v8世界探险(3) - v8的抽象语法树结构
AST的结构
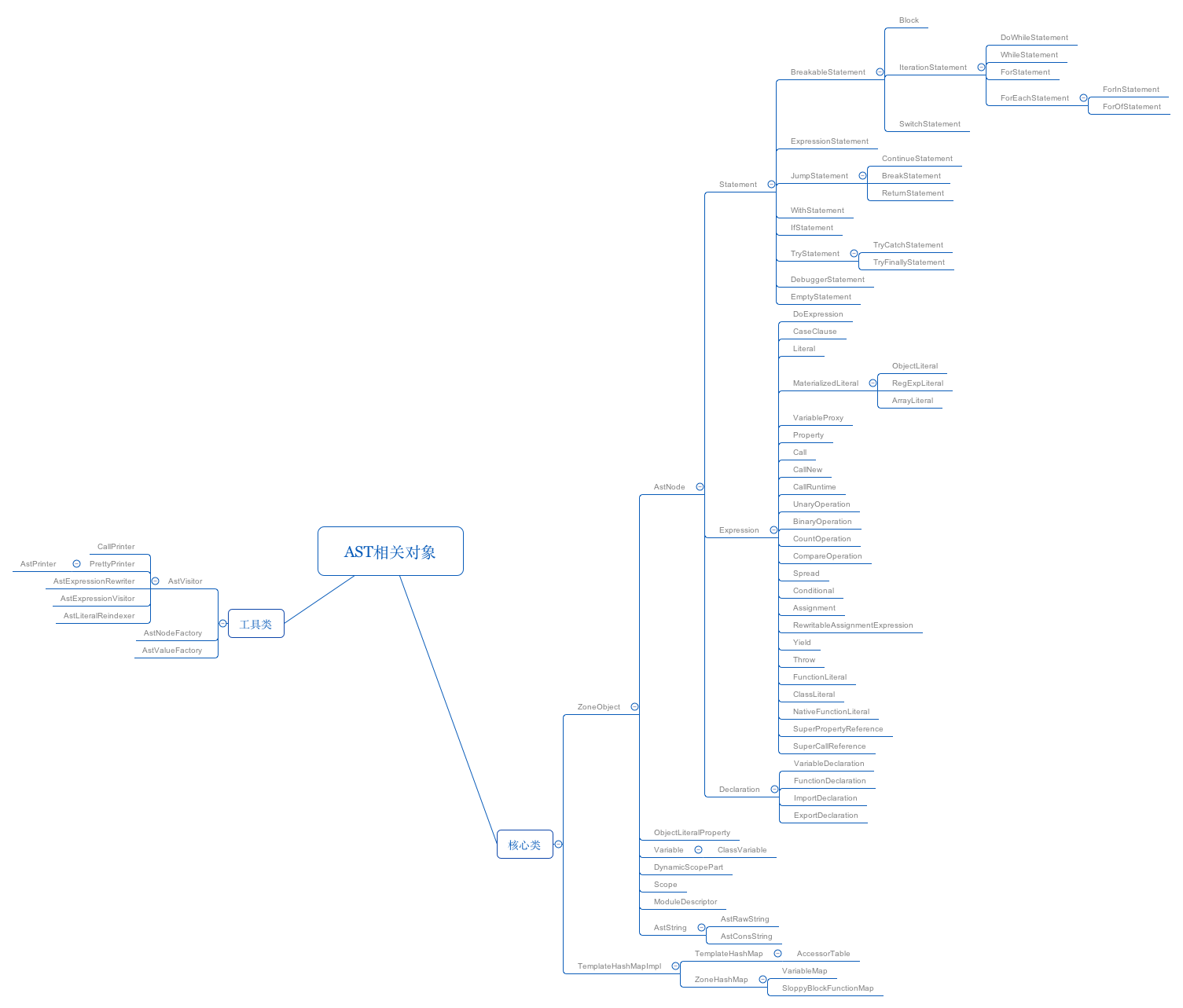
首先,我们还是先来看一下地图:
基于Zone的内存分配
AST对象都是基于Zone进行内存管理的,Zone是多次分配临时块对象,然后可以一次性释放掉。
我们看一下Zone的定义,在src/zone.h中:
// The Zone supports very fast allocation of small chunks of
// memory. The chunks cannot be deallocated individually, but instead
// the Zone supports deallocating all chunks in one fast
// operation. The Zone is used to hold temporary data structures like
// the abstract syntax tree, which is deallocated after compilation.
