转自:http://blog.csdn.net/chengdong1314/article/details/52796086
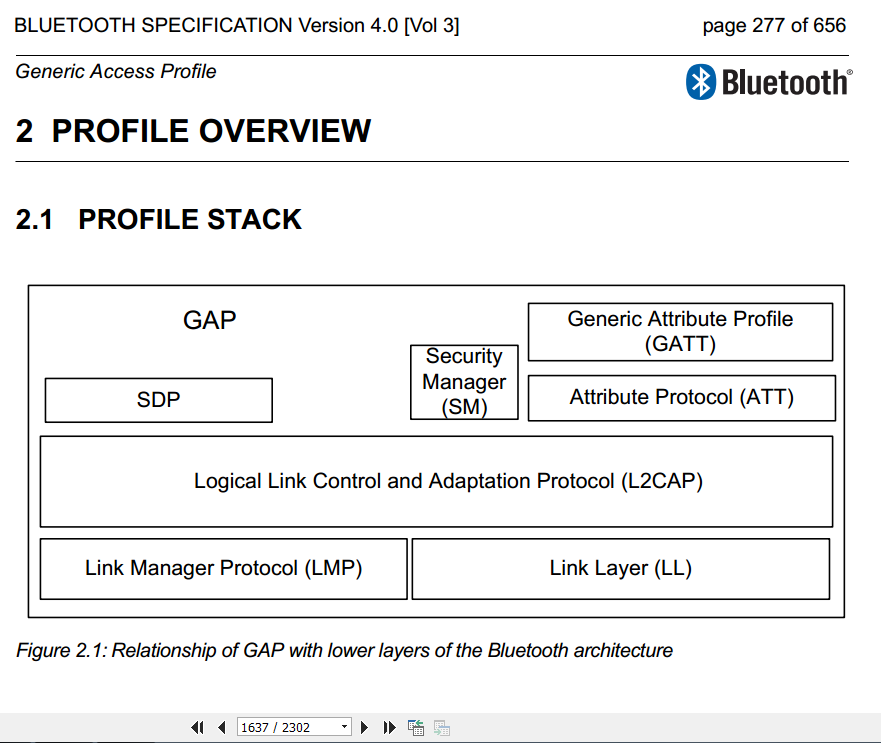
协议栈简图
UUID解析
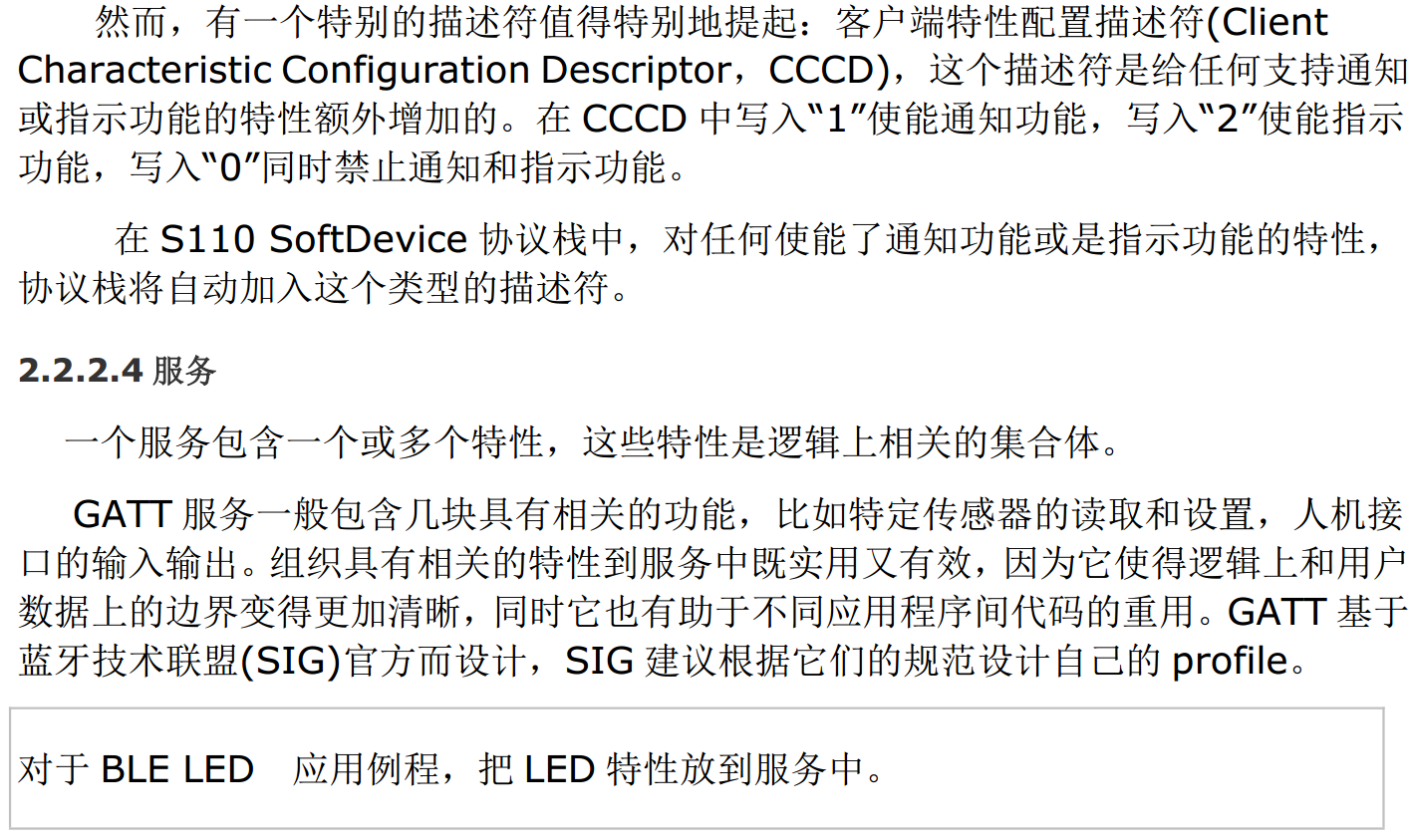
摘录于:清风电子的《手把手教你用蓝牙:蓝牙LED任务读写原理任务详解.pdf》
蓝牙Service、属性、Characteristic、描述符以及profile的关系
下面内容摘录于:清风电子的《手把手教你用蓝牙:蓝牙LED任务读写原理任务详解.pdf》
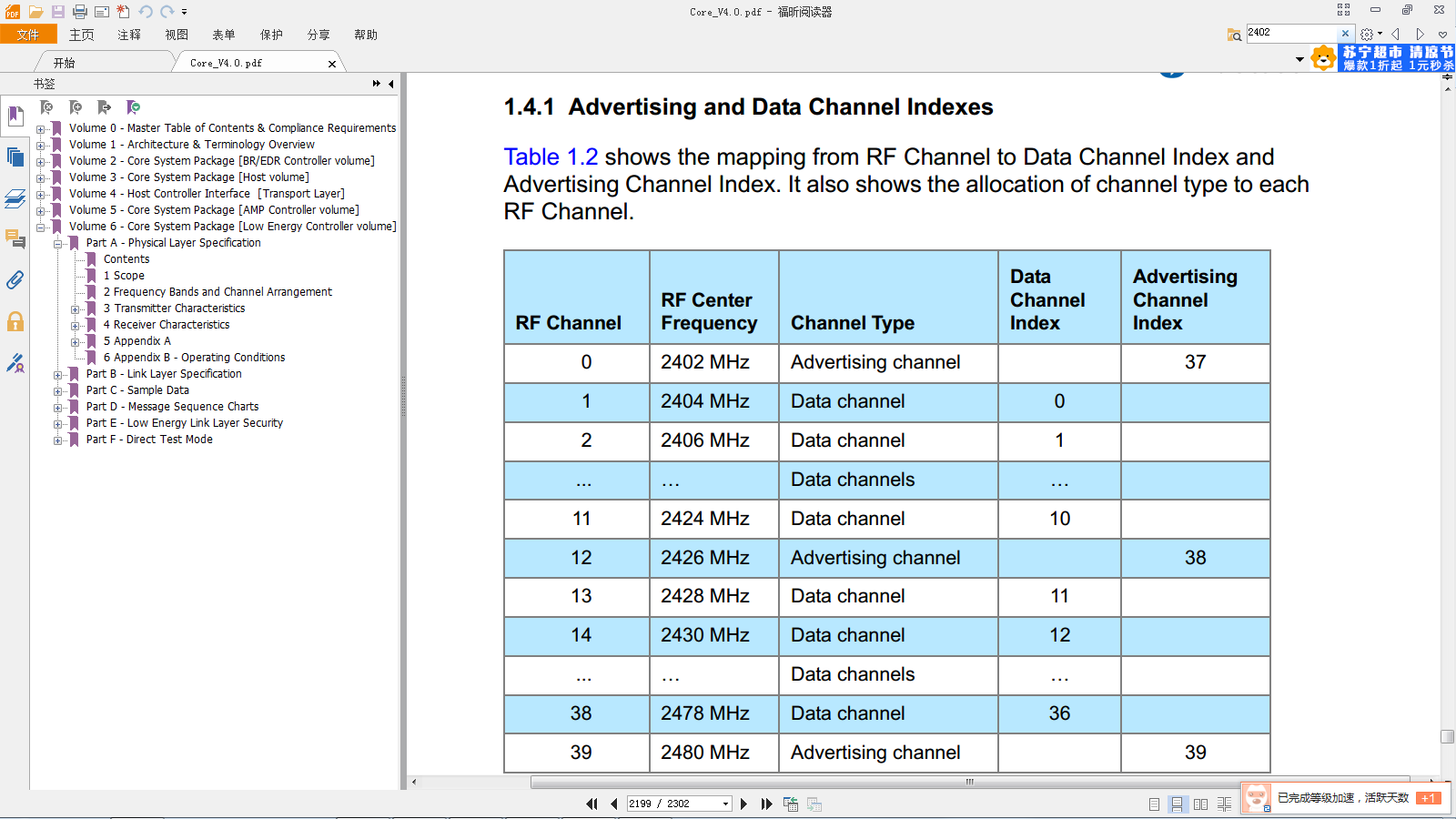
蓝牙无线通道Advertising and Data Channel Indexes
缩写词
acl定义如下:

SUC的定义如下:
规范中缩写词的定义摘录如下:
| 1 LIST OF ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS page:207 [Vol 1] |
| Acronym or abbreviation | Writing out in full | Which means |
| 8DPSK /4 DQPSK A A2MP AAD AC ACI ACK ACL ACL-C ACL-U ACO AD ADVB ADVB-C ADVB-U Adv_idx AES AGC AFH AGC AHS AIFSN AMP | 8 phase Differential Phase Shift Keying pi/4 Rotated Differential Quater nary Phase Shift Keying AMP Manager Protocol Additional Authentical Data Access Category Access Category Index Acknowledge/ACKnowledgement Asynchronous Connection-ori ented [logical transport] ACL Control [logical link] (LMP) ACL User [logical link] (L2CAP) Authenticated Ciphering Offset Advertising Data LE Advertising Broadcast LE Advertising Broadcast Control (Logical Link) LE Advertising Broadcast User Data (Logical Link) Advertising channel index Advanced Encryption Standard Automatic Gain Control Adaptive Frequency Hopping Automatic Gain Control Adapted Hop Sequence Arbitration Interframe Space Num ber Alternate MAC PHY | 3 Mbps modulation type used by Enhanced Data rate 2 Mbps modulation type used by Enhanced Data Rate Reliable or time-bounded, bi-direc tional, point-to-point. |
