转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/crazy1235/article/details/70472982
MemoryCache
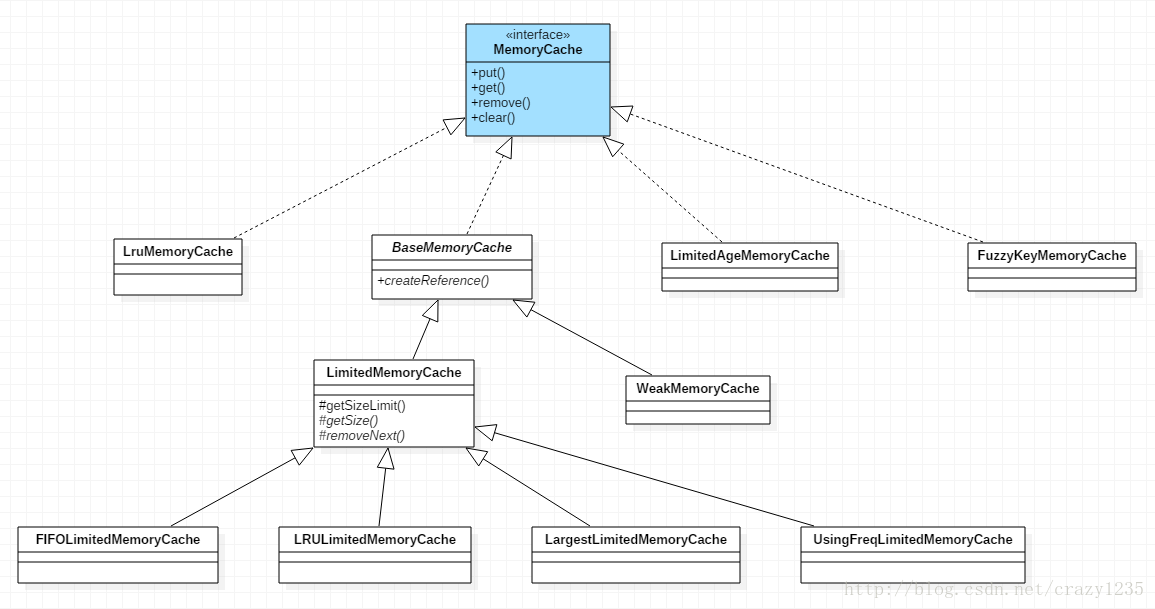
从上图可以看出 MemoryCache 是内存缓存的接口,里面定义了内存缓存的先关操作,比如:读取一个缓存,放入一个缓存,移除一个缓存,清空缓存!
ImageLoaderConfiguration builder的时候
private void initEmptyFieldsWithDefaultValues() {
// 省略代吗
if (memoryCache == null) {
memoryCache = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createMemoryCache(context, memoryCacheSize);
}
if (denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory) {
memoryCache = new FuzzyKeyMemoryCache(memoryCache, MemoryCacheUtils.createFuzzyKeyComparator());
}
// 省略代吗
}可以看到,当memoryCache为空时,会通过工厂方法分配一个缓存策略。
当不允许缓存同一张图片多种尺寸时,创建了一个 FuzzyKeyMemoryCache 缓存策略!
在 DefaultConfigurationFactory 中,UIL给我们初始化了默认的内存缓存策略!
public static MemoryCache createMemoryCache(Context context, int memoryCacheSize) {
if (memoryCacheSize == 0) {
ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
int memoryClass = am.getMemoryClass();
if (hasHoneycomb() && isLargeHeap(context)) {
memoryClass = getLargeMemoryClass(am);
}
memoryCacheSize = 1024 * 1024 * memoryClass / 8;
}
return new LruMemoryCache(memoryCacheSize);
}默认策略是 LruMemoryCache 。缓存大小为app可获得最大内存的1/8
LruMemoryCache
当超过我们设置的缓存容量时,优先删除最近最久为使用的缓存!
内部维护一个 LinkedHashMap
private final LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap> map;
private int size; // 当前缓存的大小
private final int maxSize; // 最大允许缓存总量的大小@Override
public final Bitmap get(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
synchronized (this) {
return map.get(key);
}
}get() 不用多说,直接从map里面根据key取出bitmap即可!
@Override
public final Bitmap remove(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
synchronized (this) {
Bitmap previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= sizeOf(key, previous);
}
return previous;
}
}remove 也是,直接从map移除对应key的那条记录!
最主要的是put() 函数!它涉及到,当容量超过maxSize时要移除部分缓存的操作!
@Override
public final boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
synchronized (this) {
size += sizeOf(key, value);
// 1.
Bitmap previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= sizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
// 2.
trimToSize(maxSize);
return true;
}注释1处,当previous不为空时,表示之前已经有该key对应的缓存,现在需要放入新的bitmap对象。
所以就需要把之前的给移除掉! 新的缓存放在map的最后一位!
所以此时map最前面的就是最近最久为使用的!!!
private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
String key;
Bitmap value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName() + ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<String, Bitmap> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= sizeOf(key, value);
}
}
}trimToSize() 有个while循环,只要size >maxSize 就不断的从LinkedHashMap 的头部取出一条删除!
@Override
public void clear() {
trimToSize(-1); // -1 will evict 0-sized elements
}清空缓存的操作直接调用 trimToSize 传入-1,这样直到map为空break循环!
LimitedAgeMemoryCache
不限制缓存大小,限制缓存存货周期!当超过我们设置的时间长度就会被删除!
private final long maxAge;
private final Map<String, Long> loadingDates = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Long>());@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
boolean putSuccesfully = cache.put(key, value);
if (putSuccesfully) {
loadingDates.put(key, System.currentTimeMillis()); //当前时间!
