Mybatis深入之初始化过程
一:简介
这篇开始是根据Mybatis源码来对Mybatis进行更深入的学习、当然、精力有限、还做不到学习的面面俱到。
Mybatis初始化过程可以用一句话概括:就是将Mybatis的配置信息加载到一个类中、供后面Mybatis进行各种操作时使用、这个类叫:Configuration——见名知意。当然这个类的功能并不仅限与存放配置文件信息。
二:整体流程
下面是一段正常情况下从加载配置到执行sql语句的代码:
String mybatisConfigPath = "config/mybatis/mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(mybatisConfigPath);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
int count = (Integer)sqlSession.selectOne("org.alien.mybatis.samples.mapper.AuthorMapper.getAllAuthorsCount");
System.out.println(count);
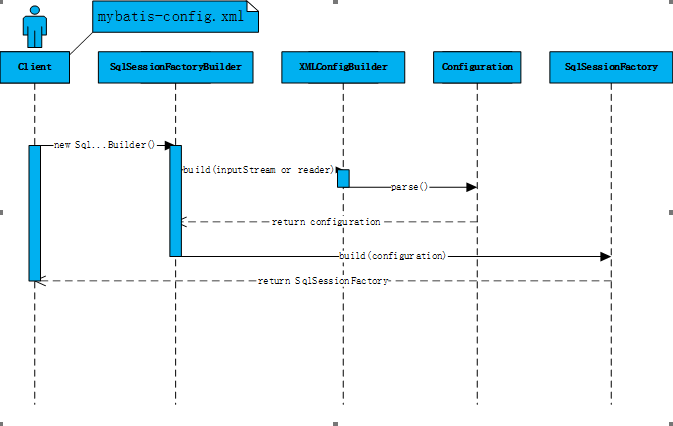
初始化过程在上面代码中就是获取SqlSessionFactory的过程。
初始化过程流程图:
参照流程图、初始化大致步骤:
- 加载配置文件
- 解析配置文件、将配置文件中的信息装载到Configuration中。
- 根据Configuration创建SqlSessionFactory并返回。
三:详细过程
3.1 加载配置文件
这一步很简单、从代码层面上来看就是将配置文件以流的形式读取到程序中、并将其作为参数传递给SqlSessionFactoryBuilder以供后面创建SqlSessionFactory。其提供了许多重载的方法供我们选择:
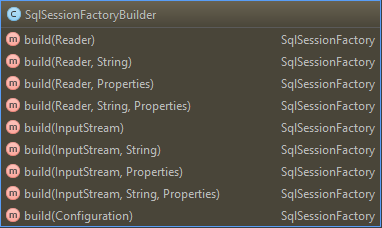
但是其最后都是调用核心方法(从这里也可以看出、初始化过程就是构造填充Configuration过程):
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}3.2解析配置文件
解析配置文件的入口是在SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中的:public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties)
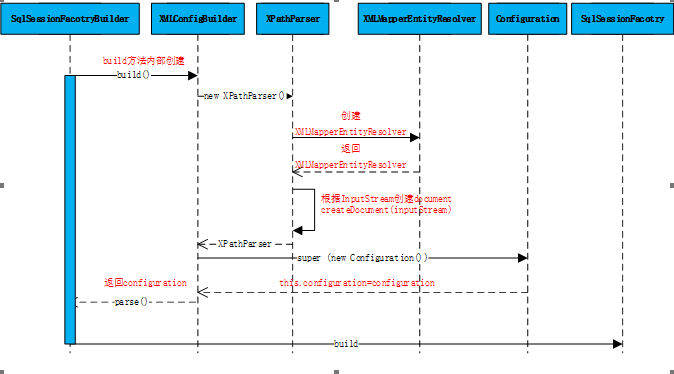
流程图:
3.2.1 整理流程:
- 创建MybatisDTD文件实体类:XMLMapperEntityResolver.
- 根据配置文件流信息和上一步创建的EntityResolver创建配置文件解析类:XPathParser用于解析配置文件内容.
- 将前两部创建的对象作为XMLConfigBuilder的构造函数参数传递、创建XMLConfigBuiler对象.
- 调用XMLConfigBuilder.parse()创建Configuration对象并将配置文件信息装配到Configuration对象中.
下面从代码的角度来看上面流程主要代码。这里从代码执行角度进行分析。
3.2.2 代码流程
- 从
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()开始:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//创建解析文件并装配Configuration的类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//这里分开写、清楚一点。解析配置文件、装配Configuration并返回
Configuration configuration = parser.parse();
//根据Configuration创建SqlSessionFactory并返回
return build(configuration);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}先看XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);到底创建了一个什么样的XMLConfigBuilder。
具体构造方法:
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}- 这里只关心inputstream参数、其他的可以自行研究、其实是不同build方法传递的不同参数。
- 从上面可以看出要想先构建XMLConfigBuilder、首先需要创建XMLMapperEntityResolver、并以其作为创建XPathParser对象的参数之一。
2、XMLMapperEntityResolver的创建:new XMLMapperEntityResolver()、即只需调用其无参构造函数即可。其源码就不再贴了、就是将Mybatis的DTD文件加载到一个私有集合中private static final Map<String, String> doctypeMap = new HashMap<String, String>();并向外提供一个用户获取DTD的InputSource的方法public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId);
