STL学习系列之五——关联容器
关联容器:
利用键,STL的关联容器能直接保存和提取键。
4个关联容器分别为:multiset,set,multimap,map。每个关联容器都按有序的方式维护者它的键。对关联容器的迭代遍历是根据这个容器的排序顺序进行的。
multiset和set提供了对值的集合的操作,其中的值都是键,每个键并不存在一个关联值。
multimap和map提供了与键相关联的值的操作(这些值有时被称作映射值)。
multiset和set的主要区别是:multiset允许重复的键,set不允许。
multimap和map的主要区别是:multimap允许用重复的键保存关联值,而map允许用唯一的键保存关联值。
1.multiset
multiset关联容器提供了键的快速保存于提取,并允许重复的键。
元素的顺序由比较函数对象确定,e.g.在一个整数multiset中,元素能够通过比较函数对象less<int>按键的升序排序。
multiset支持双向迭代器(而不是随机访问迭代器)
下列demo1演示了一个按升序保存整数的multiset关联容器。
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
typedef multiset<int,less<int>> Ims;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
const int SIZE = 10;
int a[SIZE]={7,22,9,1,18,30,100,22,85,13};
Ims intMultiset;
ostream_iterator<int> output(cout," ");
//count函数用于计算multiset中当前保存的值15的出现次数
cout<<"现在这里有"<<intMultiset.count(15)<<"个值15在这个multiset里\n";
//将值15两次添加到multiset中
intMultiset.insert(15);
intMultiset.insert(15);
cout<<"插入后,这里有"<<intMultiset.count(15)<<"个15在multiset里\n";
//find函数返回一个迭代器或常量迭代器,指向最先找到值的位置,
//如果没有找到这个值,则返回一个等于调用end函数所返回值的迭代器或常量迭代器
Ims::const_iterator result;
result=intMultiset.find(15);
if (result!=intMultiset.end())
{
cout<<"发现值15\n";
}
result=intMultiset.find(20);
if (result==intMultiset.end())
{
cout<<"没有发现值20\n";
}
//使用insert函数将数组a的元素插入到Multiset中
intMultiset.insert(a,a+SIZE);
cout<<"出入后,multiset包含:\n";
copy(intMultiset.begin(),intMultiset.end(),output);//copy算法将multiset中的元素赋值到标准输出
//使用lower_bound和upper_bound函数,搜索值22在Multiset中最早出现的位置以及最后一次出现位置之后的那个位置
//这两个函数都返回指向适当位置的iterator,或const_iterator。如果没有找到值,则返回等于end函数所返回的迭代器
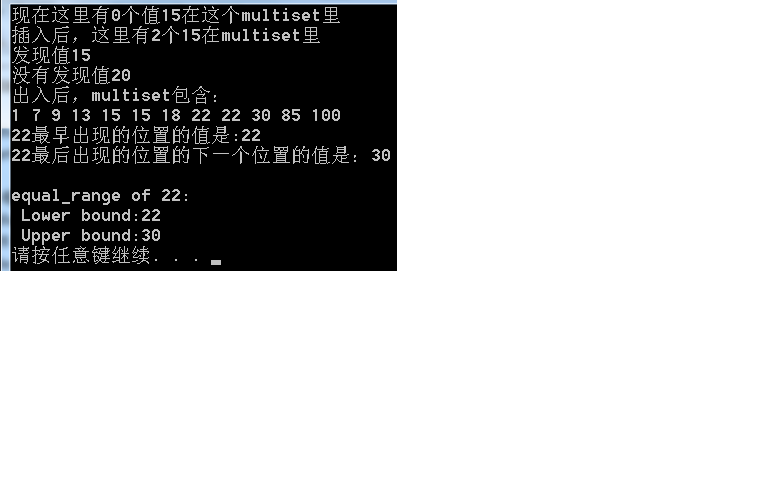
cout<<"\n22最早出现的位置的值是:"
<<*(intMultiset.lower_bound(22));
cout<<"\n22最后出现的位置的下一个位置的值是:"
<<*(intMultiset.upper_bound(22));
//实例化pair类的一个实例p。pair类的对象用于将一对值关联。
pair<Ims::const_iterator,Ims::const_iterator> p;
p=intMultiset.equal_range(22);
cout<<"\n\nequal_range of 22:"<<"\n Lower bound:"
<<*(p.first)<<"\n Upper bound:"<<*(p.second);
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.set关联容器
Set关联容器用于快速保存与提取不同的键。Set的实现与multiset相同,区别在于set键必须是唯一的。因此,如果试图在set中插入重复的键,则会忽略它。
Set支持双向迭代器,(而不是随机访问迭代器)。
下面的demo2演示了一个包含double值的set。
