如文字不清,请 “右键->图片另存为” 下载后查看大图
-------------------------
原文及翻译文本
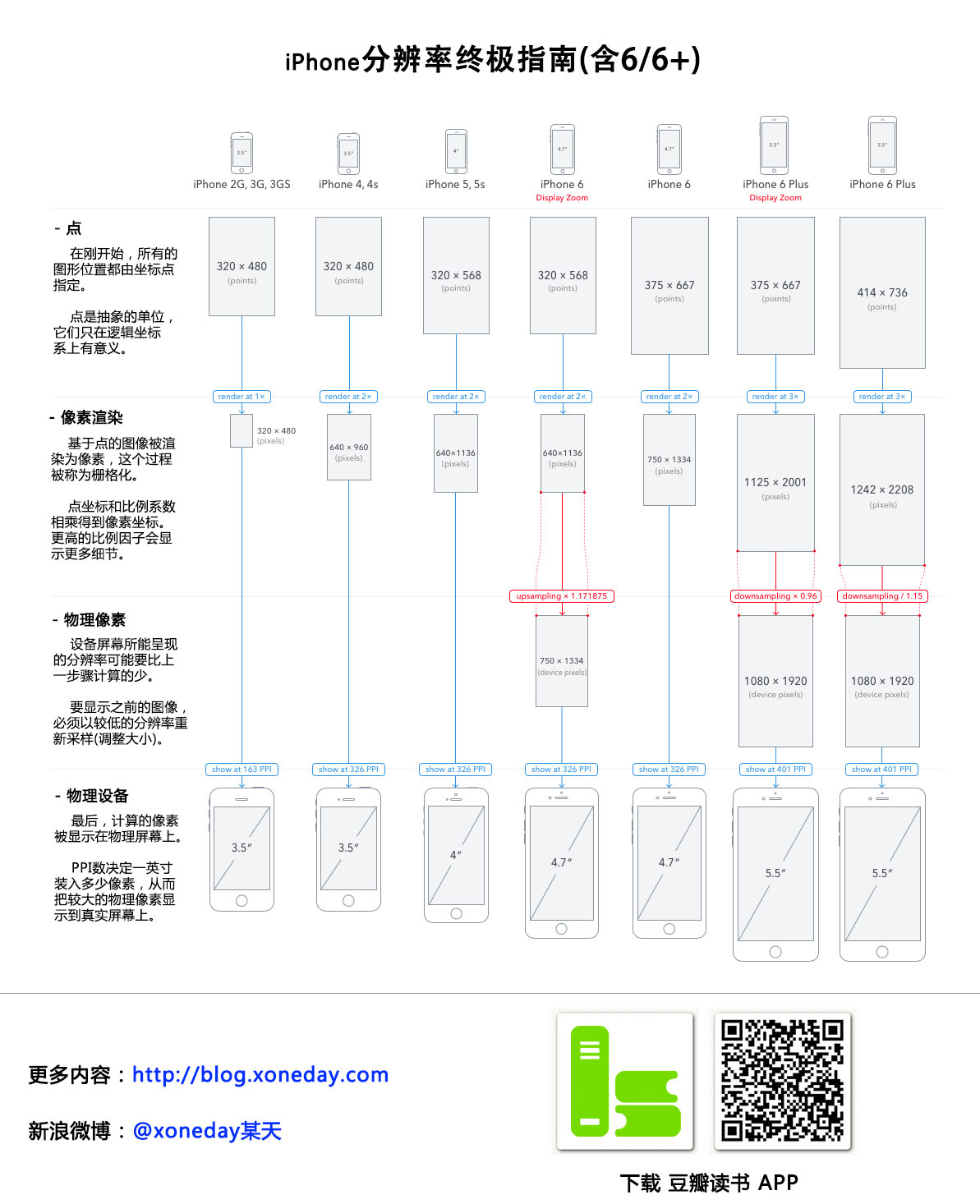
Points
点
At the beginning, coordinates of all drawings are specified in points.
在一开始,所有的图形位置都由坐标点指定。
Points are abstract units, they only make sense in this mathematical coordinate space.
点是抽象的单位,它们只在逻辑坐标系上有意义。
Rendered Pixels
像素渲染
Point-based drawings are rendered into pixels. This process is known as rasterization
基于点的图像被渲染为像素,这个过程被称为栅格化。
Point coordinates are multiplied by scale factor to get pixel coordinates. Higher scale factors result in higher level of detail.
点坐标和比例系数相乘得到像素坐标。更高的比例因子会显示更多细节。
Physical Pixels
物理像素
The device screen may have lower pixel resolution than the image rendered in previous step.
设备屏幕所能呈现的分辨率可能要比上一步骤底。
Before the image can be displayed, it must be downsampled (resized) to lower pixel resolution.
要显示之前的图像,必须以较低的像素分辨率重新采样(调整大小)。
Physical Device
物理设备
Finally, computed pixels are displayed on the physical screen.
最后,计算的像素被显示在物理屏幕上。
The PPI number tells you how many pixels fit into one inch and thus how large the pixels appear in the real world.
PPI数决定一英寸装入多少像素,从而把较大的物理像素显示到真实屏幕上。







 本文探讨了基于点的图像如何被渲染成像素的过程,包括从抽象坐标到具体像素坐标转换的方法,以及图像最终在物理设备上的显示方式。
本文探讨了基于点的图像如何被渲染成像素的过程,包括从抽象坐标到具体像素坐标转换的方法,以及图像最终在物理设备上的显示方式。
















 1744
1744

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








