版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载,请注明出处。若是商业用途,请事先联系作者。
Kruskal算法
Kruskal算法
求解最小生成树的另一种常见算法是Kruskal算法,它比Prim算法更直观。从直观上看,Kruskal算法的做法是:每次都从剩余边中选取权值最小的,当然,这条边不能使已有的边产生回路。
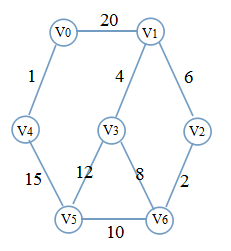
手动求解会发现Kruskal算法异常简单,下面是一个例子
先对边的权值排个序:1(0,1) 2(2,6) 4(1,3) 6(1,2) 8(3,6) 10(5,6) 12(3,5) 15(4,5) 20(0,1)
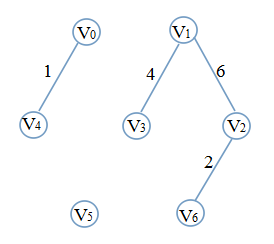
首选边1(0,1)、2(2,6)、4(1,3)、6(1,2),此时的图是这样
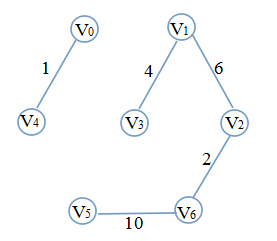
显然,若选取边8(3,6)会出现环,则必须抛弃8(3,6),选择下一条10(5,6)没有问题,此时图变成这样
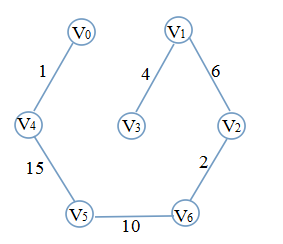
显然,12(3,5)同样不可取,选取15(4,5),边数已达到要求,算法结束。最终的图是这样的
算法逻辑人很容易理解,但用代码判断当前边是否会引起环的出现,则很棘手。
算法说明
为了判断环的出现,我们换个角度来理解Kruskal算法的做法:初始时,把图中的n个顶点看成是独立的n个连通分量,从树的角度看,也是n个根节点。我们选边的标准是这样的:若边上的两个顶点从属于两个不同的连通分量,则此边可取,否则考察下一条权值最小的边。
于是问题又来了,如何判断两个顶点是否属于同一个连通分量呢?这个可以参照并查集的做法解决。它的思路是:如果两个顶点的根节点是一样的,则显然是属于同一个连通分量。这也同样暗示着:在加入新边时,要更新父节点。具体细节看代码:
代码
- #include<iostream>
- #include<algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- #define MAXWEIGHT 100
- /*
- 全局变量
- numV顶点数
- numE边数
- */
- int numV, numE;
- //边
- typedef struct edge_tag
- {
- int tail;
- int head;
- int weight;
- }Edge;
- //检测边
- bool checkEdge(int tail, int head, int weight)
- {
- if (tail == head
- || tail < 0 || tail >= numV
- || head < 0 || head >= numV
- || weight <= 0 || weight >= MAXWEIGHT)
- return false;
- return true;
- }
- //输入边
- void inputEdge(Edge *edge, int numE)
- {
- int i, tail, head, weight;
- cout << "输入边的起点、终点和权值" << endl;
- i = 0;
- while (i < numE)
- {
- cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
- while (!checkEdge(tail, head, weight))
- {
- cout << "输入错误!重新输入" << endl;
- cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
- }
- edge[i].tail = tail;
- edge[i].head = head;
- edge[i].weight = weight;
- i++;
- }
- }
- int cmp(const void *edge1, const void *edge2)
- {
- return ((Edge*)edge1)->weight - ((Edge*)edge2)->weight;
- }
- //并查集的常见操作
- /*
- 压缩查找
- 查找child的根节点
- */
- int Find(int child, int *parent)
- {
- if (parent[child] == child)
- return child;
- parent[child] = Find(parent[child], parent); //压缩路径
- return parent[child];
- }
- //合并
- bool Union(Edge *e, int *parent, int *childs)
- {
- //处于同一个棵树中,则不能合并,否则会出现环
- int root1, root2;
- root1 = Find(e->tail, parent);
- root2 = Find(e->head, parent);
- if (root1 != root2)
- {
- //把小树合并到大树根下
- if (childs[root1] > childs[root2])
- {
- parent[root2] = root1;
- childs[root1] += childs[root2] + 1;
- }
- else
- {
- parent[root1] = root2;
- childs[root2] += childs[root2] + 1;
- }
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- /*
- Kruskal算法
- 求最小生成树
- */
- void Kruskal(int numV, int numE)
- {
- //边的集合
- Edge *edge = new Edge[numE];
- inputEdge(edge, numE);
- /*
- parent[i]是顶点i的父顶点
- childs[i]是顶点i的孩子数
- child的复数是children,这里的childs是杜撰的
- */
- int *parent = new int[numV];
- int *childs = new int[numV];
- //初始化
- for (int i = 0; i < numV; i++)
- {
- /*
- 初始时,每一个顶点都是根,且无孩子
- 把每个顶点的的父节点设置为自身下标,也是标明类别
- */
- parent[i] = i;
- childs[i] = 0;
- }
- //对边按权值进行从小到大排序
- qsort(edge, numE, sizeof(Edge), cmp);
- int i, count;
- i = count = 0;
- cout << "最小生成树的边..." << endl;
- while (i < numE)
- {
- if (Union(&edge[i], parent, childs))
- {
- cout << edge[i].tail << "---" << edge[i].head << endl;
- count++;
- }
- if (count == numV - 1) //边数达到要求
- break;
- i++;
- }
- if (count != numV - 1)
- cout << "此图为非连通图!无法构成最小生成树。" << endl;
- delete[]edge;
