Linux2.6.32下SPI驱动的移植如下图所示:
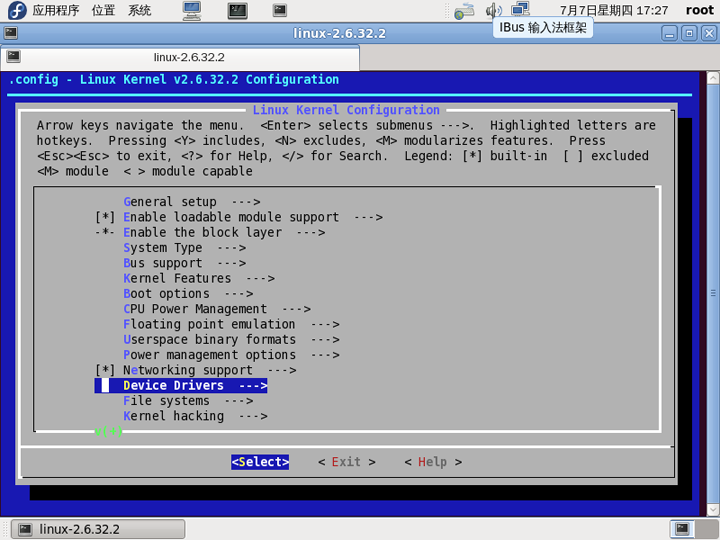
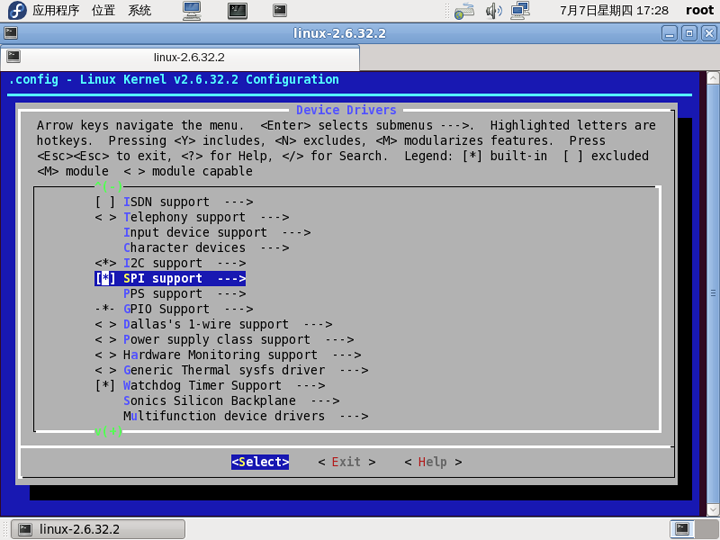
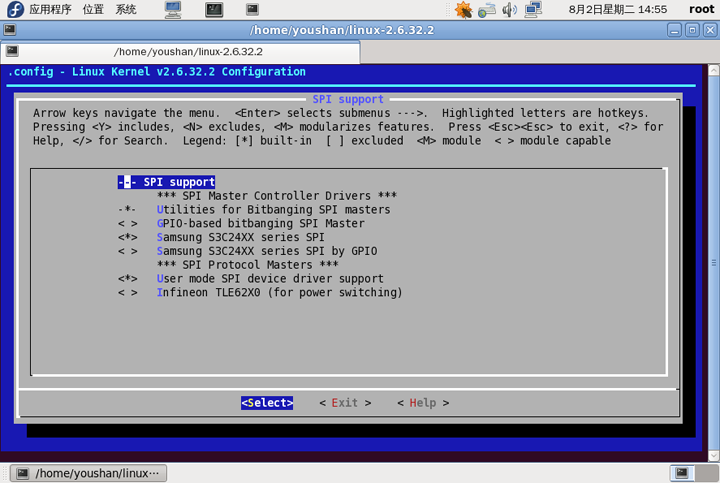
下面需要修改部分内核代码,具体操作如下:
1. 修改arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-mini2440.c文件
在include头文件代码行之后增加如下代码
//spi add by shiguang
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <mach/spi.h>
static struct spi_board_info s3c2410_spi0_board[] = {
[0] = {
.modalias = "spidev",
.bus_num = 0,
.chip_select = 0,
.irq = IRQ_EINT9,
.max_speed_hz = 500*1000,
},
};
static struct s3c2410_spi_info s3c2410_spi0_platdata = {
.pin_cs = S3C2410_GPG(2),
.num_cs = 1,
.bus_num = 0,
};
//end add spi
modalias的名字一定要是spidev,这一点要注意.
