继之前做完
的题目之后,我又做了LeetCode上关于树的题目:https://leetcode.com/tag/tree/
在做的过程中有些题没有思路,于是便看了 Discuss 或者《Cracking the coding Interview》和算法导论等书籍,下面从 Easy ~ Hard 给出答案:
这里二叉树的结构是:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
Easy
Balanced Binary Tree
检查一个二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。平衡二叉树的定义是:任意一个节点的两个子树高度差不超过1。
根据定义,我们可以找出每个节点的左右子树的高度,再相减,大于1的话则不是平衡二叉树。我们在算高度的时候直接检查是否是平衡的,不是直接返回-1,是则返回这个树的高度。
public class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(checkHeight(root) == -1){
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
private int checkHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int l = checkHeight(root.left);
if(l == -1) return -1;
int r = checkHeight(root.right);
if(r == -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(l - r) > 1) return -1;
else return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}
}
Binary Tree Paths
打印所有根节点到叶子节点的路径
直接前序遍历,遇到叶子节点打印出来。
public class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) path(res, "", root);
return res;
}
private void path(List<String> res, String s, TreeNode root){
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) res.add(s + root.val);
if (root.left != null) path(res, s + root.val + "->", root.left);
if (root.right != null) path(res, s + root.val + "->", root.right);
}
}
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
二叉树层序遍历
思路:我们只需要遍历整棵树,在遍历的时候需要一个标志记住遍历到了第几层。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
getLevel(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
private void getLevel(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res, int level){
if(root == null) return;
List<Integer> list = null;
if(res.size() == level) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(list);
} else {
list = res.get(level);
}
list.add(root.val);
getLevel(root.left, res, level+1);
getLevel(root.right, res, level+1);
}
}
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
把二叉树的每一层的结点从下到上打印出来。
如给定二叉树:
返回:
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
create(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
private void create(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res, int level){
if(root == null) return;
List<Integer> list = null;
if(res.size() == level){
//该层不在链表中
list = new LinkedList<>();
res.add(0, list);
} else {
list = res.get(res.size() - level - 1);
}
list.add(root.val); //前序遍历
create(root.left, res, level + 1);
create(root.right, res, level + 1);
}
}
Symmetric Tree
判断一颗二叉树是否是镜像二叉树
public class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return helper(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean helper(TreeNode left, TreeNode right){
if(left == null || right == null) return left == right; // == 比较的是是否是同一个对象,这里只有left和right都是null的时候才会返回true
if(left.val != right.val) return false;
return helper(left.left, right.right) && helper(left.right, right.left);
}
}
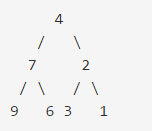
Invert Binary Tree
反转二叉树
如给定二叉树:
返回:
public class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return root;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
root.left = invertTree(right);
root.right = invertTree(left);
return root;
}
}
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
在一颗二叉查找树里面找两个结点的第一个公共祖先。
思路:这是一颗二叉查找树,可以利用它的性质:root.left.val <= root.val < root.right.val ,有下面三种情况:
- p.val <= root.val < q.val :则root就是第一个公共祖先
- p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val : 则去root.left子树里面找第一个公共祖先
- p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val : 则去root.right子树里面找第一个公共祖先
public class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while((root.val - p.val) * (root.val - q.val) > 0){
root = p.val < root.val? root.left: root.right;
}
return root;
}
}
Same Tree
判断两颗二叉树是否相等。
public class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null || q == null) return p == q;
if(p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
返回一颗二叉树的最小深度。
public class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
return (left == 0 || right == 0) ? left + right + 1: Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
}
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
返回一颗二叉树的最大深度。
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
Path Sum
给定一颗二叉树和一个值sum,判断这个值sum是否是由二叉树的某一个根节点到叶子节点的路径上结点的值的和(路径和)。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root != null && root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == root.val) return true;
else if(root == null) return false;
else {
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum-root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum-root.val);
}
}
}
Medium
Kth Smallest Element in a BST
返回一颗二叉查找树的第k小的元素
public class Solution {
int count = 0;
int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
traverse(root, k);
return val;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root, int k){
if(root == null) return;
traverse(root.left, k);
count++;
if(k == count) val = root.val;
traverse(root.right, k);
}
}
Count Complete Tree Nodes
计算完全二叉树的结点的个数
思路:利用完全二叉树的性质,深度为n的完全二叉树的,去掉第n层变为满二叉树。则完全二叉树的结点个数为n-1的满二叉树加上最下面一层的个数
public class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
else if(root.left == null) return 1;
int height = 0;
int sum = 0;
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur.left != null){
sum += (1<<height); //1左移height位
height++;
cur = cur.left;
}
return sum + countLastLevel(root, height);
}
private int countLastLevel(TreeNode root, int height){
if(height == 1)
if(root.right != null) return 2;
else if(root.left != null) return 1;
else return 0;
TreeNode lastNode = root.left;
int currHeight = 1;
while(currHeight<height) {
currHeight++;
lastNode = lastNode.right;
}
if(lastNode == null) return countLastLevel(root.left, height - 1);
else return (1 << (height - 1)) + countLastLevel(root.right, height - 1);
}
}
Binary Tree Right Side View
从上到下打印二叉树每层的右边结点
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
helper(list, root, 0);
return list;
}
private void helper(List<Integer> res, TreeNode root, int level){