//
// Note: There is no need to initialize the Zone; the first time an
// allocation is attempted, a segment of memory will be requested
// through a call to malloc().
//
// Note: The implementation is inherently not thread safe. Do not use
// from multi-threaded code.
class Zone final {
public:
Zone();
~Zone();
// Allocate 'size' bytes of memory in the Zone; expands the Zone by
// allocating new segments of memory on demand using malloc().
void* New(size_t size);
template <typename T>
T* NewArray(size_t length) {
DCHECK_LT(length, std::numeric_limits<size_t>::max() / sizeof(T));
return static_cast<T*>(New(length * sizeof(T)));
}
// Deletes all objects and free all memory allocated in the Zone. Keeps one
// small (size <= kMaximumKeptSegmentSize) segment around if it finds one.
void DeleteAll();
// Deletes the last small segment kept around by DeleteAll(). You
// may no longer allocate in the Zone after a call to this method.
void DeleteKeptSegment();
// Returns true if more memory has been allocated in zones than
// the limit allows.
bool excess_allocation() const {
return segment_bytes_allocated_ > kExcessLimit;
}
size_t allocation_size() const { return allocation_size_; }
private:
// All pointers returned from New() have this alignment. In addition, if the
// object being allocated has a size that is divisible by 8 then its alignment
// will be 8. ASan requires 8-byte alignment.
#ifdef V8_USE_ADDRESS_SANITIZER
static const size_t kAlignment = 8;
STATIC_ASSERT(kPointerSize <= 8);
#else
static const size_t kAlignment = kPointerSize;
#endif
// Never allocate segments smaller than this size in bytes.
static const size_t kMinimumSegmentSize = 8 * KB;
// Never allocate segments larger than this size in bytes.
static const size_t kMaximumSegmentSize = 1 * MB;
// Never keep segments larger than this size in bytes around.
static const size_t kMaximumKeptSegmentSize = 64 * KB;
// Report zone excess when allocation exceeds this limit.
static const size_t kExcessLimit = 256 * MB;
// The number of bytes allocated in this zone so far.
size_t allocation_size_;
// The number of bytes allocated in segments. Note that this number
// includes memory allocated from the OS but not yet allocated from
// the zone.
size_t segment_bytes_allocated_;
// Expand the Zone to hold at least 'size' more bytes and allocate
// the bytes. Returns the address of the newly allocated chunk of
// memory in the Zone. Should only be called if there isn't enough
// room in the Zone already.
Address NewExpand(size_t size);
// Creates a new segment, sets it size, and pushes it to the front
// of the segment chain. Returns the new segment.
inline Segment* NewSegment(size_t size);
// Deletes the given segment. Does not touch the segment chain.
inline void DeleteSegment(Segment* segment, size_t size);
// The free region in the current (front) segment is represented as
// the half-open interval [position, limit). The 'position' variable
// is guaranteed to be aligned as dictated by kAlignment.
Address position_;
Address limit_;
Segment* segment_head_;
};ZoneObject
基于Zone分配,v8封装了ZoneObject来作为AST对象的基类。
// ZoneObject is an abstraction that helps define classes of objects
// allocated in the Zone. Use it as a base class; see ast.h.
class ZoneObject {
public:
// Allocate a new ZoneObject of 'size' bytes in the Zone.
void* operator new(size_t size, Zone* zone) { return zone->New(size); }
// Ideally, the delete operator should be private instead of
// public, but unfortunately the compiler sometimes synthesizes
// (unused) destructors for classes derived from ZoneObject, which
// require the operator to be visible. MSVC requires the delete
// operator to be public.
