Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.

Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
Analysis:
想了半天,也想不出来O(n)的解法,于是上网google了一下。
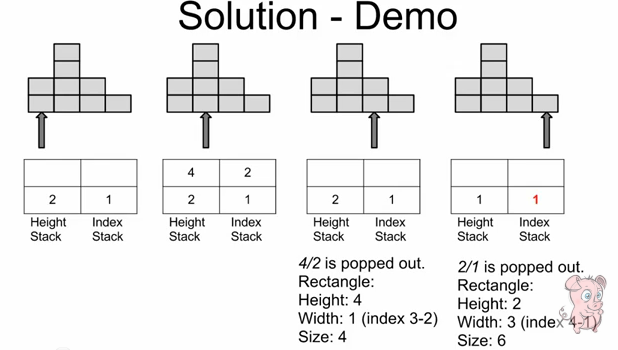
如下图所示,从左到右处理直方,i=4时,小于当前栈顶(及直方3),于是在统计完区间[2,3]的最大值以后,消除掉阴影部分,然后把红线部分作为一个大直方插入。因为,无论后面还是前面的直方,都不可能得到比目前栈顶元素更高的高度了。
Case 1: current > previous (top of height stack)
Push current height and index as candidate rectangle start position.
Case 2: current = previous
Ignore.
Case 3: current < previous
Need keep popping out previous heights, and compute the candidate rectangle with height and width (current index - previous index). Push the height and index to stacks.
(Note: it is better use another different example to walk through the steps, and you will understand it better).
int area = 0;
if(height.length<=0) return area;
if(height.length==1) return height[0];
height = Arrays.copyOf(height, height.length+1);
height[height.length-1]=0;
Stack<Integer> index = new Stack<>();
int i=0;
while(i<height.length){
if(index.empty() || height[i]>=height[index.peek()]) index.push(i++);
else {
int temp = index.pop();
area = Math.max(area, height[temp]*(index.empty()?i:i-index.peek()-1));
}
}
return area;c++
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) {
int maxArea = 0;
height.push_back(0);
stack<int> stk;
int i=0;
while(i<height.size()){
if(stk.empty() || height[stk.top()] <= height[i])
stk.push(i++);
else{
int t = stk.top();
stk.pop();
maxArea = max(maxArea, height[t]*(stk.empty()? i:i-stk.top()-1));
}
}
return maxArea;
}



























 594
594

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