| AMP_ASSOC AMP-U AR_ADDR ARQ ASB ASB-U ATT B BB BCH BD_ADDR BER BT C CAC CL CCM CCMP CKLN CLK CLKE CODEC COF CRC CTS CVSD | Alternate MAC PHY association information AMP User Asynchronous/Isochro nous Logical Link Access Request Address Automatic Repeat Request Active Slave Broadcast [logical transport] ASB User [logical link] (L2CAP) Attribute Protocol Baseband Bose, Chaudhuri & Hocquenghem Bluetooth Device Address Bit Error Rate Bandwidth Time Channel Access Code Connectionless Counter with Cipher Block Chain ing-Message Authentication Code CTR with CBC-MAC Protocol Native Clock Master Clock Estimated Clock COder DECoder Ciphering Offset Cyclic Redundancy Check Clear to send Continuous Variable Slope Delta Modulation | Unreliable, uni-directional broad cast to any devices synchronized with the physical channel. Type of code The persons who discovered these codes in 1959 (H) and 1960 (B&C) |
| D DA DAC DCE DCE DCI DEVM DFS DH DHK DIAC DIV DM DPSK DQPSK DSAP DTE DTM DUT DV E ECWmax | Destination address Device Access Code Data Communication Equipment Data Circuit-Terminating Equip ment Default Check Initialization Differential Error Vector Magnitude Dynamic Frequency Selection Data-High Rate Diversifier Hiding Key Dedicated Inquiry Access Code Diversifier Data - Medium Rate Differential Phase Shift Keying Differential Quaternary Phase Shift Keying Destination Service Access Point Data Terminal Equipment Direct Test Mode Device Under Test Data Voice Enhanced Contention Window maximum | In serial communications, DCE refers to a device between the communication endpoints whose sole task is to facilitate the commu nications process; typically a modem Measure of modulation error used for Enhanced Data Rate transmit ter testing Data packet type for high rate data Data packet type for medium rate data Generic description of Enhanced Data Rate modulation Modulation type used by Enhanced Data Rate In serial communications, DTE refers to a device at the endpoint of the communications path; typically a computer or terminal. Data packet type for data and voice |