// ZoneObjects should never be deleted individually; use
// Zone::DeleteAll() to delete all zone objects in one go.
void operator delete(void*, size_t) { UNREACHABLE(); }
void operator delete(void* pointer, Zone* zone) { UNREACHABLE(); }
};AstNode
AstNode继承自ZoneObject,是所有的语句、表达式和声明的基类。
class AstNode: public ZoneObject {
public:
#define DECLARE_TYPE_ENUM(type) k##type,
enum NodeType {
AST_NODE_LIST(DECLARE_TYPE_ENUM)
kInvalid = -1
};
#undef DECLARE_TYPE_ENUM
void* operator new(size_t size, Zone* zone) { return zone->New(size); }
explicit AstNode(int position): position_(position) {}
virtual ~AstNode() {}
virtual void Accept(AstVisitor* v) = 0;
virtual NodeType node_type() const = 0;
int position() const { return position_; }
// Type testing & conversion functions overridden by concrete subclasses.
#define DECLARE_NODE_FUNCTIONS(type) \
bool Is##type() const { return node_type() == AstNode::k##type; } \
type* As##type() { \
return Is##type() ? reinterpret_cast<type*>(this) : NULL; \
} \
const type* As##type() const { \
return Is##type() ? reinterpret_cast<const type*>(this) : NULL; \
}
AST_NODE_LIST(DECLARE_NODE_FUNCTIONS)
#undef DECLARE_NODE_FUNCTIONS
virtual BreakableStatement* AsBreakableStatement() { return NULL; }
virtual IterationStatement* AsIterationStatement() { return NULL; }
virtual MaterializedLiteral* AsMaterializedLiteral() { return NULL; }
// The interface for feedback slots, with default no-op implementations for
// node types which don't actually have this. Note that this is conceptually
// not really nice, but multiple inheritance would introduce yet another
