查找的概念
搜索引擎用的是静态查找
代码(静态查找and动态查找)
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "SeqList.h"
#define SIZE 20
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
void print_array(int a[], int len)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
printf("%d, ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int static_search(int a[], int len, int key)
{//静态查找
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
if( a[i] == key )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
void print_list(SeqList* list)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<SeqList_Length(list); i++)
{
printf("%d, ", (int)SeqList_Get(list, i));
}
printf("\n");
}
int dynamic_search(SeqList* list, int key)
{//动态查找
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<SeqList_Length(list); i++)
{
if( (int)SeqList_Get(list, i) == key )
{
ret = i;
SeqList_Delete(list, i);
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
SeqList* list = SeqList_Create(SIZE);
int a[SIZE] = {0};
int i = 0;
int key = 0;
int index = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++)
{
a[i] = rand() % 100;
SeqList_Insert(list, (SeqListNode*)(rand() % 100), i);
//加入链表 动态查找
}
key = rand() % 100;
printf("Static Search Demo\n");
printf("Key: %d\n", key);
printf("Array: \n");
print_array(a, SIZE);
index = static_search(a, SIZE, key);
if( index >= 0 )
{
printf("Success: a[%d] = %d\n", index, a[index]);
}
else
{
printf("Failed!\n");
}
printf("Dynamic Search Demo\n");
printf("Key: %d\n", key);
printf("List: \n");
print_list(list);
index = dynamic_search(list, key);
if( index >= 0 )
{
printf("Success: list[%d] = %d\n", index, key);
}
else
{
printf("Failed!\n");
}
print_list(list);
return 0;
}</span></strong>小结
顺序表和有序表查找
顺序表查找
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 20
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
void print_array(int a[], int begin, int end)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=begin; i<=end; i++)
{
printf("%d, ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int another_search(int a[], int len, int key)
{
int ret = len;
a[0] = key;
//优化顺序查找
while( a[ret] != key )
{//只需比较一次,提高效率
ret--;
}
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int a[SIZE + 1] = {0};
int i = 0;
int key = 0;
int index = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for(i=1; i<=SIZE; i++)
{
a[i] = rand() % 100;
}
key = rand() % 100;
printf("Another Search Demo\n");
printf("Key: %d\n", key);
printf("Array: \n");
print_array(a, 1, SIZE);
index = another_search(a, SIZE, key);
if( index > 0 )
{
printf("Success: a[%d] = %d\n", index, a[index]);
}
else
{
printf("Failed!\n");
}
return 0;
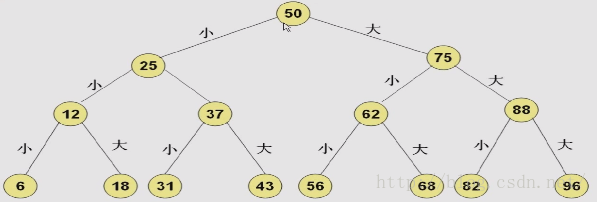
}</span></strong>二分查找(有序查找的一种)
插值查找
插值查找的速度比二分查找快,但是插值查找需要进行浮点数计算,因此,从稳定性上,插值不如二分查找
小结
