排列。
• Panel默认的布局管理器。
2) BorderLayout(边界布局管理器)
•东,南,西,北,中
• Frame默认的布局管理器。没有指定布局时,全部居中
3) GridLayout(网格布局管理器)
•规则的矩阵
4) CardLayout(卡片布局管理器)
•选项卡
5) GridBagLayout(网格包布局管理器)
•非规则的矩阵
5. 事件监听机制
1) 需要导入子包java.awt.event.*;
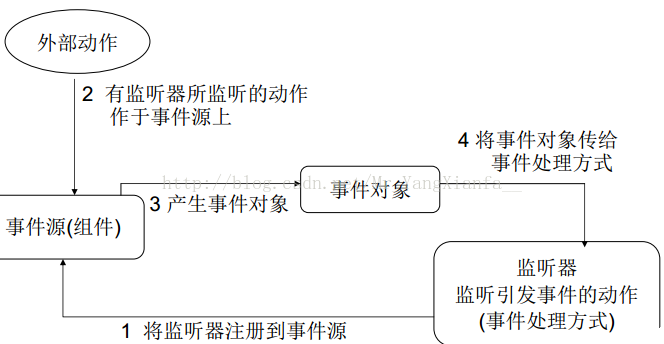
2) 事件监听机制组成:
事件源(就是awt包或者swing包中的那些图形界面组件。)
事件(每一个事件源都有自己特有的对应事件和共性事件,Event)
监听器(将可以触发某一个事件的动作(不只一个动作)都已封装到了监听器中。Listener)
事件处理(引发事件后处理方式)
3) 前三者,在java中都已经定义好了。
直接获取其对象来用就可以了。
我们要做的事情是,就是对产生的动作进行处理。
4) 事件监听机制流程图:
5) void addWindowListener(WindowListener l) :添加指定的窗口侦听器,以从此窗口接收窗口事件。WindowListener是一个接口类型参数,所以要复写接口里的所有方法。为了方便,直接传入WindowListener的子类,WindowAdapter。
6) WindowAdapter:
接收窗口事件的抽象适配器(Adapter)类。此类中的方法为空。此类存在的目的是方便创建侦听器对象。
扩展此类可创建 WindowEvent侦听器并为所需事件重写该方法。(如果要实现 WindowListener 接口,则必须定义该接口内的所有方法。此抽象类将所有方法都定义为 null,所以只需针对关心的事件定义方法。)
6. 编程思想
1) 确定事件源(容器或组件)
2) 通过事件源对象的addXXXListener()方法将侦听器注册到该事件源上。
3) 该方法中接收XXXListener的子类对象,或XXXListener的子类XXXAdapter的子类对象。
4) 一般用匿名内部类来表示。
5) 在覆盖方法的时候,方法的参数一般是XXXEvent类型的变量接收。
6) 事件触发后会把事件打包成对象传递给该变量。(其中包括事件源对象。通过getSource()或者, getComponent()获取。)
7. 窗体事件
windowActivated(WindowEvent e): 激活窗口时调用。
void windowClosing(WindowEvent e):窗口正处在关闭过程中时调用。
windowOpened(WindowEvent e): 已打开窗口时调用。
怎么使用?
<span style="color:#000000;">/*
创建图形化界面:
1,创建frame窗体。(选择一个容器)
2,对窗体进行基本设置。
比如大小,位置,布局。(设置布局管理器setLayout)
3,定义组件。
4,将组件通过窗体的add方法添加到窗体中。
5,添加组件的事务处理。
6,让窗体显示,通过setVisible(true)
图形化界面有自己的线程
*/
class test
{
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args)
{
Frame f = new Frame("my awt");
f.setSize(500,400);
f.setLocation(300,200);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());//单独指定布局管理器
//setLayout(null);表示不要布局管理器。
Button b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
f.add(b);
//窗体事件
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)//窗口事件
{
System.out.println("closing...");
System.exit(0);
}
publicvoid windowActivated(WindowEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Activated...");
}
publicvoid windowOpened(WindowEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Opened...");
}
});
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
/*
class MyWin implements WindowListener
{
//覆盖7个方法。可以我只用到了关闭的动作。
//其他动作都没有用到,可是却必须复写。
}
//因为WindowListener的子类WindowAdapter已经实现了WindowListener接口。
//并覆盖了其中的所有方法。那么我只要继承自Windowadapter覆盖我需要的方法即可。
class MyWin extends WindowAdapter
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
//System.out.println("window closing---"+e.toString());
System.exit(0);
}
}
*/
//练习,定义一个窗体,在窗体中添加一个按钮具备关闭该窗体的功能。
</span>
Action事件-按钮具备功能
getSource():返回最初发生 Event 的对象。
getParent():获取此组件的父级。
请看如下案例:
class test
{
//定义该图形中所需的组件的引用。
private Frame f;
private Button but;
test()
{
init();
}
publicvoid init()
{
f = new Frame("my frame");
//对frame进行基本设置。
f.setBounds(300,100,600,500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
but = new Button("my button");
//将组件添加到frame中
f.add(but);
//显示之前加载一下窗体上事件。
myEvent();
//显示窗体;
f.setVisible(true);
}
privatevoid myEvent()
{
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)//窗口事件
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
//需求:让按钮具备退出程序的功能
/*
按钮就是事件源。
那么选择哪个监听器呢?