// vtable entry per node, something we don't want for space reasons.
virtual void AssignFeedbackVectorSlots(Isolate* isolate,
FeedbackVectorSpec* spec,
FeedbackVectorSlotCache* cache) {}
private:
// Hidden to prevent accidental usage. It would have to load the
// current zone from the TLS.
void* operator new(size_t size);
friend class CaseClause; // Generates AST IDs.
int position_;
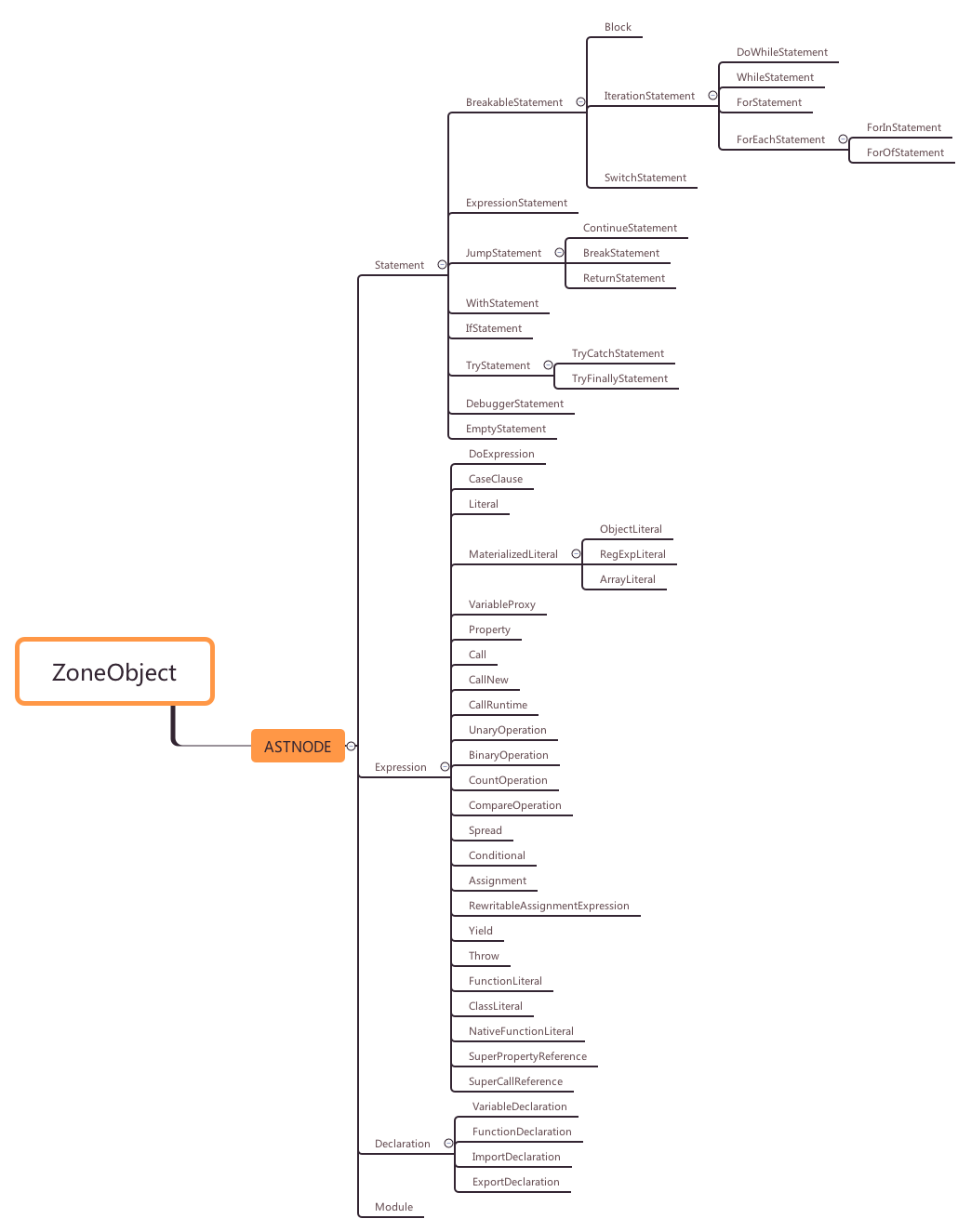
};AstNode的子类有4个大类:
* Statement: 语句
* Expression: 表达式
* Declaration: 声明
* Module: ES6新增的模块
我们来一张AstNode的图,大家加深一下印象:
声明
Declaration是AstNode4大类中最简单的,它只有四个直接子类:
* VariableDeclaration: 变量声明
* FunctionDeclaration: 函数声明
* ImportDeclaration: 引用其它模块声明
* ExportDeclaration: 导出声明
class Declaration : public AstNode {
public:
VariableProxy* proxy() const { return proxy_; }
VariableMode mode() const { return mode_; }
Scope* scope() const { return scope_; }
virtual InitializationFlag initialization() const = 0;
virtual bool IsInlineable() const;
protected:
Declaration(Zone* zone, VariableProxy* proxy, VariableMode mode, Scope* scope,
int pos)
: AstNode(pos), mode_(mode), proxy_(proxy), scope_(scope) {
DCHECK(IsDeclaredVariableMode(mode));
}
private:
VariableMode mode_;
VariableProxy* proxy_;
// Nested scope from which the declaration originated.
Scope* scope_;
};变量声明
class VariableDeclaration final : public Declaration {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(VariableDeclaration)
InitializationFlag initialization() const override {
return mode() == VAR ? kCreatedInitialized : kNeedsInitialization;
}
bool is_class_declaration() const { return is_class_declaration_; }
...
