程序运行会分配一个沙盒文件,沙盒文件的文件名每次运行都会变化,文件夹名只一次有效,沙盒一般会保存程序一些信息,缓存等数据,还可以进行病毒的测试.
沙盒里有三个文件夹 Documents,libary,tmp.
Documents文件夹:保存用户想要保存的一些信息,比如收藏的内容,设置信息.
Library文件夹:用来保存开发人员存储的一些东西.
caches缓存文件夹:用来对缓存信息进行存储,清除缓存就是删除该文件夹.
Preferences用来保存一些信息,NSUserDefaults创建的plist文件保存在这个文件里.
tmp临时文件夹:存储临时文件.
NSBundle指的是当前工程的文件夹,在里面和可以获取图片等的信息,应用程序会在编译的时候把文件变成只读文件,存入到NSBundle里.
一.把简单的对象存入本地.
ViewController.m
- (void)viewDidLoad {
1.把字符串写入到本地.
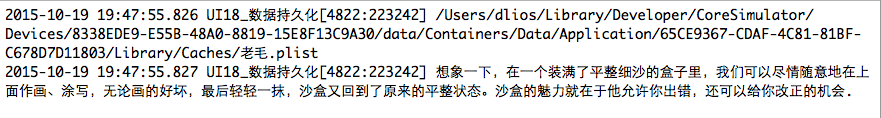
NSString *str = @"想象一下,在一个装满了平整细沙的盒子里,我们可以尽情随意地在上面作画、涂写,无论画的好坏,最后轻轻一抹,沙盒又回到了原来的平整状态.沙盒的魅力就在于他允许你出错,还可以给你改正的机会.";
NSArray *sandBox = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *sandBoxPath = sandBox[0];
NSString *docPath = [sandBoxPath stringByAppendingString:@"/老毛.plist"];
[str writeToFile:docPath atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSLog(@"%@", docPath);
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:docPath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
2.把数组对象写入到本地.
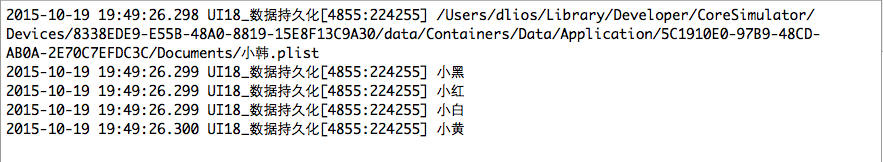
NSArray *arr = @[@"小黑", @"小红", @"小白", @"小黄"];
NSArray *sandBox = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *sandBoxPath = sandBox[0];
NSString *arrPath = [sandBoxPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"小韩.plist"];
[arr writeToFile:arrPath atomically:YES];
NSLog(@"%@", arrPath);
NSArray *receiveArr = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:arrPath];
for (NSString *str in receiveArr) {
NSLog(@"%@", str);
}
1.指定文件保存的沙盒文件路径.
2.拼接要保存的文件路径.
3.根据路径,把数据写入.
4.按照文件路径,从本地在读取数据.
3.把字典写入到本地.
NSDictionary *dic = @{@"1":@"2", @"3":@"4", @"5":@"6"};
NSArray *sandBox = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *sandBoxPath = sandBox[0];
NSString *dicPath = [sandBoxPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"kaka.MP4"];
[dic writeToFile:dicPath atomically:YES];
NSLog(@"%@", dicPath);
NSDictionary *receiveDic = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:dicPath];
NSLog(@"%@", receiveDic);
NSUserDefaults *user = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
[user setObject:@"xiaohan" forKey:@"userName"];
NSLog(@"%@", NSHomeDirectory());
}

Student.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Student : NSObject<NSCopying>
@property(nonatomic, copy)NSString *name;
@property(nonatomic, copy)NSString *hobby;
@property(nonatomic, assign)NSInteger age;
@property(nonatomic, retain)NSNumber *number;
- (instancetype)initWithName:(NSString *)name hobby:(NSString *)hobby
age:(NSInteger)age
number:(NSNumber *)number;
@end
Student.m
#import "Student.h"
@implementation Student
- (instancetype)initWithName:(NSString *)name hobby:(NSString *)hobby
age:(NSInteger)age
number:(NSNumber *)number {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.age = age;
self.name = name;
self.hobby = hobby;
self.number = number;
}
return self;
}
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder {
[aCoder encodeObject:self.name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeObject:self.hobby forKey:@"hobby"];
[aCoder encodeObject:self.number forKey:@"number"];
[aCoder encodeInteger:self.age forKey:@"age"];
}
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
self.hobby = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"hobby"];
self.number = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"number"];
self.age = [aDecoder decodeIntegerForKey:@"age"];
}
return self;
}
@end
4.把复杂对象,写入到本地.
Student *stu = [[Student alloc] init]
stu.name = @"小黑"
stu.hobby = @"小红"
stu.number = @100
stu.age = 30
// 归档操作.
// 找沙盒路径.
NSArray *sandBox = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)
NSString *sandBoxPath = sandBox[0]
NSString *docPath = [sandBoxPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"小黄.MP4"]
NSLog(@"%@",docPath)
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:stu toFile:docPath]
// 反归档.
Student *tempStu = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:docPath]
NSLog(@"%@, %@", tempStu.name, tempStu.hobby)
// 把复杂对象放到数组里进行归档和反归档的操作
Student *stu1 = [[Student alloc] initWithName:@"小红" hobby:@"男" age:20 number:@100]
Student *stu2 = [[Student alloc] initWithName:@"小黄" hobby:@"女" age:21 number:@200]
Student *stu3 = [[Student alloc] initWithName:@"小白" hobby:@"女" age:22 number:@300]
Student *stu4 = [[Student alloc] initWithName:@"小黑" hobby:@"男" age:23 number:@400]
NSArray *arr = @[stu1, stu2, stu3, stu4]
for (Student *aaa in arr) {
NSLog(@"%@, %@, %ld, %@", aaa.name, aaa.hobby, aaa.age, aaa.number)
}
// 把复杂对象保存到数组中,然后整体进行归档和反归档的操作
// NSArray因为本身就签署了NSCoding协议,所以可以直接进行归档和反归档操作,自己写的复杂类也必须签NSCoding协议,实现方法,否则就会崩溃.

将plist文件,进行归档与反归档.
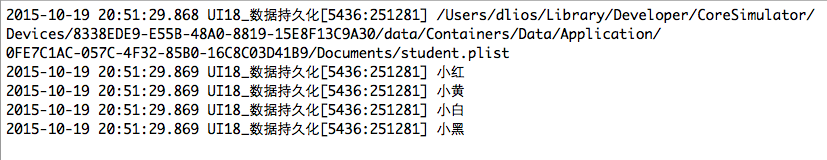
NSArray *sandBox1 = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *sandBoxPath1 = sandBox1[0];
NSString *docPath1 = [sandBoxPath1 stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"student.plist"];
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:arr toFile:docPath1];
NSLog(@"%@", docPath1);
NSArray *temp = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:docPath];
for (Student *stu in temp) {
NSLog(@"%@", stu.name);
}
5.文件管理
NSArray *sandBox2 = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *sandBoxPath2 = sandBox2[0];
NSFileManager *manager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSString *docPath2 = [sandBoxPath2 stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"ything"];
[manager createDirectoryAtPath:docPath2 withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil];
NSLog(@"********%@", docPath2);

6.删除文件夹,文件.
BOOL result = [manager removeItemAtPath:docPath2 error:nil];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"删除成功");
} else {
NSLog(@"删除失败");
}





























 9万+
9万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








