1:深度优先
1.1:前序遍历
- Visit the root.
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Traverse the right subtree.
伪代码:
preorder(node) if node == null then return visit(node) preorder(node.left) preorder(node.right) | iterativePreorder(node)
parentStack = empty stack
parentStack.push(null)
top = node
while ( top != null )
visit( top )
if ( top.right != null )
parentStack.push(top.right)
if ( top.left != null )
parentStack.push(top.left)
top = parentStack.top();
parentStack.pop(); |
1.2:中序遍历
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Visit root.
- Traverse the right subtree.

伪代码:
inorder(node) if node == null then return inorder(node.left) visit(node) inorder(node.right) | iterativeInorder(node)
parentStack = empty stack
while (not parentStack.isEmpty() or node ≠ null)
if (node ≠ null)
parentStack.push(node)
node = node.left
else
node = parentStack.pop()
visit(node)
node = node.right |
1.3:后序遍历
postorder(node) if node == null then return postorder(node.left) postorder(node.right) visit(node) | iterativePostorder(node)
parentStack = empty stack
lastnodevisited = null
while (not parentStack.isEmpty() or node ≠ null)
if (node ≠ null)
parentStack.push(node)
node = node.left
else
peeknode = parentStack.peek()
if (peeknode.right ≠ null and lastnodevisited ≠ peeknode.right)
/* if right child exists AND traversing node from left child, move right */
node = peeknode.right
else
parentStack.pop()
visit(peeknode)
lastnodevisited = peeknode |
1.4:java代码实现三种遍历
树的结构是
10
/ \
5 12
/ \
4 7
/ \
5 12
/ \
4 7
代码中我主要解释下让我一直纠结的递归法了,总是对递归法执行的顺序有疑惑。详细可以看《Thinking In Algorithm》09.彻底理解递归
public class Preorder{
/*******************************递归法****************************/
//递归前序遍历 print:10,5,4,7,12
public static void preorder(TNode node){
if(node!=null){
System.out.println(node.getValue()) ;
preorder(node.getLeft()) ;
preorder(node.getRight()) ;
}
}
//递归中序遍历 print: 4,5,7,10,12
public static void inorder(TNode node){
if(node!=null){
inorder(node.getLeft()) ;
System.out.println(node.getValue()) ;
inorder(node.getRight()) ;
}
}
//递归后序遍历 print: 4,7,5,12,10
public static void postorder(TNode node){
if(node!=null){
postorder(node.getLeft()) ;
postorder(node.getRight()) ;
System.out.println(node.getValue()) ;
}
}
/*******************************非递归*****************************/
//非递归前序遍历 print:10,5,4,7,12
public static void iterativePreorder(TNode node){
MyStack parentStack = new MyStack() ;
parentStack.push(node) ;
while(!parentStack.isEmpty()){
TNode temp = parentStack.getFirst().getValue() ;
System.out.println(temp.getValue()) ;
parentStack.pop() ;
if(temp.getRight()!=null){ parentStack.push(temp.getRight()) ;}
if(temp.getLeft()!=null){ parentStack.push(temp.getLeft()) ;}
}
}
//非递归中序遍历 print: 4,5,7,10,12
public static void iterativeInorder(TNode node){
MyStack mystack = new MyStack() ;
while(!mystack.isEmpty()||node!=null){
if(node!=null){
mystack.push(node) ;
node = node.getLeft() ;
}else{
node = mystack.pop().getValue() ;
System.out.println(node.getValue()) ;
node = node.getRight() ;
}
}
}
//非递归后序遍历 print: 4,7,5,12,10
public static void iterativePostorder(TNode node){
MyStack mystack = new MyStack() ;
TNode temp = null ;
TNode peeknode = null ;
while(!mystack.isEmpty()||node!=null){
if(node!=null){
mystack.push(node) ;
node = node.getLeft() ;
}else{
peeknode = mystack.getFirst().getValue() ;
if(peeknode.getRight()!=null&&temp!=peeknode.getRight()){
node = peeknode.getRight() ;
}else{
mystack.pop() ;
System.out.println(peeknode.getValue()) ;
temp = peeknode ;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
MyTree mytree = new MyTree() ;
mytree.insert(10) ;
mytree.insert(5);
mytree.insert(12);
mytree.insert(4);
mytree.insert(7);
preorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
inorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
postorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
iterativePreorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
iterativeInorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
iterativePostorder(mytree.getRoot()) ;
}
}
/*****************二叉树的实现****************/
class TNode{
private int value ;
private TNode left ;
private TNode right ;
public TNode(int value){ this.value = value ;}
public void setLeft(int value){ this.left = new TNode(value) ;}
public void setRight(int value){ this.right = new TNode(value) ;}
public TNode getLeft(){ return this.left ;}
public TNode getRight(){ return this.right ;}
public int getValue(){ return this.value ;}
}
class MyTree{
private TNode root ;
public void setRoot(int value){ this.root = new TNode(value) ;}
public TNode getRoot(){ return this.root ;}
public void insert(int value){
TNode x = this.root ;
TNode y = null ;
while(x!=null){
y = x ;
if(value<x.getValue()){ x = x.getLeft() ;}
else{ x = x.getRight() ;}
}
if(y == null){ setRoot(value) ;}
else if(value<y.getValue())
{ y.setLeft(value) ;}
else{ y.setRight(value) ;}
}
}
/*****************栈的实现****************/
class StackNode{
public TNode item ;
public StackNode next ;
public StackNode(){ ;}
public StackNode(TNode item){ this.item = item ;}
public TNode getValue(){ return item ;}
}
class MyStack{
int N ; //size of myStack
StackNode first ; // the top of stack
//size of mystack
public int size(){ return N ;}
//empty or not
public boolean isEmpty(){ return N==0 ;}
public StackNode getFirst(){ return this.first ;}
public void push(TNode item){
if(isEmpty()){
first = new StackNode() ;
first.item = item;
N++;
}else{
StackNode oldfirst = first;
first = new StackNode() ;
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
N++;
}
}
public StackNode pop(){
StackNode top = first ;
first = first.next; // delete first node
N--;
return top ;
}
}2.广度遍历
广度遍历比较简单,就是层次遍历
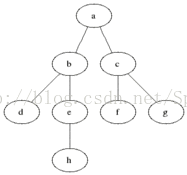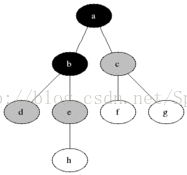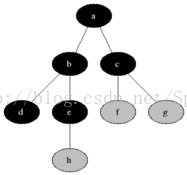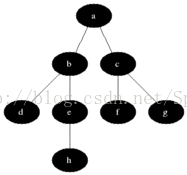
伪代码
levelorder(root)
q = empty queue
q.enqueue(root)
while not q.empty do
node := q.dequeue()
visit(node)
if node.left ≠ null then
q.enqueue(node.left)
if node.right ≠ null then
q.enqueue(node.right)










 本文深入探讨了二叉树的深度优先搜索(包括前序、中序、后序遍历)和广度优先搜索算法。通过具体代码实现,详细解释了递归与非递归方法,并对比了不同遍历方式的执行顺序和效率。
本文深入探讨了二叉树的深度优先搜索(包括前序、中序、后序遍历)和广度优先搜索算法。通过具体代码实现,详细解释了递归与非递归方法,并对比了不同遍历方式的执行顺序和效率。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