int declaration_group_start() const { return declaration_group_start_; }
protected:
VariableDeclaration(Zone* zone, VariableProxy* proxy, VariableMode mode,
Scope* scope, int pos, bool is_class_declaration = false,
int declaration_group_start = -1)
: Declaration(zone, proxy, mode, scope, pos),
is_class_declaration_(is_class_declaration),
declaration_group_start_(declaration_group_start) {}
bool is_class_declaration_;
int declaration_group_start_;
};函数声明
函数声明的最主要结构就是有一个FunctionLiteral函数文本的指针。
class FunctionDeclaration final : public Declaration {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(FunctionDeclaration)
FunctionLiteral* fun() const { return fun_; }
void set_fun(FunctionLiteral* f) { fun_ = f; }
InitializationFlag initialization() const override {
return kCreatedInitialized;
}
bool IsInlineable() const override;
protected:
FunctionDeclaration(Zone* zone,
VariableProxy* proxy,
VariableMode mode,
FunctionLiteral* fun,
Scope* scope,
int pos)
: Declaration(zone, proxy, mode, scope, pos),
fun_(fun) {
DCHECK(mode == VAR || mode == LET || mode == CONST);
DCHECK(fun != NULL);
}
private:
FunctionLiteral* fun_;
};引用模块声明
引用的模块名,保存在两个AstRawString指针中。
class ImportDeclaration final : public Declaration {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(ImportDeclaration)
const AstRawString* import_name() const { return import_name_; }
const AstRawString* module_specifier() const { return module_specifier_; }
void set_module_specifier(const AstRawString* module_specifier) {
DCHECK(module_specifier_ == NULL);
module_specifier_ = module_specifier;
}
InitializationFlag initialization() const override {
return kNeedsInitialization;
}
protected:
ImportDeclaration(Zone* zone, VariableProxy* proxy,
const AstRawString* import_name,
const AstRawString* module_specifier, Scope* scope, int pos)
: Declaration(zone, proxy, IMPORT, scope, pos),
import_name_(import_name),
module_specifier_(module_specifier) {}
private:
const AstRawString* import_name_;
const AstRawString* module_specifier_;
};导出声明
导出声明是ES6引入的Module的功能,可以导出变量,也可以导出函数,例:
//导出常量
export const sqrt = Math.sqrt;
//导出函数
export function square(x) {
return x * x;
}导出声明的类定义如下:
class ExportDeclaration final : public Declaration {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(ExportDeclaration)
InitializationFlag initialization() const override {
return kCreatedInitialized;
}
protected:
ExportDeclaration(Zone* zone, VariableProxy* proxy, Scope* scope, int pos)
: Declaration(zone, proxy, LET, scope, pos) {}
};这其中通过一个宏DECLARE_NODE_TYPE来输出导出的类型. 不禁让人联想起了MFC中著名的DECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP宏,不知道v8这部分的作者是不是有MFC的经历,哈哈
#define DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(type) \
void Accept(AstVisitor* v) override; \
AstNode::NodeType node_type() const final { return AstNode::k##type; } \