| ECWmim ED EDCA EDIV EDR EFS EIR EIRP EOC ER EPR ERP eSCO eSCO-S ESS ETSI F FCC FCS FDMA FEC | Enhanced Contention Window minimum Erroneous Data Enhanced Distributed Channel Access Encrypted Diversifier Enhanced Data Rate Extended Flow Specification Extended Inquiry Response Effective Isotropic Radiated Power Extreme Operating Conditions Encryption Root Encryption Pause Resume Extended Rate PHY conforming to Clause 19 Extended Synchronous Connec tion Oriented [logical transport] Stream eSCO (unframed) Extended Service Set European Telecommunications Standards Institute Federal Communications Commission Frame Check Sequence Frequency Division Multiple Access Forward Error Correction code | Host supplied information transmit ted in the inquiry responses sub state. Equivalent power that an isotropic antenna must transmit to provide the same field power density Mode allowing the device to initiate the pause and resume encryption sequence Bi-directional, symmetric or asym metric, point-to-point, general reg ular data, limited retransmission. used to support isochronous data delivered in a stream without fram ing |
| FH FHS FHSS FIFO FIPS FM G GAP GATT GFSK GIAC GTM H HCI HEC HID HV HW I IAC IC IEC IEEE IETF IFS IP IPv4 IPv6 IR | Frequency Hopping Frequency Hop Synchronization Frequency Hopping Spread Spec trum First In First Out Federal Information Processing Standards Frequency Modulation Generic Access Profile Generic Attribute Protocol Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying General Inquiry Access Code Generic Test Methodology Host Controller Interface Header-Error-Check Human Interface Device High