- delete[]parent;
- delete[]childs;
- }
- //检测顶点数和边数
- bool checkVE(int numV, int numE)
- {
- if (numV <= 0 || numE <= 0 || numE > numV*(numV - 1) / 2)
- return false;
- return true;
- }
- int main()
- {
- cout << "******Kruskal***by David***" << endl;
- cout << "输入顶点数、边数 ";
- cin >> numV >> numE;
- while (!checkVE(numV, numE))
- {
- cout << "输入数据有问题!重新输入 ";
- cin >> numV >> numE;
- }
- cout << endl << "Kruskal..." << endl;
- Kruskal(numV, numE);
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAXWEIGHT 100
/*
全局变量
numV顶点数
numE边数
*/
int numV, numE;
//边
typedef struct edge_tag
{
int tail;
int head;
int weight;
}Edge;
//检测边
bool checkEdge(int tail, int head, int weight)
{
if (tail == head
|| tail < 0 || tail >= numV
|| head < 0 || head >= numV
|| weight <= 0 || weight >= MAXWEIGHT)
return false;
return true;
}
//输入边
void inputEdge(Edge *edge, int numE)
{
int i, tail, head, weight;
cout << "输入边的起点、终点和权值" << endl;
i = 0;
while (i < numE)
{
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
while (!checkEdge(tail, head, weight))
{
cout << "输入错误!重新输入" << endl;
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
}
edge[i].tail = tail;
edge[i].head = head;
edge[i].weight = weight;
i++;
}
}
int cmp(const void *edge1, const void *edge2)
{
return ((Edge*)edge1)->weight - ((Edge*)edge2)->weight;
}
//并查集的常见操作
/*
压缩查找
查找child的根节点
*/
int Find(int child, int *parent)
{
if (parent[child] == child)
return child;
parent[child] = Find(parent[child], parent); //压缩路径
return parent[child];
}
//合并
bool Union(Edge *e, int *parent, int *childs)
{
//处于同一个棵树中,则不能合并,否则会出现环
int root1, root2;
root1 = Find(e->tail, parent);
root2 = Find(e->head, parent);
if (root1 != root2)
{
//把小树合并到大树根下
if (childs[root1] > childs[root2])
{
parent[root2] = root1;
childs[root1] += childs[root2] + 1;
}
else
{
parent[root1] = root2;
childs[root2] += childs[root2] + 1;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
Kruskal算法
求最小生成树
*/
void Kruskal(int numV, int numE)
{
//边的集合
Edge *edge = new Edge[numE];
inputEdge(edge, numE);
/*
parent[i]是顶点i的父顶点
childs[i]是顶点i的孩子数
child的复数是children,这里的childs是杜撰的
*/
int *parent = new int[numV];
int *childs = new int[numV];
//初始化
for (int i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
/*
初始时,每一个顶点都是根,且无孩子
把每个顶点的的父节点设置为自身下标,也是标明类别
*/
parent[i] = i;
childs[i] = 0;
}
//对边按权值进行从小到大排序
qsort(edge, numE, sizeof(Edge), cmp);
int i, count;
i = count = 0;
cout << "最小生成树的边..." << endl;
while (i < numE)
{
if (Union(&edge[i], parent, childs))
{
cout << edge[i].tail << "---" << edge[i].head << endl;
count++;
}
if (count == numV - 1) //边数达到要求
break;
i++;
}
if (count != numV - 1)
cout << "此图为非连通图!无法构成最小生成树。" << endl;
delete[]edge;
delete[]parent;
delete[]childs;
}
//检测顶点数和边数
bool checkVE(int numV, int numE)
{
if (numV <= 0 || numE <= 0 || numE > numV*(numV - 1) / 2)
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
cout << "******Kruskal***by David***" << endl;
cout << "输入顶点数、边数 ";
cin >> numV >> numE;
while (!checkVE(numV, numE))
{
cout << "输入数据有问题!重新输入 ";
cin >> numV >> numE;
}
cout << endl << "Kruskal..." << endl;
Kruskal(numV, numE);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
转载请注明出处,本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangxiangdavaid/article/details/38414683
若有所帮助,顶一个哦!
专栏目录:
-
顶
- 1
-
踩
- 1























 138
138

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