friend class AstNodeFactory;Statement
Statement表示语句。毕竟JavaScript还是语句式为主的,表达式是为语句服务的,所以Statement对应了js程序的每一个基本执行元素。
class Statement : public AstNode {
public:
explicit Statement(Zone* zone, int position) : AstNode(position) {}
bool IsEmpty() { return AsEmptyStatement() != NULL; }
virtual bool IsJump() const { return false; }
virtual void MarkTail() {}
};语句有对于流程的控制,所以定义了IsJump和MarkTail两个函数。
IsJump用于控制是否是跳转型的指令。JumpStatement就是专为跳转而生的,所以JumpStatement的定义就一条有用的,IsJump返回true:
class JumpStatement : public Statement {
public:
bool IsJump() const final { return true; }
protected:
explicit JumpStatement(Zone* zone, int pos) : Statement(zone, pos) {}
};MarkTail是用来标识语句结束的,比如我们看看Block的MarkTail的实现:
void MarkTail() override {
if (!statements_.is_empty()) statements_.last()->MarkTail();
}如果语句列表不为空,那么语句列表中最后一条就标识为尾巴。
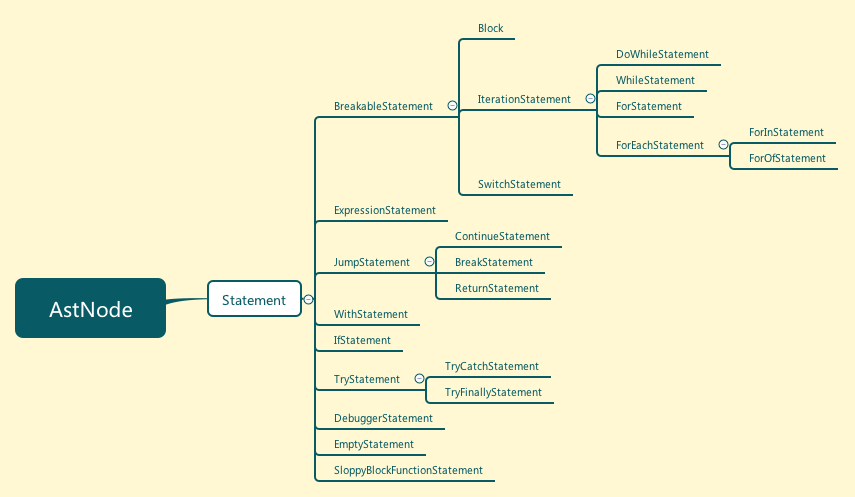
语句的定义很简单,下面的子类却不少:
* BreakableStatement: 所有流程中可以退出和跳转的语句
* Block:块语句当然是BreakableStatement,一个块也是流程的控制结构
* IterationStatement: 循环语句是可中断的啊,有两种中断方法:break和continue
* DoWhileStatement: do while循环语句
* WhileStatement: while循环语句
* ForStatement: for循环语句
* ForEachStatement: for each型循环,适用于集合遍历的循环形式
* ForInStatement: for in循环语句
* ForOfStatement: ES6新增,使用迭代器的for of循环
* SwitchStatement: switch语句
* ExpressionStatement: 表达式语句,整条语句由一条表达式构成
* JumpStatement: 流程跳转型指令
* ContinueStatement: continue语句
* BreakStatement: break语句
* ReturnStatement: return语句
* WithStatement: with语句
* IfStatement: if语句
* TryStatement: try语句
* TryCatchStatement: try catch语句
* TryFinallyStatement: try finally语句
* DebuggerStatement: 调试用途,我暂时也不知道它是做什么的
* EmptyStatement: 空语句
* SloppyBlockFunctionStatement: ES2016 Annex B3.3定义的可被覆盖的其它语句的代理
我们也画一张图来加深一下对于Statement的印象:
IterationStatement
循环类语句的特点是要支持continue语句的落脚点,就是要记录,执行continue的时候该回到哪里。
break就不用考虑了,跳到结尾就好了么。
class IterationStatement : public BreakableStatement {
public:
// Type testing & conversion.
IterationStatement* AsIterationStatement() final { return this; }
Statement* body() const { return body_; }
void set_body(Statement* s) { body_ = s; }
static int num_ids() { return parent_num_ids() + 1; }
BailoutId OsrEntryId() const { return BailoutId(local_id(0)); }
virtual BailoutId ContinueId() const = 0;
virtual BailoutId StackCheckId() const = 0;
// Code generation
Label* continue_target() { return &continue_target_; }
protected:
IterationStatement(Zone* zone, ZoneList<const AstRawString*>* labels, int pos)
: BreakableStatement(zone, labels, TARGET_FOR_ANONYMOUS, pos),
body_(NULL) {}
static int parent_num_ids() { return BreakableStatement::num_ids(); }
void Initialize(Statement* body) { body_ = body; }
private:
int local_id(int n) const { return base_id() + parent_num_ids() + n; }
Statement* body_;
Label continue_target_;
};DoWhileStatement
DoWhileStatement比普通的IterationStatement多了一个while时的表达式。