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
//使用了一个typedef,为函数对象less<double>按升序保存double值的set对象创建一个新的类型名
typedef set<double,less<double>> DoubleSet;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
const int SIZE = 5;
double a[SIZE] ={2.1,4.2,9.5,2.1,3.7};
//使用新的类型名DoubleSet实例化了一个doubleSet对象。构造函数调用取得数组a中位于a和a+SIZE之间的元素,并将它们插入到set中
DoubleSet doubleSet(a,a+SIZE);
ostream_iterator<double> output(cout," ");
cout<<"doubleSet包含:";
copy(doubleSet.begin(),doubleSet.end(),output);//使用copy算法输出set的内容
//注意:2.1在数组中出现了2次,但在doubleSet中只出现一次
//定义一个pair对象,它由一个DoubleSet的const_iterator和一个布尔值组成,这个对象保存了insert函数的结果
pair<DoubleSet::const_iterator,bool> p;
//使用insert函数将值13.8保存到set中。所返回的pair对象p,包含了指向set中值13.8的一个迭代器p.first和一个布尔值
//如果值被插入,则布尔值为真;如果没有被插入(由于它已经在set中存在),则布尔值为假
p = doubleSet.insert(13.8);
cout<<"\n\n"<<*(p.first)
<<(p.second ? " was":" was not")<<" inserted";
cout<<"\ndoubleSet 包含:";
copy(doubleSet.begin(),doubleSet.end(),output);
p = doubleSet.insert(9.5);
cout<<"\n\n"<<*(p.first)
<<(p.second ? " was":" was not")<<" inserted";
cout<<"\ndobuleSet 包含:";
copy(doubleSet.begin(),doubleSet.end(),output);
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

3.multimap关联容器
multimap关联容器用于键以及关联值(键/值对)的快速保存与提取。
multimap和map中的元素都是键/值对而不是单个的值。插入到一个multimap或者map时,使用的是一个包含键和值的pair对象。
键的顺序由比较器函数对象确定。
multimap中允许重复的键,因此多个不同的值能够与同一键相关联。这通常成为一对多关系。
multimap支持双向迭代器(而不是随机访问迭代器)。
multimap的实现能够高效地搜索一个指定键相配对的所有值。
下面是demo3:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
//用typedef定义了别名Mmid,表示一个multimap类型,其键类型为int,与键相关联的值为double类型,并且元素是按升序排列的
typedef multimap<int,double,less<int>> Mmid;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Mmid pairs; //用新类型实例化一个multimap对象pairs
//使用count函数确定键为15的键/值对的数量
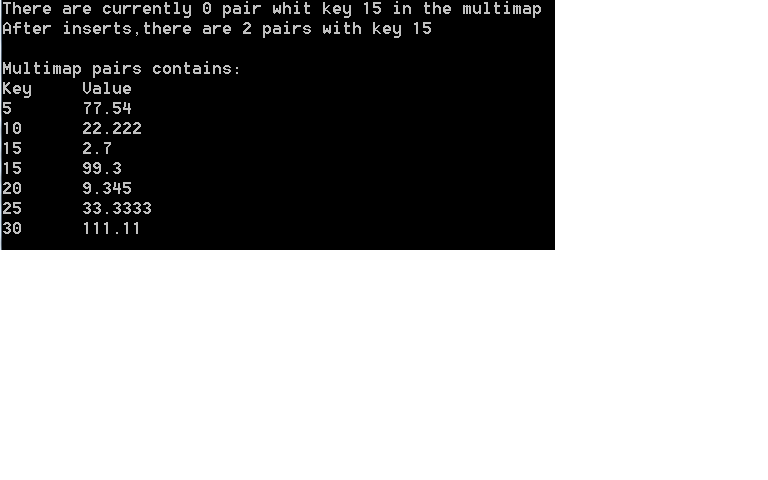
cout<<"There are currently "<<pairs.count(15)
<<" pair whit key 15 in the multimap\n";
//使用insert函数在这个multimap中添加新的键/值对
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(15,2.7));
//表达式Mmid::value_type(15,2.7)创建了一个pair对象,其中first是int类型的键(15),second是double类型的值(2.7)
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(15,99.3));
cout<<"After inserts,there are "<<pairs.count(15)
<<" pairs with key 15\n\n";