quality Voice Hardware Inquiry Access Code Industry Canada International Electrotechnical Commission Institute of Electronic and Electrical Engineers Internet Engineering Task Force Inter Frame Space Internet Protocol Internet Protocol version 4 Internet Protocol version 6 Identity | Modulation Type e.g. HV1 packet |
| IrDA IRK ISM ISO IUT ITU IV IVm IVs J JRL K KCC L L2CAP LAP LC LC LCP LE LE-C LE-U LFSR LL LLCP | Infra-red Data Association Identity Root Key Industrial, Scientific, Medical International Organization for Stan dardization Implementation Under Test International Telecommunication Union Initialization Vector Initialization Vector (master) Initialization Vector (slave) Japanese Radio Law Korea Communications Commis sion Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Lower Address Part Link Controller Link Control [logical link] Link Control Protocol Low Energy Low Energy Control (link) LE User [logical link] Linear Feedback Shift Register Link Layer Link Layer Control Protocol | Link Controller (or baseband) part of the Bluetooth protocol stack. Low level Baseband protocol handler The control logical links LC and ACL-C are used at the link control level and link manager level, respectively. |
| LLID LM LMP LR LSB LSO LSTO LT_ADDR LTK M M MAC MAC MD Mbps MIC MIIT MITM MMI MS MSC MSB MSC MSO MTU N NAK NAP | Logical Link Identifier Link Manager Link Manager Protocol Loudness Rating Least Significant Bit Least Significant Octet Link Supervision Timeout Event Logical Transport ADDRess Long-Term Key Master or Mandatory Medium Access Control Message Authentication Code More Data Million (Mega) bits per second Message Integrity Check Ministry of Industry and Informa tion Technology Man-in-the-middle Man Machine Interface