通过关闭窗体示例了解到,想要知道哪个组件具备什么样的特有监听器。
需要查看该组件对象的功能。
通过查阅button的描述。发现按钮支持一个特有监听器addActionListener。
此监听器没有适配器
*/
but.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
privateintcount = 1;
publicvoid actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)//活动事件
{
//让按钮具备退出程序的功能
System.out.println("退出,按钮干的");
System.exit(0);
//让按钮具备生成按钮的功能
/*f.add(new Button("Button-"+(count++)));
f.setVisible(true);
f.validate();*/
//让按钮具备生成按钮的功能
/*System.out.println(e.getSource());
Button b = (Button)e.getSource();
System.out.println(b.getParent());
Frame f1 = (Frame)b.getParent();
f1.add(new Button("button~"+count++));
f1.validate();*/
}
});
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args)
{
new test();
}
}
鼠标事件+键盘事件
1. 鼠标事件:
MouseListener类方法:
1) void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e):鼠标按键在组件上单击(按下并释放)时调用。
2) void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e):鼠标进入到组件上时调用。
3) void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) :鼠标离开组件时调用。
4) void mousePressed(MouseEvent e):鼠标按键在组件上按下时调用。
5) void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e):鼠标按钮在组件上释放时调用。
MouseEvent类方法:
1) getClickCount():返回与此事件关联的鼠标单击次数。
2. 键盘事件
1) KeyListener类方法
2) void keyPressed(KeyEvent e):按下某个键时调用此方法。
3) void keyReleased(KeyEvent e):释放某个键时调用此方法。
4) void keyTyped(KeyEvent e):键入某个键时调用此方法。
KeyEvent类中的方法:
1) char getKeyChar():返回与此事件中的键关联的字符。
2) int getKeyCode():返回与此事件中的键关联的整数 keyCode。
3) static String getKeyText(int keyCode):KeyEvent. getKeyTex()返回描述 keyCode 的 String,如 "HOME"、"F1" 或 "A"等其他由多个键盘码组成的按键,如:shift,alt等。
4) boolean isControlDown():返回 Control 修饰符在此事件上是为 down。
5) boolean isShiftDown():返回 Shift 修饰符在此事件上是否为 down。
6) boolean isAltDown():返回 Alt 修饰符在此事件上是否为 down。
7) void Consume():使用此事件,以便不会按照默认的方式由产生此事件的源代码来处理此事件。即取消掉产生的此次事件,屏蔽键。
3. 怎么使用?
class test
{
private Frame f;
private Button but;
private TextField tf;
test()
{
init();
}
publicvoid init()
{
f = new Frame("my frame");
f.setBounds(300,100,600,500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
tf = new TextField(20);
but = new Button("my button");
f.add(tf);
f.add(but);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
privatevoid myEvent()
{
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
//文本框添加事件
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter()
{
publicvoid keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
int code = e.getKeyCode();
if(!(code>=KeyEvent.VK_0 && code<=KeyEvent.VK_9))//限制按键范围
{
System.out.println(code+".....是非法的");
e.consume();//取消掉产生的此次事件
}
}
});
//给But添加一个键盘监听。
but.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter()
{
publicvoid keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
//按下多个按键(组合键)产生事件
if(e.isControlDown() && e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
//System.exit(0);
System.out.println("ctrl+enter is run");
//System.out.println(KeyEvent.getKeyText(e.getKeyCode())+"...."+e.getKeyCode());//按下由多个键盘编码组成的按键,shift,alt等
}
});
/*
//按钮活动事件
but.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
System.out.println("action ok");
}
});
*/
/*
//鼠标事件
but.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter()
{
private int count = 1;
private int clickCount = 1;
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e)
{
System.out.println("鼠标进入到该组件"+count++);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
{
if(e.getClickCount()==2)//返回与此事件关联的鼠标单击次数。
System.out.println("双击动作"+clickCount++);
}
});
*/
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args)
{
new test();
}
} 列出指定目录内容+对话框Dialog
Dialog(Dialog owner,String title, boolean modal) :
构造一个最初不可见的Dialog,它带有指定的所有者Dialog、标题和模式。
owner - dialog 的所有者,如果此 dialog 没有所有者,则该参数为 null
title - dialog 的标题,如果此 dialog 没有标题,则该参数为 null
modal - 指定在显示的时候是否阻止用户将内容输入到其他顶级窗口中。如果该参数为 false,则 dialog 是 MODELESS;如果该参数为 true,则模式类型属性被设置为 DEFAULT_MODALITY_TYPE
如:
publicclass test
{
private Frame f;
private Button but;
private TextArea ta;
private TextField tf;
//一般不把对话框对象定义在外部,此处为了方便阅读。
//只有发生误操作,才生成该对象,不该窗体加载完就生成对话框
private Dialog dl;
private Label lb;
private Button but1;
test()
{
init();
}
publicvoid init()
{
f = new Frame("my test");
f.setBounds(300, 200, 370, 500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
tf = new TextField(30);
but = new Button("->转到");