//在multimap中再插入5个pair对象
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(30,111.11));
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(10,22.222));
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(25,33.3333));
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(20,9.345));
pairs.insert(Mmid::value_type(5,77.54));
cout<<"Multimap pairs contains:\nKey\tValue\n";
for (Mmid::const_iterator iter = pairs.begin();
iter != pairs.end();++iter)
{
cout<<iter->first <<'\t'<<iter->second<<'\n';
}
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4.map关联容器
map关联容器执行唯一的键与关联值的快速保存和提取。
Map中不允许重复的键,每个值都只能与一个键相关联。这种通常称为一对一映射。
Map也被称为关联数组。在map的下标运算符[]中提供键,能够在map中搜出与这个键相关联的值。
Map中任何位置都可以执行插入和删除操作。
下面demo4演示了map关联容器
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef map<int,double,less<int>> Mid;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Mid pairs;
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(15,2.7));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(30,111.11));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(5,1010.1));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(10,22.22));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(25,33.333));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(5,77.54));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(20,9.345));
pairs.insert(Mid::value_type(15,99.3));
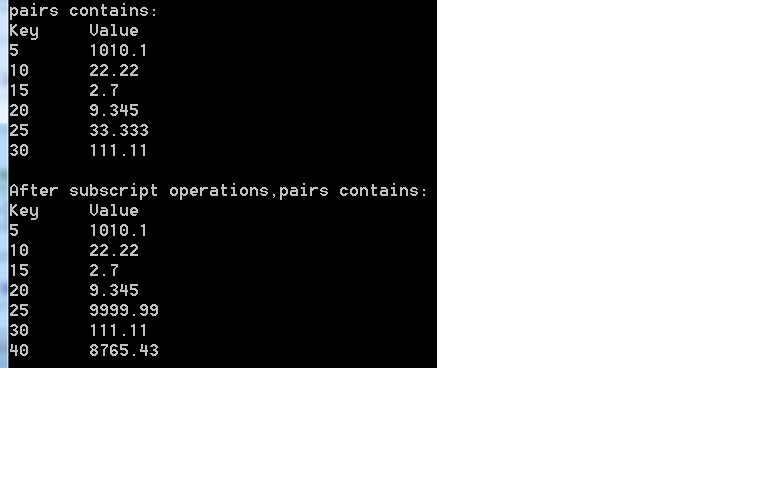
cout<<"pairs contains:\nKey\tValue\n";
for (Mid::const_iterator iter = pairs.begin();
iter != pairs.end(); ++iter)
{
cout<<iter->first<<'\t'<<iter->second<<'\n';
}
//使用map下标运算符。当下标值为map中已经存在的键时,这个运算符就返回相关联值的引用;
//当下标值不是这个map中已经存在的键时,这个运算符就将这个键插入到map中,并返回一个引用,它能够用来将一个值与这个键相关联
pairs[25] = 9999.99; //用一个新值9999.99替换了与键25相关联的值
pairs[40] = 8765.43; //在这个map中插入一个新的键/值对
cout<<"\nAfter subscript operations,pairs contains:\nKey\tValue\n";
for (Mid::const_iterator iter2 = pairs.begin();
iter2 != pairs.end(); iter2++)
{
cout<<iter2->first<<'\t'<<iter2->second<<'\n';
}
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:






















 149
149











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