二分查找代码
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 20
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
void println(int array[], int len)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void swap(int array[], int i, int j)
{
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
void SelectionSort(int array[], int len) // O(n*n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = -1;
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
k = i;
for(j=i; j<len; j++)
{
if( array[j] < array[k] )
{
k = j;
}
}
swap(array, i, k);
}
}
//二分查找
int binary_search(int a[], int low, int high, int key) // O(logn)
{
int ret = -1;
if( low <= high )
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if( a[mid] == key )
{
ret = mid;
}
else if( key < a[mid] )
{
ret = binary_search(a, low, mid-1, key);
}
else if( key > a[mid] )
{
ret = binary_search(a, mid+1, high, key);
}
}
return ret;
}
//二分查找
int binary_search_ex(int a[], int low, int high, int key) // O(logn)
{//循环代替递归
int ret = -1;
while( low <= high )
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if( a[mid] == key )
{
ret = mid;
break;
}
else if( key < a[mid] )
{
high = mid - 1;
}
else if( key > a[mid] )
{
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
int interpolation_search(int a[], int low, int high, int key)
{//插值查找
int ret = -1;
while( (low <= high) && (a[low] <= key) && (key <= a[high]) )
{
float fx = 1.0f * (key - a[low]) / (a[high] - a[low]);
int mid = low + fx * (high - low);
if( a[mid] == key )
{
ret = mid;
break;
}
else if( key < a[mid] )
{
high = mid - 1;
}
else if( key > a[mid] )
{
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int a[SIZE] = {0};
int i = 0;
int key = 0;
int index = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for(i=1; i<=SIZE; i++)
{
a[i] = rand() % 100;
}
key = 50;
printf("Binary Search Demo\n");
printf("Key: %d\n", key);
printf("Array: \n");
SelectionSort(a, SIZE);
println(a, SIZE);
index = interpolation_search(a, 0, SIZE-1, key);
if( index > 0 )
{
printf("Success: a[%d] = %d\n", index, a[index]);
}
else
{
printf("Failed!\n");
}
return 0;
}</span></strong>斐波那契数列
黄金比例又称黄金分割,是指事物各部分间一定的数学比例关系,即将整体一分为二,较大部分与较小部分之比等于整体与较大部分之比,其比值约为1:0.618或1.618:1。
0.618被公认为最具有审美意义的比例数字,这个数值的作用不仅仅体现在诸如绘画、雕塑、音乐、建筑等艺术领域,而且在管理、工程设计等方面也有着不可忽视的作用。因此被称为黄金分
割。
大家记不记得斐波那契数列:1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89…….(从第三个数开始,后边每一个数都是前两个数的和)
然后我们会发现,随着斐波那契数列的递增,前后两个数的比值会越来越接近0.618,利用这个特性,我们就可以将黄金比例运用到查找技术中。
代码
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int max_size=20;//斐波那契数组的长度
/*构造一个斐波那契数组*/
void Fibonacci(int * F)
{
F[0]=0;
F[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<max_size;++i)
F[i]=F[i-1]+F[i-2];
}
/*定义斐波那契查找法*/
int Fibonacci_Search(int *a, int n, int key) //a为要查找的数组,n为要查找的数组长度,key为要查找的关键字
{
