无论是fork还是system()出子进程,如果父进程里在open某个文件后(包括socket fd:特别是port在子进程里被占用)没有设置FD_CLOSEEXEC标志,就会引起各种不可预料的问题;
注意,这里文件描述符包括了普通文件的fd,以及socket的fd,这些都需要注意,特别是socket的fd本身又包括了本机ip,端口号等信息资源,如果该socketfd被子进程继承并占用,或者未关闭,就会导致新的父进程重新启动时不能正常使用这些网络端口,严重的就是设备掉线。
还有下面文章所说的,如果子进程继承的时候这些fd就是打开的,本身就有越权的行为可能存在,操作它不该操作的东西。
参考如下文章,更明了。
最后用一下的代码进行设置,不要直接 fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
-------------------------------------------
int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD);
flags |= FD_CLOEXEC;
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, flags);
===========
子进程socket继承问题
昨天实习的时候遇到这样一个问题,抽象起来如下:
有一个进程A,它是一个全局监控进程,监控进程B。
进程B是一个局部监控进程,监控C,C是由B fork出来的子进程。
C向B汇报,B向A汇报。
因为进程A和其他进程在不同机器上,所以所有的操作都是通过json rpc的远程调用执行的。
假设B监听11111端口,A通过这个端口与其通信。
现在我手动kill B,理论上的现象应该11111端口此时无人监听,A发rpc call的时候会报一个异常,rpc连接会断掉。
实际的情况是A会在rpc call上阻塞,观察11111端口的情况没,发现被C监听了。
分析的结果如下:
Linux下socket也是文件描述符的一种,当B fork进程C的时候,C也会继承B的11111端口socket文件描述符,当B挂了的时候,C就会占领监听权。
所以现在的需求就是在fork的时候关闭B已经打开的文件描述符。
系统给出的解决方案是:close_on_exec。当父进程打开文件时,只需要应用程序设置FD_CLOSEXEC标志位,则当fork后exec其他程序的时候,内核自动会将其继承的父进程FD关闭。
因为我用的是python的subprocess模块fork的子进程,他有一个参数close_fds可以设为True或者False:
文档说明:If close_fds is true, all file descriptors except 0, 1 and 2 will be closed before the child process is executed. (Unix only). Or, on Windows, if close_fds is true then no handles will be inherited by the child process. Note that on Windows, you cannot set close_fds to true and also redirect the standard handles by setting stdin, stdout or stderr.
意义:
close_on_exec另外的一大意义就是安全。比如父进程打开了某些文件,父进程fork了子进程,但是子进程就会默认有这些文件的读取权限,但是很多时候我们并不想让子进程有这么多的权限。
试想一下这样的场景:在Webserver中,首先会使用root权限启动,以此打开root权限才能打开的端口、日志等文件。然后降权到普通用户,fork出一些worker进程,这些进程中再进行解析脚本、写日志、输出结果等进一步操作。
然而这里,就会发现隐含一个安全问题:子进程中既然继承了父进程的FD,那么子进程中运行的脚本只需要继续操作这些FD,就能够使用普通权限“越权”操作root用户才能操作的文件。
系统提供的close_on_exec就可以有效解决这个问题。
========================================
我们经常会碰到需要fork子进程的情况,而且子进程很可能会继续exec新的程序。这就不得不提到子进程中无用文件描述符的问题!
fork函数的使用本不是这里讨论的话题,但必须提一下的是:子进程以写时复制(COW,Copy-On-Write)方式获得父进程的数据空间、堆和栈副本,这其中也包括文件描述符。刚刚fork成功时,父子进程中相同的文件描述符指向系统文件表中的同一项(这也意味着他们共享同一文件偏移量)。
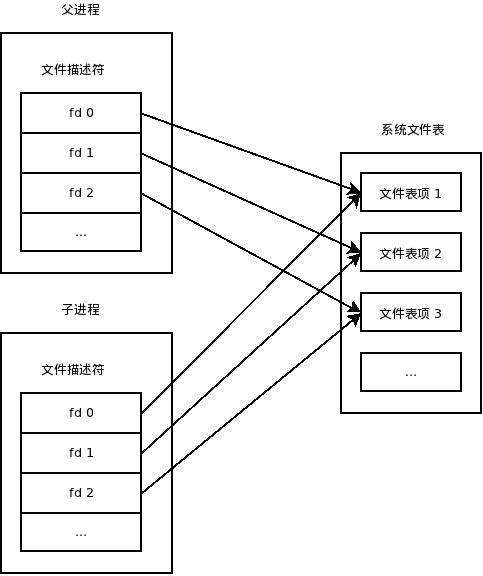
接着,一般我们会调用exec执行另一个程序,此时会用全新的程序替换子进程的正文,数据,堆和栈等。此时保存文件描述符的变量当然也不存在了,我们就无法关闭无用的文件描述符了。所以通常我们会fork子进程后在子进程中直接执行close关掉无用的文件描述符,然后再执行exec。
但是在复杂系统中,有时我们fork子进程时已经不知道打开了多少个文件描述符(包括socket句柄等),这此时进行逐一清理确实有很大难度。我们期望的是能在fork子进程前打开某个文件句柄时就指定好:“这个句柄我在fork子进程后执行exec时就关闭”。其实时有这样的方法的:即所谓的 close-on-exec。
close-on-exec的实现只需要调用系统的fcntl就能实现,很简单几句代码就能实现:
- int fd=open("foo.txt",O_RDONLY);
- int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD);
- flags |= FD_CLOEXEC;
- fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, flags);
这样,当fork子进程后,仍然可以使用fd。但执行exec后系统就会字段关闭子进程中的fd了。
-------------------------------------------------------- 分割线 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
最近好好看了一下open函数,其中flags参数可以传入O_CLOEXEC标记 [注意:linux 2.6.23才开始支持此标记]
这样就可以一步实现上面的提到的close-on-exec的效果。
===================================
分类: Linux
2013-07-21 21:28
758人阅读
收藏
举报
查看手册man socket
- NAME
- socket - create an endpoint for communication
-
- SYNOPSIS
- #include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
- #include <sys/socket.h>
-
- int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
NAME
socket - create an endpoint for communication
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
- Since Linux 2.6.27, the type argument serves a second purpose: in addition to specifying a socket type, it may include the bitwise OR of any of the follow‐
- ing values, to modify the behavior of socket():
-
- SOCK_NONBLOCK Set the O_NONBLOCK file status flag on the new open file description. Using this flag saves extra calls to fcntl(2) to achieve the same
- result.
-
- SOCK_CLOEXEC Set the close-on-exec (FD_CLOEXEC) flag on the new file descriptor. See the description of the O_CLOEXEC flag in open(2) for reasons why
- this may be useful.
Since Linux 2.6.27, the type argument serves a second purpose: in addition to specifying a socket type, it may include the bitwise OR of any of the follow‐
ing values, to modify the behavior of socket():
SOCK_NONBLOCK Set the O_NONBLOCK file status flag on the new open file description. Using this flag saves extra calls to fcntl(2) to achieve the same
result.
SOCK_CLOEXEC Set the close-on-exec (FD_CLOEXEC) flag on the new file descriptor. See the description of the O_CLOEXEC flag in open(2) for reasons why
this may be useful.
在创建socket的时候在type字段或上SOCK_CLOEXEC
socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0);






















 1038
1038











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








