Regionals 2015 >> Asia - Tehran >> 7530 - Cafebazaar
题目链接:7530
题目大意:一个公司有n个开发者,有m个APP可开发。其中一些开发者必选,一些APP必选。已知每个开发者开发每个APP的收益,求最大收益。(每个开发者最多开发一个APP,每个APP最多一个人开发)
题目思路:
解法一:二分图最佳匹配(KM算法)
增加一些虚开发者和虚app,非必要app可以被虚开发者开发,收益为0,反过来非必要开发者可以开发虚app,收益为0。然后虚开发者也可以开发虚app,收益为0,这样的设定可以使得km的构图条件能满足。
注意:必要的开发者和其对应不可开发的app直接设置为一个负的INF2值,使得他们之间有边可走但是如果真的要选择这条边最后答案得出来肯定是负数。也就是不存在可行方案。同理必要的app和其对应不可的开发者
权值的设置:
if (存在一个重要的app)边权值加INF
if (存在一个重要的开发者)边权值加INF
//最多可加两个INF
然后套用模板即可。
以下是代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define MOD 1000000000
const int N = 105;
const ll INF = 100000000000000LL;
const ll INF2 = 1000000000000LL;
int nx,ny;//两边的点数 nx,第一队的个数,ny,第二队的个数。注意 nx <= ny,否则会死循环。
ll g[N][N];//二分图描述 g[i][j],i属于第一队,j属于第二队。
ll linker[N],lx[N],ly[N];//y中各点匹配状态,x,y中的点标号
ll slack[N];
bool visx[N],visy[N];
bool DFS(int x)
{
visx[x] = true;
for(int y = 0; y < ny; y++)
{
if(visy[y])continue;
ll tmp = lx[x] + ly[y] - g[x][y];
if(tmp == 0)
{
visy[y] = true;
if(linker[y] == -1 || DFS(linker[y]))
{
linker[y] = x;
return true;
}
}
else if(slack[y] > tmp)
slack[y] = tmp;
}
return false;
}
ll KM()
{
memset(linker,-1,sizeof(linker));
memset(ly,0,sizeof(ly));
for(int i = 0;i < nx;i++)
{
lx[i] = -INF;
for(int j = 0;j < ny;j++)
if(g[i][j] > lx[i])
lx[i] = g[i][j];
}
for(int x = 0;x < nx;x++)
{
for(int i = 0;i < ny;i++)
slack[i] = INF;
while(true)
{
memset(visx,false,sizeof(visx));
memset(visy,false,sizeof(visy));
if(DFS(x))break;
ll d = INF;
for(int i = 0;i < ny;i++)
if(!visy[i] && d > slack[i])
d = slack[i];
for(int i = 0;i < nx;i++)
if(visx[i])
lx[i] -= d;
for(int i = 0;i < ny;i++)
{
if(visy[i])ly[i] += d;
else slack[i] -= d;
}
}
}
ll res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < ny;i++)
if(linker[i] != -1)
res += g[linker[i]][i];
return res;
}
int imp[105];
int imb[105];
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(cin >> n >> m)
{
if(n == 0 && m == 0) break;
memset(imp,0,sizeof(imp));
memset(imb,0,sizeof(imb));
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
nx = ny = max(n,m);
int t,x,a,b;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> x;
imp[x-1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
g[x-1][i] = -INF2;
/*不能设置为INF,因为设置为INF就是没有点相连,
但是设置为INF2(小于INF)表示这条边可以连,如果你一定要连,连出来是负值,则无答案*/
}
}
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> x;
imb[x-1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
g[i][x-1] = -INF2;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> a >> b;
g[i][a - 1] = b;
if (imp[i]) g[i][a - 1] += MOD;
if (imb[a - 1]) g[i][a - 1] += MOD;
}
}
ll ans = KM();
if (ans < 0) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ans % MOD << endl;
}
}
/*
2 4
1 1
1 3
2 1 8 2 10
3 2 2 3 10 4 50
4 3
3 1 2 4
2 1 3
1 1 200
2 2 700 3 200
2 2 300 3 100
1 1 500
*/解法二:最大费用可行流
理论:
概念区分:
最小费用最大流:首先保证流量最大,其次费用最小
最小费用可行流:保证费用最小
做法区别:
最小费用最大流:不断找最短路进行增广,直到找不到增广路。
最小费用可行流:不断找最短路进行增广,直到找到的最短路长度为正或找不到。
根据题意可知,这道题要用 最小费用可行流 解,而不是最小费用最大流
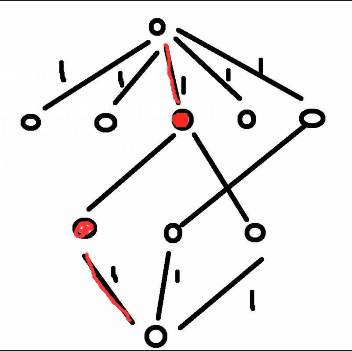
虚设一个起点和终点,如图所示,容量都为1,如果存在必做的app或开发者,这条边权值设置为INF。