然后在函数__initmini2440_machine_init的开头增加下列代码
//spi add by shiguang
s3c_device_spi0.dev.platform_data=&s3c2410_spi0_platdata;
spi_register_board_info(s3c2410_spi0_board,ARRAY_SIZE(s3c2410_spi0_board));
//end spi
在mini2440_devices数组的最后中添加
&s3c_device_spi0,// add by shiguang
2.修改drivers/spi/spi_s3c24xx.c文件
在文件开头增加下列代码
//add by shiguang
#include <mach/regs-gpio.h>
在s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup函数结尾增加下列代码
// add by shiguang
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(hw->pdata->pin_cs,S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT);
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(0x8B, S3C2410_GPIO_SFN2);
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(0x8C, S3C2410_GPIO_SFN2);
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(0x8D, S3C2410_GPIO_SFN2);
// end add
3. 最后重新编译内核
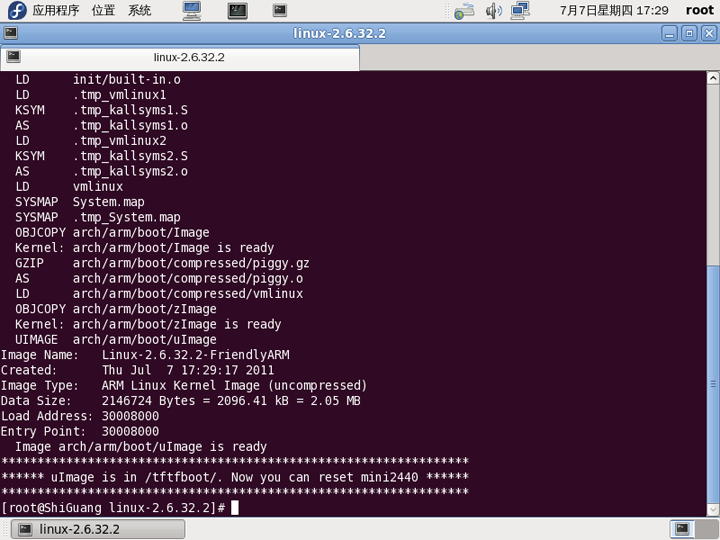
重启mini2440,查看/dev下的设备文件
[root@ShiGuang /]# ls /dev/spidev0.0 -l
crw-rw---- 1 root root 153, 0 Jan 1 08:00 /dev/spidev0.0
[root@ShiGuang /]#
4. 应用程序测试
- /*
- * SPI testing utility (using spidev driver)
- *
- * Copyright (c) 2007 MontaVista Software, Inc.
- * Copyright (c) 2007 Anton Vorontsov <avorontsov@ru.mvista.com>
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License.