int low=0;
int high=n-1;
int F[max_size];
Fibonacci(F);//构造一个斐波那契数组F
int k=0;
while(n>F[k]-1)//计算n位于斐波那契数列的位置
++k;
int * temp;//将数组a扩展到F[k]-1的长度
temp=new int [F[k]-1];
memcpy(temp,a,n*sizeof(int));
for(int i=n;i<F[k]-1;++i)
temp[i]=a[n-1];
while(low<=high)
{
int mid=low+F[k-1]-1;
if(key<temp[mid])
{
high=mid-1;
k-=1;
}
else if(key>temp[mid])
{
low=mid+1;
k-=2;
}
else
{
if(mid<n)
return mid; //若相等则说明mid即为查找到的位置
else
return n-1; //若mid>=n则说明是扩展的数值,返回n-1
}
}
delete [] temp;
return -1;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a[] = {0,16,24,35,47,59,62,73,88,99};
int key=100;
int index=Fibonacci_Search(a,sizeof(a)/sizeof(int),key);
cout<<key<<" is located at:"<<index;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
} </span></strong>斐波那契查找的核心是:
1)当key=a[mid]时,查找成功;
2)当key<a[mid]时,新的查找范围是第low个到第mid-1个,此时范围个数为F[k-1] - 1个,即数组左边的长度,所以要在[low, F[k - 1] - 1]范围内查找;
3)当key>a[mid]时,新的查找范围是第mid+1个到第high个,此时范围个数为F[k-2] - 1个,即数组右边的长度,所以要在[F[k - 2] - 1]范围内查找。
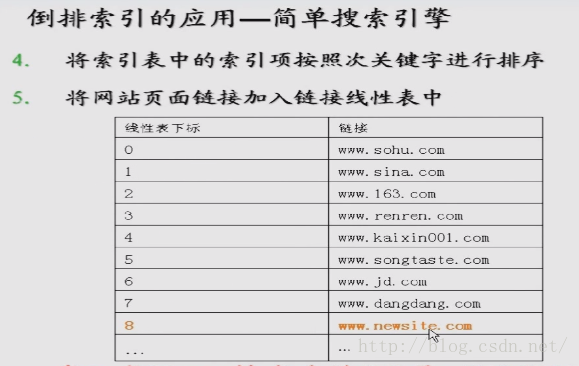
线性索引查找
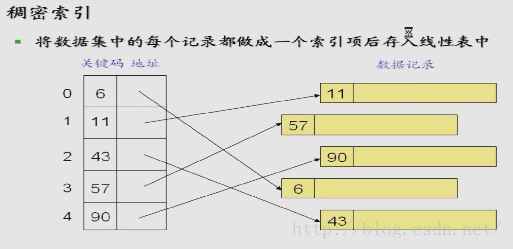
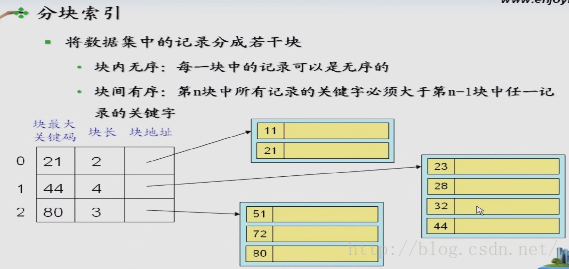
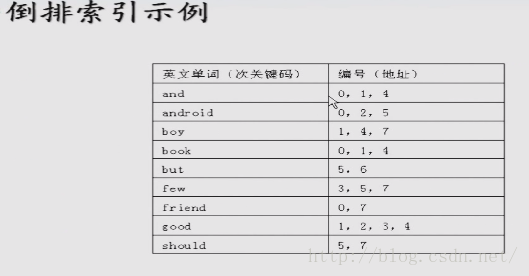
索引的概念
线性索引
小结
思考:
一、数组中一个只出现一次的整数
题目:一个数组中,有一个数字只出现一次,其他数字都出现两次,写出程序找出这个数字。
思路:利用异或运算,如果是两个相同的数,那么他们的结果就是0,剩下的就是只出现一次的数。
代码如下:
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
//find a number,which appearing once in an array
int FindNumAppearOnce(int arr[], int iLen)
{
int iNumAppearOnce;
iNumAppearOnce = arr[0];
for(int i = 1; i < iLen; i++)
iNumAppearOnce ^= arr[i];
return iNumAppearOnce;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = {1,2,2,3,3,4,4};
printf("%d\n",FindNumAppearOnce(arr, 7));
return 0;
} </span></strong>二、数组中两个只出现一次的整数
思路:我们要让这两个只出现一次的数分别在两组,然后两组分别异或运算找出只出现一次的数。方法是,首先所有的数进行异或运算,得到的是只出现一次的两个数的异或运算结果。然后根据这个结果中第一次出现1的位(从右开始算),将数组分为两组。为什么可以分成两组?因为异或运算为1就是只出现一次的那两个数的那两个bit位不同,其他的数都抵消了。
代码如下:
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
int FindIndexOfBit1(int n)
{
int indexOfBit1 = 0;
while(((1 & n) == 0) && indexOfBit1 < 32){
n >>= 1;
indexOfBit1++;
}
return indexOfBit1;
}
int IsBit1(int n, int indexOfBit1){
n >>= indexOfBit1;
return n & 1;
}
//find two number,which appearing once in an array
//Input:arr - an array
// iLen - the length of the array
// pNum1 - number 1 founded
// pNum2 - number 2 founded
void FindNumAppearOnce(int arr[], int iLen, int *pNum1, int *pNum2)
{
if(iLen < 2)
return;
//get num1^num2
int resultOfExclusiveOr = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
resultOfExclusiveOr ^= arr[i];
//get index of the first bit
int indexOfBit1 = FindIndexOfBit1(resultOfExclusiveOr);
*pNum1 = *pNum2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++){
if(IsBit1(arr[i], indexOfBit1))
*pNum1 ^= arr[i];
else
*pNum2 ^= arr[i];
}