class DoWhileStatement final : public IterationStatement {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(DoWhileStatement)
void Initialize(Expression* cond, Statement* body) {
IterationStatement::Initialize(body);
cond_ = cond;
}
Expression* cond() const { return cond_; }
void set_cond(Expression* e) { cond_ = e; }
static int num_ids() { return parent_num_ids() + 2; }
BailoutId ContinueId() const override { return BailoutId(local_id(0)); }
BailoutId StackCheckId() const override { return BackEdgeId(); }
BailoutId BackEdgeId() const { return BailoutId(local_id(1)); }
protected:
DoWhileStatement(Zone* zone, ZoneList<const AstRawString*>* labels, int pos)
: IterationStatement(zone, labels, pos), cond_(NULL) {}
static int parent_num_ids() { return IterationStatement::num_ids(); }
private:
int local_id(int n) const { return base_id() + parent_num_ids() + n; }
Expression* cond_;
};WhileStatement
WhileStatement对应了while循环,其实除了表达式的判断位置不同,它与DoWhileStatement的结构是基本一样的:
class WhileStatement final : public IterationStatement {
public:
DECLARE_NODE_TYPE(WhileStatement)
void Initialize(Expression* cond, Statement* body) {
IterationStatement::Initialize(body);
cond_ = cond;
}
Expression* cond() const { return cond_; }
void set_cond(Expression* e) { cond_ = e; }
static int num_ids() { return parent_num_ids() + 1; }
BailoutId ContinueId() const override { return EntryId(); }
BailoutId StackCheckId() const override { return BodyId(); }
BailoutId BodyId() const { return BailoutId(local_id(0)); }
protected:
WhileStatement(Zone* zone, ZoneList<const AstRawString*>* labels, int pos)
: IterationStatement(zone, labels, pos), cond_(NULL) {}
static int parent_num_ids() { return IterationStatement::num_ids(); }
private:
int local_id(int n) const { return base_id() + parent_num_ids() + n; }
Expression* cond_;
};ForStatement
前面大家已经被代码轰炸得差不多了,下面就不重复贴完整代码,只贴干货。
for循环的特点是有三个表达式,分别对应:初始条件,结束条件和下一个的处理三种操作,对应到代码中是这样的:
Statement* init_;
Expression* cond_;
Statement* next_;IfStatement
if语句有两个分支,所以有两个尾巴:
void MarkTail() override {
then_statement_->MarkTail();
else_statement_->MarkTail();
}if有一个条件判断,外加then和else两个执行块:
Expression* condition_;
Statement* then_statement_;
Statement* else_statement_;Expression
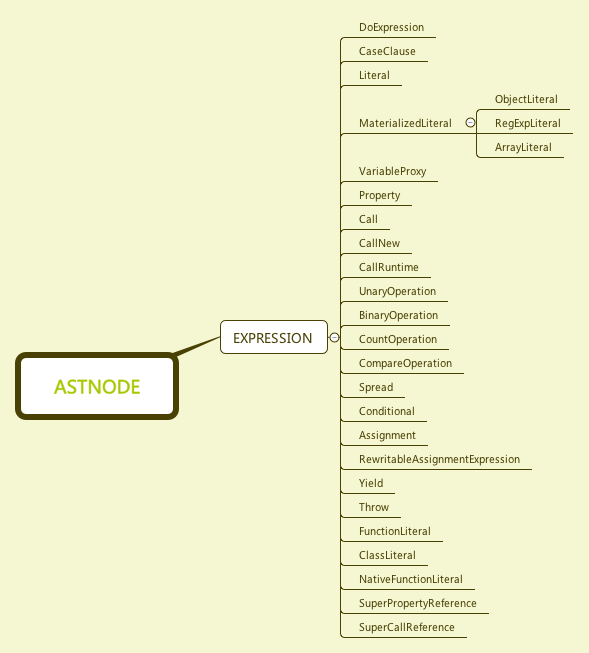
表达式解释一向都是语法分析的重点,后面我们再详细展开介绍,这里我们先看下表达式分类图:
表达式包括对于对象、类、函数、数组、正则表达式等字面量的表示,一元,二元,比较等运算等操作。
针对于字面和表达式,v8还提供了AstVisitor工具类集来帮助访问和修改。
其它
像变量、AstString等组件并不属于AstNode,而是直接从ZoneObject派生出来的。后面用到的时候我们再详细介绍。
小结
v8的语法分析,最终会生成一棵抽象语法树AST。这些声明、语句、表达式和模块都以AstNode的形式来保存。
AstNode和变量,AstString等对象都是基于Zone方式多次分配,一次性回收来进行内存管理的。
Statement是语句,主要对应分支、循环、跳转、异常处理等流程控制上的操作。
Expression是表达式,构成了语句的组成部分,相对比较复杂。








 本文深入剖析V8引擎中抽象语法树(AST)的结构,包括基于Zone的内存管理、核心节点类型如声明、语句及表达式,并探讨其如何支持JavaScript的执行。
本文深入剖析V8引擎中抽象语法树(AST)的结构,包括基于Zone的内存管理、核心节点类型如声明、语句及表达式,并探讨其如何支持JavaScript的执行。

















 796
796

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