建图:
* 从S向所有开发者连边,容量是1,如果是关键开发者边权是+INF,否则是0。
* 开发者向能开发的APP连边,容量是1,边权是开发报酬
* APP向汇点连边,容量是1,如果是关键APP边权是+INF,否则是0
然后套用最小费用流模板,因为求最大费用,存值是边权都为负数即可。
以下是代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef long long flow_t;
typedef long long cost_t;
const int MAXN = 10000;
const int MAXM = 100000;
const flow_t INF = 1e9;
const flow_t inf = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int from, to, nx;
flow_t cap, flow;
cost_t cost;
Edge() {}
Edge(int _from, int _to, int _nx, flow_t _cap, cost_t _cost):
from(_from), to(_to), nx(_nx), cap(_cap), flow(0), cost(_cost) {}
} E[MAXM];
cost_t dis[MAXN];
int G[MAXN], pre[MAXN], vis[MAXN];
int sz, N; //S源点, T汇点
void init(int n)
{
memset(G, -1, sizeof(G[0]) * n);
sz = 0; N = n;
}
void addedge(int u, int v, flow_t f, cost_t c) //u -> v
{
E[sz] = Edge(u, v, G[u], f, +c); G[u] = sz++;
E[sz] = Edge(v, u, G[v], 0, -c); G[v] = sz++;
}
bool extand(int S, int T)
{
std::queue<int> Q;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis[0]) * N);
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre[0]) * N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) dis[i] = inf;
Q.push(S); vis[S] = 1; dis[S] = 0;
while (!Q.empty()) {
int u = Q.front();
Q.pop(); vis[u]=0;
for (int it = G[u]; ~it; it = E[it].nx)
{
int v = E[it].to;
if (E[it].cap > E[it].flow && dis[v] > dis[u] + E[it].cost)
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + E[it].cost, pre[v] = it;
if (!vis[v]) Q.push(v), vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
return dis[T] <= 0; // 改成dis[T] <= 0 求可行流,改成dis[T] < inf 求最小费用最大流
}
std::pair<flow_t, cost_t> solve(int S, int T)
{
flow_t MaxFlow = 0;
cost_t MinCost = 0;
while (extand(S, T))
{
flow_t aug = inf;
for (int it = pre[T]; ~it; it = pre[E[it].from])
{
aug = std::min(aug, E[it].cap - E[it].flow);
}
MinCost += aug * dis[T], MaxFlow += aug;
for (int it = pre[T]; ~it; it = pre[E[it].from])
{
E[it].flow += aug, E[it ^ 1].flow -= aug;
}
}
return std::make_pair(MaxFlow, MinCost);
}
int imp[1005];
int imb[1005];
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(cin >> n >> m)
{
if(n == 0 && m == 0) break;
memset(imp,0,sizeof(imp));
memset(imb,0,sizeof(imb));
init(n + m + 2);
//0为虚拟起点
int t1,t2,t,x,a,b;
cin >> t;
t1 = t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> x;
imp[x] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!imp[i]) addedge(0,i,1,0);
else addedge(0,i,1,-INF);
}
cin >> t;
t2 = t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> x;
imb[x + n] = 1;
}
for (int i = n + 1; i < n + m + 1; i++)
{
if (!imb[i]) addedge(i,n + m + 1,1,0);
else addedge(i,n + m + 1,1,-INF);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> a >> b;
addedge(i,a + n,1,-b);
}
}
pair<flow_t, cost_t> ans = solve(0,1 + n + m);
long long tmp = (t1 + t2) * INF * -1;
if (ans.second > tmp) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << (ans.second * -1) % INF << endl;
}
return 0;
}

























 1572
1572

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