}
return putSuccesfully;
}由于没有限制大小,所以put操作没有什么特别的限制!
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
loadingDates.remove(key);
return cache.remove(key);
}@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Long loadingDate = loadingDates.get(key);
if (loadingDate != null && System.currentTimeMillis() - loadingDate > maxAge) {
cache.remove(key);
loadingDates.remove(key);
}
return cache.get(key);
}get() 操作回去判断缓存的存货周期,如果大于maxAge,则会从Map中删除!!!
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
loadingDates.remove(key);
return cache.remove(key);
}@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
loadingDates.clear();
}FuzzyKeyMemoryCache
denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory = true;如果不允许缓存同一张图片的多个尺寸,则使用 FuzzyKeyMemoryCache 做策略,同一个图片新的尺寸会覆盖缓存中该图片老的尺寸。
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
// Search equal key and remove this entry
synchronized (cache) {
String keyToRemove = null;
for (String cacheKey : cache.keys()) {
if (keyComparator.compare(key, cacheKey) == 0) {
keyToRemove = cacheKey;
break;
}
}
if (keyToRemove != null) {
cache.remove(keyToRemove);
}
}
return cache.put(key, value);
}BaseMemoryCache
它是一个实现了 MemoryCache 主要函数的抽象类。以引用的方式保存bitmap,便于虚拟机在内存不足时回收缓存对象。
private final Map<String, Reference<Bitmap>> softMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Reference<Bitmap>>());Reference 可以是 WeakReference or SoftReference !
子类需要实现它的抽象方法:
protected abstract Reference<Bitmap> createReference(Bitmap value);WeakMemoryCache
它以 WeakReference < Bitmap > 做为 value , 实现了BaseMemoryCache。
实现了createReference(Bitmap value)函数,直接创建一个 WeakReference < Bitmap > (value)做为缓存 value。
@Override
protected Reference<Bitmap> createReference(Bitmap value) {
return new WeakReference<Bitmap>(value);
}
}LimitedMemoryCache
也是继承于 BaseMemoryCache!
限制存储容量的内存缓存策略!
最大容量为16M
private static final int MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB = 16;
private static final int MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE = MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB * 1024 * 1024;所以会在 put 的时候判断是否超出上限,然后根据具体的子类策略删除某些缓存!
protected abstract int getSize(Bitmap value); // 每个元素大小
protected abstract Bitmap removeNext(); // 决定删除的对象LRULimitedMemoryCache
继承自 LimitedMemoryCache!
限制总容量的内存缓存策略,会在缓存满时优先删除最近最少使用的缓存!
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 1.1f;
private final Map<String, Bitmap> lruCache = Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap>(INITIAL_CAPACITY, LOAD_FACTOR, true));使用 LinkedHashMap 做缓存!
LinkedHashMap 第三个参数表示是否需要根据访问顺序(accessOrder)排序。
true 表示根据accessOrder排序,最近访问的跟最新加入的一样放到最后面;
false 表示按照之前的顺序插入。
这里为 true ,所以当缓存满时,会删除map首位的元素!
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Bitmap mostLongUsedValue = null;
synchronized (lruCache) {
Iterator<Entry<String, Bitmap>> it = lruCache.entrySet().iterator();
if (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, Bitmap> entry = it.next();
mostLongUsedValue = entry.getValue();
it.remove();
}
}
return mostLongUsedValue;
}LargestLimitedMemoryCache
优先删除最大的缓存!!
public class LargestLimitedMemoryCache extends LimitedMemoryCache private final Map<Bitmap, Integer> valueSizes = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Bitmap, Integer>());@Override
protected Reference<Bitmap> createReference(Bitmap value) {
return new WeakReference<Bitmap>(value);
}也是使用 WeakReference< Bitmap >
重点看 removeNext()
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer maxSize = null;
Bitmap largestValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = valueSizes.entrySet();
synchronized (valueSizes) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (largestValue == null) {
largestValue = entry.getKey();
maxSize = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer size = entry.getValue();
if (size > maxSize) {
maxSize = size;
largestValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
valueSizes.remove(largestValue);
return largestValue;
}
for循环找到最大的元素,然后从map中删除!
FIFOLimitedMemoryCache
限制缓存总容量的大小,并且会在缓存满时优先删除最先加入的缓存!
private final List<Bitmap> queue = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList<Bitmap>());@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
return queue.remove(0);
}removeNext 直接删除列表首元素!
UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache
限制总缓存容量大小,并且会在缓存满时优先删除使用次数最少的缓存!
private final Map<Bitmap, Integer> usingCounts = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Bitmap, Integer>());每次get() 都将当前缓存使用次数 +1
@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
Integer usageCount = usingCounts.get(value);
if (usageCount != null) {
usingCounts.put(value, usageCount + 1);
}
}
return value;
}@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer minUsageCount = null;
Bitmap leastUsedValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = usingCounts.entrySet();
synchronized (usingCounts) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (leastUsedValue == null) {
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
minUsageCount = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer lastValueUsage = entry.getValue();
if (lastValueUsage < minUsageCount) {
minUsageCount = lastValueUsage;
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
usingCounts.remove(leastUsedValue);
return leastUsedValue;
}removeNext 中 循环找出使用次数最多的元素,并删除!
OK!以上就是UIL库中提供的基础中内存缓存策略!
























 305
305











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








