具体题目如下:
有四个线程1、2、3、4,
线程1的功能就是输出1,线程2的功能就是输出2,以此类推.........
现在有四个文件A B C D,
初始都为空。现要让四个文件呈如下格式:
A:1 2 3 4 1 2....
B:2 3 4 1 2 3....
C:3 4 1 2 3 4....
D:4 1 2 3 4 1....
以上就是我看到的一个多线程相关的面试题,看完了 ,就想想怎么实现。
下面就看代码
理论上讲,都是从main方法走起,
package com.lxk.threadTest.mianShiTest.googleTest;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* 有四个线程1、2、3、4。
* <p>
* 线程1的功能就是输出1,线程2的功能就是输出2,
* <p>
* 以此类推......... 现在有四个文件A B C D,
* 初始都为空。现要让四个文件呈如下格式:
* A:1 2 3 4 1 2....
* B:2 3 4 1 2 3....
* C:3 4 1 2 3 4....
* D:4 1 2 3 4 1....
* <p>
* Created by lxk on 2017/7/14
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriteUtil util = new FileWriteUtil();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
service.execute(new WriteRunnable(util, 1, '1'));
service.execute(new WriteRunnable(util, 2, '2'));
service.execute(new WriteRunnable(util, 3, '3'));
service.execute(new WriteRunnable(util, 4, '4'));
service.shutdown();
//new Thread(new WriteRunnable(util, 1, '1')).start();
//new Thread(new WriteRunnable(util, 2, '2')).start();
//new Thread(new WriteRunnable(util, 3, '3')).start();
//new Thread(new WriteRunnable(util, 4, '4')).start();
}
}上面关于启动线程,有2中方式,
第一种,也就是未注释的,略显高级点,看类名大概就知道使用的是个线程池的东西。这个实现姿势有很多种。这只是其中的一个。
第二种,也就是下面注释的代码,也不low,是我们常见的启动线程 的方式。
然后就是我们说的那个实现多线程的类的实现啦
package com.lxk.threadTest.mianShiTest.googleTest;
/**
* Created by lxk on 2017/7/14
*/
public class WriteRunnable implements Runnable {
private final FileWriteUtil util;
private int threadNum;
private char value;
/**
* @param util 写文件工具类
* @param threadNum 线程号
* @param value 写的字符
*/
public WriteRunnable(FileWriteUtil util, int threadNum, char value) {
this.util = util;
this.threadNum = threadNum;
this.value = value;
}
public void run() {
/*
* 假设循环6次,一直循环可以使用while(true)或者for(;;)
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
synchronized (util) {
while (threadNum != util.getCurrentThreadNum()) {
try {
util.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
util.write(value, threadNum);
util.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
最后,就是这个写文件的类啦。
package com.lxk.threadTest.mianShiTest.googleTest;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 此类,是四个线程共享的,
* <p>
* Created by lxk on 2017/7/14
*/
public class FileWriteUtil {
private int currentThreadNum = 1;
/**
* 记录将字符写入文件的次数
*/
private int count = 0;
private String currentFileName;
public void write(char value, int threadNum) {
getCurrentFileName();
FileWriter writer = null;
try {
//生成文件位置
writer = new FileWriter("D:/test/test/" + currentFileName + ".txt", true);
writer.write(value + " ");
System.out.printf(
"ThreadNum=%d is executing. %c is written into file file%s.txt \n",
currentThreadNum, value, currentFileName);
writer.flush();
//System.out.println(count);//
count++;
currentThreadNum = threadNum;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (null != writer) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
getNextThreadNum();
}
public int getCurrentThreadNum() {
return currentThreadNum;
}
public void setCurrentThreadNum(int currentThreadNum) {
this.currentThreadNum = currentThreadNum;
}
/**
* 根据写的次数,判断该写哪个文件了?A,B,C,D.
*/
private void getCurrentFileName() {
int temp = count % 4;
switch (temp) {
case 0:
currentFileName = "A";
break;
case 1:
currentFileName = "B";
break;
case 2:
currentFileName = "C";
break;
case 3:
currentFileName = "D";
break;
default:
currentFileName = "E";
}
}
private void getNextThreadNum() {
if (count % 4 == 0) {
if (currentThreadNum < 3) {
currentThreadNum += 2;
} else {
currentThreadNum = (currentThreadNum + 2) % 4;
}
} else {
if (currentThreadNum == 4) {
currentThreadNum = 1;
} else {
currentThreadNum++;
}
}
}
}
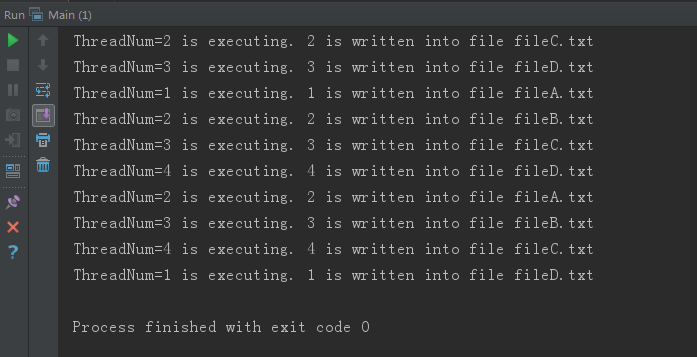
最后,就是看下代码实际运行的结果。
从打印结果看,看到了是四个线程在跑,而且分别写入到ABCD四个文件去。
注意,图中的红线框,奥,也可以不注意啦。
其实,说得最透彻点,就是这四个线程,轮着执行,
每次,都是有一个线程可以执行,这的执行也就是写文件啦,然后其他的三个都稍息,也是wait()啦。
等这个线程执行完毕之后,也就是写文件完毕之后,唤醒另外三个在wait()的线程,然后,设置一下,下一个可以处于运行态的线程,然后又开始重复了。
不能执行的,都wait(),如此往复。
这里有个需要注意的是。
这四个线程都在共享操作的就是那个写文件工具类。也就是对这个上锁。四个线程用的是一个锁,那就可以保证线程安全啦。
理论,是这个理论,但是,真让你写,可不一定能分分钟就写好。























 4927
4927

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








