One of the most powerful aspects of jQuery is its ability to make selecting elements in the DOM easy. The Document Object Model serves as the interface between JavaScript and a web page; it provides a representation of the source HTML as a network of objects rather than as plain text.

jquery最有力的能力之一是它使选择DOM结构中元素的变的容易的能力。文档对象模型作为js和网页的接口存在,他提供了基础html作为对象网而不是简单的文本的存在。
This network takes the form of a "family tree" of elements on the page. When we refer to the relationships that elements have with one another, we use the same terminology that we use when referring to family relationships: parents, children, and so on. A simple example can help us understand how the family tree metaphor applies to a document, as follows:
<html>
<head>
<title>the title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
<p>This is yet another paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
网状结构在网页上表现为家庭图谱的形式。当我们涉及到一个元素和其他元素的关系时,我们使用实际到家庭关系的术语:双亲,子代等等。一个简单的例子可以帮助我们理解家庭图谱如何映射到文档中的,如下:
<html>
<head>
<title>the title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
<p>This is yet another paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<head>
<title>the title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
<p>This is yet another paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
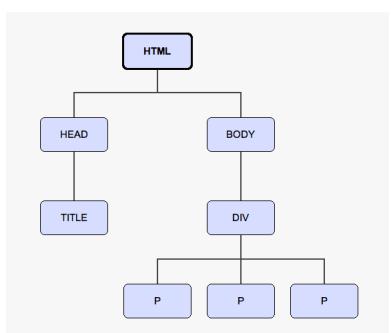
Here, <html>is the ancestorof all the other elements; in other words, all the other elements are descendantsof <html>. The <head>and <body>elements are not only descendants, but childrenof <html>, as well. Likewise, in addition to being the ancestor of <head>and <body>, <html>is also their parent. The <p>elements are children (and descendants) of <div>, descendants of <body>and <html>, and siblingsof each other, as shown in the following diagram:

在这里,<html>是所有其他元素的祖先,换句话说,所有其他元素是<html>的后代。 <head>和<body>元素不仅仅是后代元素,还是<html>的子代元素。同样的,<html>不仅仅是他们的祖先元素,也是他们的父代。<p>元素是<div>的子代元素也是后代元素,也是<body>和<html>的后代元素,也是其他<p>的兄弟元素。正如下面的图表展示的那样。

To help visualize the family tree structure of the DOM, you can use a number of software tools, such as the Firebug plugin for Firefox, or the Web Inspector in Safari or Chrome.
为了帮助让DOM结构的家庭书结构变的更加形象,你可以使用一些软件工具,比如firefox上的firebug插件,或者Safari或者Chrome上的web探测器。
With this tree of elements at our disposal, we'll be able to use jQuery to efficiently locate any set of elements on the page. Our tools to achieve this are jQuery selectors and traversal methods.
With this tree of elements at our disposal, we'll be able to use jQuery to efficiently locate any set of elements on the page. Our tools to achieve this are jQuery selectors and traversal methods.
通过我们使用的元素树状图,我们可以使用jquery去有效的定位网页上的任何元素。我们实现这一点的工具就是jquery选择器和遍历方法。
An important point to note, before we begin, is that the resulting set of elements from selectors and methods is always wrapped in a jQuery object. These jQuery objects are very easy to work with when we want to actually do something with the things that we find on a page. We can easily bind eventsto these objects and add slick effectsto them, as well as chainmultiple modifications or effects together. Nevertheless, jQuery objects are different from regular DOM elements or node lists, and as such do not necessarily provide the same methods and properties for some tasks. In the final part of this chapter, therefore, we will look at ways to directly access the DOM elements that are wrapped in a jQuery object.
An important point to note, before we begin, is that the resulting set of elements from selectors and methods is always wrapped in a jQuery object. These jQuery objects are very easy to work with when we want to actually do something with the things that we find on a page. We can easily bind eventsto these objects and add slick effectsto them, as well as chainmultiple modifications or effects together. Nevertheless, jQuery objects are different from regular DOM elements or node lists, and as such do not necessarily provide the same methods and properties for some tasks. In the final part of this chapter, therefore, we will look at ways to directly access the DOM elements that are wrapped in a jQuery object.
在我们开始前,一个需要指出的重要一点是选择器和方法得到的结果中石碑jquery对象包围。当我们想实际在我们从网页上查找到的元素上做一些事情的时候,使用这些jquery对象将是很容易的。我们可以很容易的在这些对象上绑定事件,为他们添加流畅的影响,同时一起链状的修改影响他们。jquery对象与常规的DOM对象或者节点列表是不相同的,并没有必要的为一些任务添加相同的方法和属性。因此在这一章节的最后部分,我们将看一下直接接触被jquery对象包围着的DOM对象。






















 1168
1168

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