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = {1,5,2,2,3,3,4,4};
int a;
int b;
FindNumAppearOnce(arr, 8, &a, &b);
printf("%d %d\n", a,b);
return 0;
} </span></strong>三、数组中3个只出现一次的数字
思路:
我们要把三个不同的数分开!首先分开两组,一个不同的和两个不同的各位一组。分开的思路:参考http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/25411174201283084246412/
总之:x^a、x^b、x^c三个数字中,只有一个数字的第m位是1。作为它们的区分标准。
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">#include <stdio.h>
//
int ValueOfBit1(int iNum)
{
return iNum & ~(iNum - 1);
}
//
void Swap(int *pNum1, int *pNum2)
{
int iTemp;
iTemp = *pNum1;
*pNum1 = *pNum2;
*pNum2 = iTemp;
}
//
void PrintUniqueTwo(int arrNums[], int iLen)
{
int iXorResult = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
iXorResult ^= arrNums[i];
int iDiffBit = ValueOfBit1(iXorResult);
int iNum1, iNum2;
iNum1 = iNum2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
if(iDiffBit & arrNums[i])
iNum1 ^= arrNums[i];
else
iNum2 ^= arrNums[i];
printf("%d\n%d\n", iNum1, iNum2);
}
void PrintUniqueThree(int arrNums[], int iLen)
{
if(iLen < 3)
return;
//get a ^ b ^ c
int iXorResult = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
iXorResult ^= arrNums[i];
//get fun(fun(x ^ a) ^ fun(x ^ b) ^ fun(x ^ b))
int iFunMultiResult = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
iFunMultiResult ^= ValueOfBit1(iXorResult ^ arrNums[i]);
iFunMultiResult = ValueOfBit1(iFunMultiResult);
//get the first unique number
int iFirstUniqueNum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
if(ValueOfBit1(arrNums[i] ^ iXorResult) == iFunMultiResult)
iFirstUniqueNum ^= arrNums[i];
printf("%d\n", iFirstUniqueNum);
//move the first unique number to the end of the array
for(int i = 0; i < iLen; i++)
if(arrNums[i] == iFirstUniqueNum){
Swap(&arrNums[i], &arrNums[iLen - 1]);
break;
}
PrintUniqueTwo(arrNums, iLen - 1);
}
int main(void)
{
int arrNums[] = {2,3,4,4,1,3,5,5,0};
PrintUniqueThree(arrNums, 9);
return 0;
} </span></strong> int Find(int * a)
{
int i;//变量
for (i = 0 ;i<=1000;i++)
{
a[1000] += a[i];
}
a[1000] -= (i*(i-1))/2 //i的值为1001
return a[1000];
}<strong><span style="font-size:18px;">void FindRepeat(int array[], int length)
{
int index=array[length-1]-1;
while ( true )
{
if ( array[index]<0 )
break;
array[index]*=-1;
index=array[index]*(-1)-1;
}
cout<<"The repeat number is "<<index+1<<endl;
}</span></strong><strong><span style="font-size:18px;">*/
void FindRepeat(int array[], int length, int num)
{
int index=array[length-1]-1;
cout<<"The repeat number is ";
while ( true )
{
if ( array[index]<0 )
{
num--;
array[index]=length-num;
cout<<index+1<<'t';
}
if ( num==0 )
{
cout<<endl;
return;
}
array[index]*=-1;
index=array[index]*(-1)-1;
}
}</span></strong>













































 274
274

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