- *
- * Cross-compile with cross-gcc -I/path/to/cross-kernel/include
- */
- #include <stdint.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <getopt.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <sys/ioctl.h>
- #include <linux/types.h>
- #include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
- #define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof((a)[0]))
- static void pabort(const char *s)
- {
- perror(s);
- abort();
- }
- static const char *device = "/dev/spidev1.1";
- static uint8_t mode;
- static uint8_t bits = 8;
- static uint32_t speed = 500000;
- static uint16_t delay;
- static void transfer(int fd)
- {
- int ret;
- uint8_t tx[] = {
- 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
- 0x40, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x95,
- 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
- 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
- 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF,
- 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xBA, 0xAD,
- 0xF0, 0x0D,
- };
- uint8_t rx[ARRAY_SIZE(tx)] = {0, };
- struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
- .tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
- .rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
- .len = ARRAY_SIZE(tx),
- .delay_usecs = delay,
- .speed_hz = speed,
- .bits_per_word = bits,
- };
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
- if (ret == 1)
- pabort("can't send spi message");
- for (ret = 0; ret < ARRAY_SIZE(tx); ret++) {
- if (!(ret % 6))
- puts("");
- printf("%.2X ", rx[ret]);
- }
- puts("");
- }
- static void print_usage(const char *prog)
- {
- printf("Usage: %s [-DsbdlHOLC3]\n", prog);
- puts(" -D --device device to use (default /dev/spidev1.1)\n"
- " -s --speed max speed (Hz)\n"
- " -d --delay delay (usec)\n"
- " -b --bpw bits per word \n"
- " -l --loop loopback\n"
- " -H --cpha clock phase\n"
- " -O --cpol clock polarity\n"
- " -L --lsb least significant bit first\n"
- " -C --cs-high chip select active high\n"
- " -3 --3wire SI/SO signals shared\n");
- exit(1);
- }
- static void parse_opts(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- while (1) {
- static const struct option lopts[] = {
- { "device", 1, 0, 'D' },
- { "speed", 1, 0, 's' },
- { "delay", 1, 0, 'd' },
- { "bpw", 1, 0, 'b' },
- { "loop", 0, 0, 'l' },
- { "cpha", 0, 0, 'H' },
- { "cpol", 0, 0, 'O' },
- { "lsb", 0, 0, 'L' },
- { "cs-high", 0, 0, 'C' },
- { "3wire", 0, 0, '3' },
- { "no-cs", 0, 0, 'N' },
- { "ready", 0, 0, 'R' },
- { NULL, 0, 0, 0 },
- };
- int c;
- c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "D:s:d:b:lHOLC3NR", lopts, NULL);
- if (c == -1)
- break;
- switch (c) {
- case 'D':
- device = optarg;
- break;
- case 's':
- speed = atoi(optarg);
- break;
- case 'd':
- delay = atoi(optarg);
- break;
- case 'b':
- bits = atoi(optarg);
- break;
- case 'l':
- mode |= SPI_LOOP;
- break;
- case 'H':
- mode |= SPI_CPHA;
- break;
- case 'O':
- mode |= SPI_CPOL;
- break;
- case 'L':
- mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
- break;
- case 'C':
- mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
- break;
- case '3':
- mode |= SPI_3WIRE;
- break;
- case 'N':
- mode |= SPI_NO_CS;
- break;
- case 'R':
- mode |= SPI_READY;
- break;
- default:
- print_usage(argv[0]);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int ret = 0;
- int fd;
- parse_opts(argc, argv);
- fd = open(device, O_RDWR);
- if (fd < 0)
- pabort("can't open device");
- /*
- * spi mode
- */
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE, &mode);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't set spi mode");
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MODE, &mode);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't get spi mode");
- /*
- * bits per word
- */
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't set bits per word");
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't get bits per word");
- /*
- * max speed hz
- */
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't set max speed hz");
- ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
- if (ret == -1)
- pabort("can't get max speed hz");
- printf("spi mode: %d\n", mode);
- printf("bits per word: %d\n", bits);
- printf("max speed: %d Hz (%d KHz)\n", speed, speed/1000);
- transfer(fd);
- close(fd);
- return ret;
- }
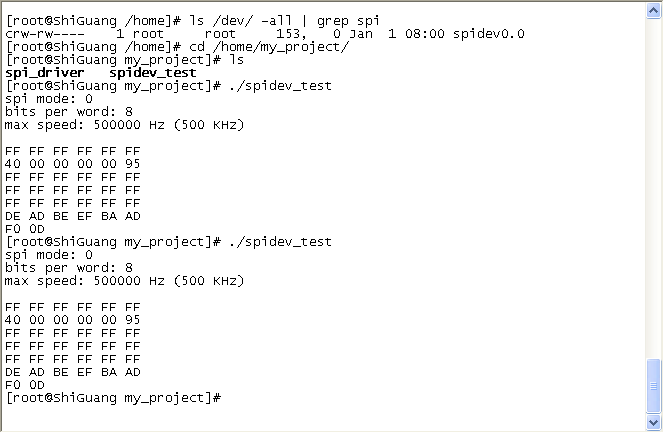
 测试完毕!OVER!
测试完毕!OVER!






















 2184
2184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