3、XPathParser的创建:
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
//填充XPathParser 部分私有属性
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
//根据InputStream来创建Document对象用于后面操作配置文件。
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
- EntityResolver就是前面的XMLMapperEntityResolver
- InputStream则是配置文件流信息
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}- 设置解析xml文件时使用的属性
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 根据InputSource创建Document
3、当XPathParser创建完成之后、回到真正执行XMLConfigBuilder创建的方法:
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
//解析文件代码只能执行一次、当解析之后此值将变为true
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
//前面实例化好的XPathParser
this.parser = parser;
}- 调用Configuration无参构造方法创建其实例对象,
- 设置XMLConfigBuilder解析装配Configuration需要用到的属性、其中最关键的
this.parser = parser也就是前面实例化好的XPathParser。 - 有兴趣的可以看一眼Configuration实例化时初始化了哪些东西基本Mybatis的默认配置在这里都能找到
4、当XMLConfigBuilder实例化好之后、接下来就是解析配置文件、装配Configuration。
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//对于parser.evalNode(String node)如何执行的、这里不关注。只需要知道parser.evalNode(String node)是干嘛的就行。 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
- 获取配置文件中configuration节点所有信息包括其子节点。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //issue #117 read properties first
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}- 从这里很明显的就看出此方法是将Mybatis配置文件各个配置项解析并装配到Configuration对象中。
5、这里只看其中一个最简单的过程——将Mybatis配置文件中的<settings>...<setting name="xxx" value="xxx"/>...<settings>解析并设置到Configuration中、其他的等后面涉及到会深入其过程之中
private void settingsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), true));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
configuration.setLogImpl(resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl")));
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
}
6、解析装配完成之后、返回Configuration
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}- 返回最终生成的DefaultSqlSessionFactory
到这里整个解析过程也就结束了。
补充:
多提一句、网上有的说SqlSessionFactory的创建用到了创建者模式、觉得并不是那么恰当、建造者模式的核心是有一个调度员来根据不同的场景来调度不同的创建者创建具体对象。而这里并没有。个人觉得只是方法的一系列的重载、来方便使用者根据不同的场景或者喜好来创建SqlSessionFactory。
更多内容:Mybatis 目录







 本文详细解析了MyBatis初始化过程,包括配置文件加载、解析及SqlSessionFactory创建。通过源码分析,阐述了Configuration对象的构建流程。
本文详细解析了MyBatis初始化过程,包括配置文件加载、解析及SqlSessionFactory创建。通过源码分析,阐述了Configuration对象的构建流程。
















 1626
1626

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