ta = new TextArea(25,45);
f.add(tf);
f.add(but);
f.add(ta);
dl = new Dialog(f,"错误提示",true);
dl.setBounds(300, 350, 370, 150);
dl.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
lb = new Label();
but1 = new Button("确定");
dl.add(lb);
dl.add(but1);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
privatevoid myEvent()
{
//添加对话框按钮的键盘事件
but1.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
publicvoid keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
if(e.getKeyCode()==e.VK_ENTER)
dl.setVisible(false);
}
});
//添加对话框按钮的活动事件
but1.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
publicvoid actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
dl.setVisible(false);
}
});
//添加对话框的关闭事件
dl.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
dl.setVisible(false);
}
});
//添加窗口的关闭事件
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
//添加窗口按钮的活动事件
but.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
publicvoid actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
myshow();
}
});
//添加文本框的键盘事件
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
publicvoid keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
if(e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
myshow();
}
});
}
privatevoid myshow()
{
String dirPath = tf.getText();
File dir = new File(dirPath);
if(dir.exists()&&dir.isDirectory())
{
ta.setText(null);
String names[] = dir.list();
for(String name:names)
{
ta.append(name+"\r\n");
}
}
else
{
String info = "您输入的路径\""+dirPath+"\"错误,请重新输入";
lb.setText(info);
dl.setVisible(true);
}
}
publicstaticvoid main(String srgs[])
{
new test();
}
}
菜单+打开,保存文件案例
MenuBar :此类封装绑定到框架的菜单栏的平台概念。为了将该菜单栏与 Frame 对象关联,可以调用该框架的 setMenuBar 方法。
Menu :此对象是从菜单栏部署的下拉式菜单组件。Menu可添加menu,menuitem(加到菜单里的菜单会有三角形标记)
MenuItem:菜单中的所有项必须属于类 MenuItem 或其子类之一。 Menu extends menuitem。可添加活动事件。
void addActionListener(ActionListener l):添加指定的动作侦听器,以从此菜单项接收动作事件。
请看如下示例:
publicclass test
{
private Frame f;
private MenuBar bar;
private Menu m,submenu,sunmenu;
private MenuItem closeItem,openItem,saveItem;
private FileDialog open,save;
private TextArea ta;
private File file;
test()
{
init();
}
publicvoid init()
{
f = new Frame("迷你记事本");
f.setBounds(300, 100, 500, 550);
bar = new MenuBar();
m = new Menu("文件");
submenu = new Menu("子菜单");
closeItem = new MenuItem("退出");
openItem = new MenuItem("打开");
sunmenu = new Menu("孙菜单");
saveItem = new MenuItem("保存");
open = new FileDialog(f,"打开目录",FileDialog.LOAD);
save = new FileDialog(f,"保存文件",FileDialog.SAVE);
ta = new TextArea();
f.setMenuBar(bar);
bar.add(m);
m.add(submenu);
m.add(openItem);
submenu.add(sunmenu);
m.add(saveItem);
m.add(closeItem);
f.add(ta);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
privatevoid myEvent()
{
//添加打开菜单事件
openItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
publicvoid actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
open.setVisible(true);
String dirPath = open.getDirectory();
String filename = open.getFile();
//处理空指针异常(java.lang.NullPointerException)
if(dirPath==null||filename==null)
return;
ta.setText("");
file = new File(dirPath,filename);
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line = null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
ta.append(line+"\r\n");
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
thrownew RuntimeException("读取失败");
}
}
});
//添加保存菜单事件
saveItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
publicvoid actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if(file==null)
{
save.setVisible(true);
String dirPath = save.getDirectory();
String filename = save.getFile();
//处理空指针异常(java.lang.NullPointerException)
if(dirPath==null||filename==null)
return;
file = new File(dirPath,filename);
}
try
{
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String contents = ta.getText();
bw.write(contents);
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}catch(IOException e1)
{
thrownew RuntimeException("写出失败");
}
}
});
//添加窗口的关闭事件
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
publicvoid windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
publicstaticvoid main(String srgs[])
{
new test();
}
}






















 534
534











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