if(root == null) return;
if(res.size() == level){
res.add(root.val);
}
helper(res, root.right, level + 1);
helper(res, root.left, level + 1);
}
}
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
二叉树的前序遍历
要求:不能用递归
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
if(root.right != null) stack.push(root.right);
if(root.left != null) stack.push(root.left);
}
}
return res;
}
}
Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
每个结点的值都只可能是0~9
从根节点到叶子节点组成一个数,如1->2->3组成123
计算每个从根节点到叶子节点的数的和
如:
返回:
12 + 13 = 25
public class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return DFS(root, 0);
}
private int DFS(TreeNode root, int sum){
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum * 10 + root.val;
}
return DFS(root.left, sum * 10 + root.val) + DFS(root.right, sum * 10 + root.val);
}
}
House Robber III
public class Solution {
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
Map<TreeNode, Integer> dp = new HashMap<>();
return robHelper(root, dp);
}
private int robHelper(TreeNode root, Map<TreeNode, Integer> dp){
if(root == null) return 0;
if(dp.containsKey(root)) return dp.get(root);
int val = 0;
if(root.left != null) val += robHelper(root.left.left, dp) + robHelper(root.left.right, dp);
if(root.right != null) val += robHelper(root.right.left, dp) + robHelper(root.right.right, dp);
int robRoot = root.val + val;
int notRobRoot = robHelper(root.left, dp) + robHelper(root.right, dp);
val = Math.max(robRoot, notRobRoot);
dp.put(root, val);
return val;
}
}
Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
转化二叉树为右链表
如:
转为:
public class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.right = pre;
root.left = null;
pre = root;
}
}
Path Sum II
给定一个二叉树和值sum,返回从根节点到叶子节点的路径和等于sum的所有路径。
思路:用回溯的万能公式
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
backTracking(root, res, new LinkedList<>(), sum);
return res;
}
private void backTracking(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> list, int sum){
if(root == null) return;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == sum) {
list.add(root.val);
res.add(new LinkedList<>(list));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
list.add(root.val);
backTracking(root.left, res, list, sum-root.val);
backTracking(root.right, res, list, sum-root.val);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
Z字形层序遍历二叉树
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
helper(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res, int level){
if(root == null) return;
List<Integer> list = null;
if(res.size() == level) {
list = new LinkedList<>();
res.add(list);
} else {
list = res.get(level);
}
if(level%2 == 1) {
list.add(0, root.val);
} else {
list.add(root.val);
}
helper(root.left, res, level+1);
helper(root.right, res, level+1);
}
}
Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
把一个排序好的数组转化为二叉搜索树
public class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null;
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int l, int r){
if(l > r) return null;
int mid = (l + r)/2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, l, mid-1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid+1, r);
return root;
}
}
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
不用递归中序遍历二叉树
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
while(!s.isEmpty() || root != null){
if(root != null){
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
} else {
root = s.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Unique Binary Search Trees
给定一个整数n,返回存储 1 ~ n 所有的二叉搜索树的个数3
思路:
我们可以用自底向上的方法,用数组:
num 存从 1~n 的每个数可以组成二叉搜索树的种数。
public class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
//1 2 3 4 和 4 5 6 7是一样的
int[] num = new int[n + 1];
num[0] = 1;
num[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <=i; j++){
num[i] += num[j-1]*num[i-j];
}
}
return num[n];
}
}
Unique Binary Search Trees II
给定一个整数n,返回所有的二叉搜索树存储1 ~ n
如 n = 3
返回:
思路:
用动态规划的方法,用自底向上的方法,用一个数组res存中间的结果,res[i] 表示当 n = i 的结果。
当 n = i+1 时,用 res[0 ~ j] 的值作为 i+1 的左右结点。
public class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {
List<TreeNode>[] res = new List[n+1];
res[0] = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
if(n == 0) return res[0];
res[0].add(null);
for(int len = 1; len <= n; len++){
res[len] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
for(TreeNode l: res[j]){
for(TreeNode r: res[len-j-1]){
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(j+1);
root.left = l;
root.right = clone(r, j+1);
res[len].add(root);
}
}
}
}
return res[n];
}
private TreeNode clone(TreeNode n, int offset) {
if (n == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(n.val + offset);
node.left = clone(n.left, offset);
node.right = clone(n.right, offset);
return node;
}
}
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
在一颗二叉树里面找两个结点的第一个公共祖先。
public class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == q || root == p) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
}
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if root == None or p == root or q == root:
return root
l = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
r = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if l == None:
return r
elif r == None:
return l
else:
return root
Recover Binary Search Tree
恢复一颗二叉查找树,这个二叉查找树有两个元素交换了位置
public class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return ;
TreeNode[] res = new TreeNode[2];
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
TreeNode prev = new TreeNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
while(!s.isEmpty() || root != null){
if(root != null){
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
} else {
root = s.pop();
if(prev.val > root.val){
res[0] = res[0] == null? prev : res[0];
res[1] = root;
}
prev = root;
root = root.right;
}
}
int temp = res[0].val;
res[0].val = res[1].val;
res[1].val = temp;
}
}










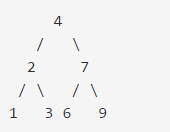

















 339
339











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








