题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/
题目:
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n?
For example,
Given n = 3, there are a total of 5 unique BST's.
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3解题思路:
学数据结构的时候,曾学过不同构的二叉树的种数为卡特兰数,其通项公式如下:
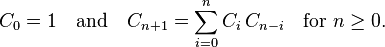
从求解子问题的角度来看本题:
1. 选取一个结点为根,就把结点切成左右子树
2. 以这个结点为根的可行二叉树数量就是左右子树可行二叉树数量的乘积
3. 所以总的数量是将以所有结点为根的可行结果累加起来。也就是上述公式。
具体解法:
从C2开始求解,直到Cn,求解过的数依次存储在数组中,以备求解其后的元素使用。若使用递归,求解速度较慢。
考点:动态规划
到目前为止,对动态规划还是没有很好的理解。
附上大神参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/linhuanmars/article/details/24761459
代码实现:
public class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
a[i] += a[j] * a[i - 1 - j];
}
}
return a[n];
}
}19 / 19 test cases passed.
Status: Accepted
Runtime: 0 ms




 本文深入探讨了如何利用卡特兰数解决计算不同构二叉搜索树的数量问题,详细解释了解题思路并提供代码实现。通过动态规划的方法,逐步求解子问题,最终得到总数。此技术适用于数据结构与算法领域,特别是二叉树相关问题。
本文深入探讨了如何利用卡特兰数解决计算不同构二叉搜索树的数量问题,详细解释了解题思路并提供代码实现。通过动态规划的方法,逐步求解子问题,最终得到总数。此技术适用于数据结构与算法领域,特别是二叉树相关问题。
















 451
451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