Mobile Station Message Sequence Chart Most Significant Bit Message Sequence Chart Most Significant Octet Maximum Transmission Unit Negative Acknowledge Non-significant Address Part | For LM peer to peer communica tion Controller can send LSTO event to Host Usually meaning the Medium Access Control code |
| NCC NESN NIST NOC O O OBEX OCF OGF OOB P PBF PCM PDU PHY PIN PM_ADDR PN PPM PPP PRBS PRNG PSB PSB-C PSB-U PSK PSTN | National Communications Com mission Next Expected Sequence Number National Institute of Standards and Technology Normal Operating Conditions Optional OBject EXchange protocol OpCode Command Field OpCode Group Field Out of Band Packet Boundary Flag Pulse Coded Modulation Protocol Data Unit Physical Layer Personal Identification Number Parked Member Address Pseudo-random Noise Part Per Million Point-to-Point Protocol Pseudo Random Bit Sequence Pseudo Random Noise Generation Parked Slave Broadcast [logical transport] PSB Control [logical link] (LMP) PSB User [logical link] (L2CAP) Phase Shift Keying Public Switched Telephone Net work | The device supports the capability to correctly handle HCI ACL Data Packets a message Unreliable, uni-directional broad cast to all piconet devices. Class of modulation types |
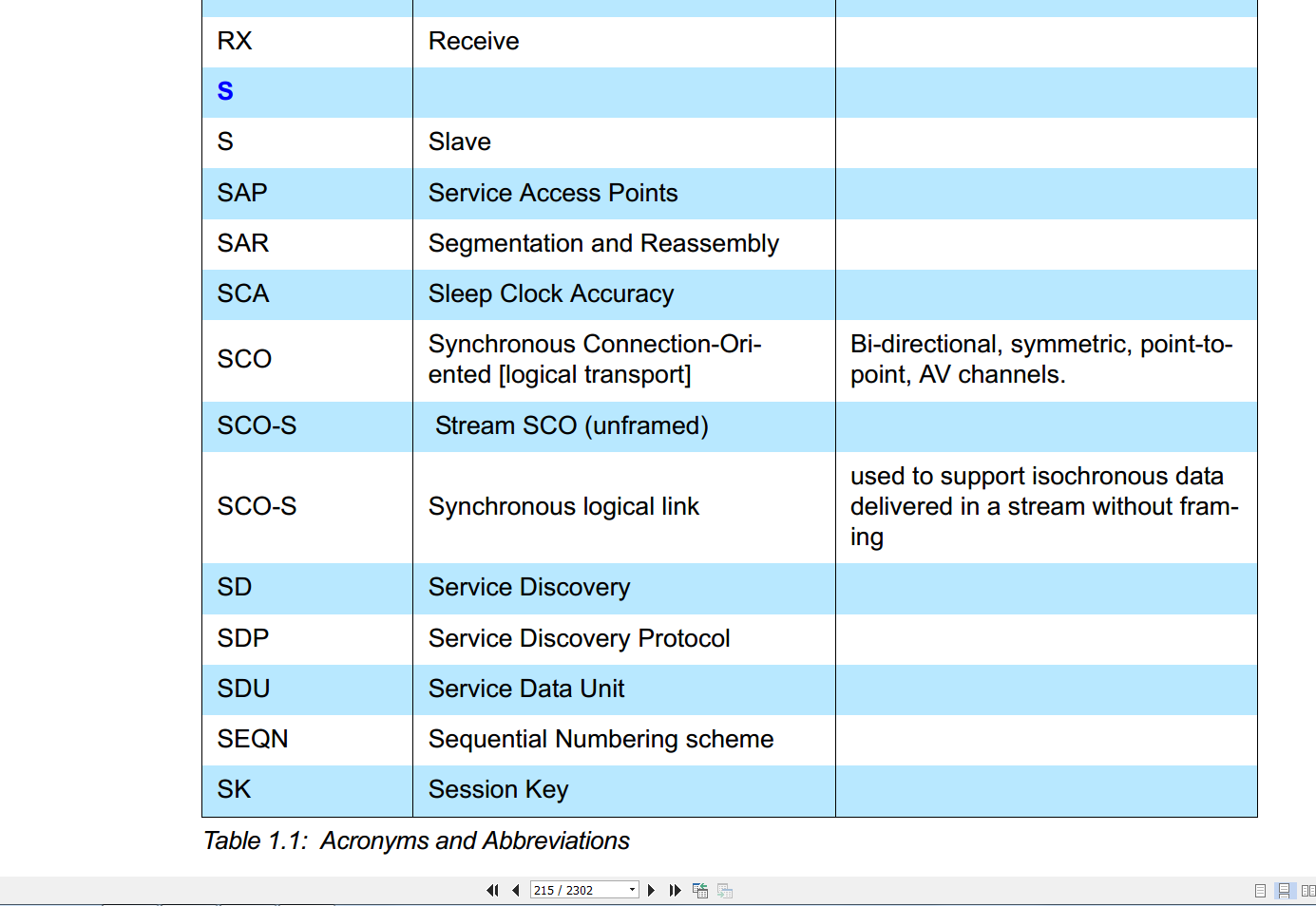
| ptt Q QoS R RAND RF RFC RFCMode RFCOMM RFU RMS RSSI RX S S SAP SAR SCA SCO SCO-S SCO-S SD SDP SDU SEQN SK | Packet Type Table Quality of Service Random number Radio Frequency Request For Comments Retransmission and Flow Control Mode Reserved for Future Use Root Mean Square Received Signal Strength Indica tion Receive Slave Service Access Points Segmentation and Reassembly Sleep Clock Accuracy Synchronous Connection-Ori ented [logical transport] Stream SCO (unframed) Synchronous logical link Service Discovery Service Discovery Protocol Service Data Unit Sequential Numbering scheme Session Key | The ptt parameter is used to select the logical transport types via LMP. Serial cable emulation protocol based on ETSI TS 07.10 Bi-directional, symmetric, point-to point, AV channels. used to support isochronous data delivered in a stream without fram ing |
| SKDm SKDs SLR SM SMP SN SRES SRK SS SSI SSP SSR STK SW T TC TCI TCP/IP TCS TDD TDMA T_IFS TK TX U UAP | Session Key Diversifier (master) Session Key Diversifier (slave) Send Loudness Ring Security Manager Security Manager Protocol Sequence Number Signed Response Signature Resolving Key Supplementary Services Signal Strength Indication Secure Simple Pairing Sniff Subrating Short Term Key Software Test Control Test Control Interface Transport Control Protocol/Inter net Protocol Telephony Control protocol Specification Time-Division Duplex Time Division Multiple Access Time Inter Frame Space Temporary Key Transmit Upper Address Part | Master portion of the Session Key Diversifier Slave portion of the Session Key Diversifier Simplifies the pairing process and improves Bluetooth security. A mode that defines the anchor points at which the master trans mits to the slave. Test Control layer for the test inter face Time interval between consecutive packets on same channel index |
| UART UI UI ULAP USB UTF-8 UUID W WAP | Universal Asynchronous receiver Transmitter User Interface Unnumbered Information Upper and Lower Address Parts Universal Serial Bus 8-bit UCS/Unicode Transformation Format Universal Unique Identifier Wireless Application Protocol |

































 1964
1964

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








