安全哈希算法(Secure Hash Algorithm)主要适用于数字签名标准 (Digital Signature Standard DSS)里面定义的数字签名算法(Digital Signature Algorithm DSA)。对于长度小于2^64位的消息,SHA1会产生一个160位的消息摘要。当接收到消息的时候,这个消息摘要可以用来验证数据的完整性。在传输的过程中,数据很可能会发生变化,那么这时候就会产生不同的消息摘要。 SHA1有如下特性:不可以从消息摘要中复原信息;两个不同的消息不会产生同样的消息摘要。
算法实现的版本比较多,以下代码来自:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhangrulzu/2936159,代码行数很少,但确实实现了想要的效果。
下载的SHA-1算法:
#include<stdio.h>
void creat_w(unsigned char input[64],unsigned long w[80])
{
int i,j;unsigned long temp,temp1;
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
j=4*i;
w[i]=((long)input[j])<<24 |((long)input[1+j])<<16|((long)input[2+j])<<8|((long)input[3+j])<<0;
}
for(i=16;i<80;i++)
{
w[i]=w[i-16]^w[i-14]^w[i-8]^w[i-3];
temp=w[i]<<1;
temp1=w[i]>>31;
w[i]=temp|temp1;
}
}
char ms_len(long a,char intput[64])
{
unsigned long temp3,p1; int i,j;
temp3=0;
p1=~(~temp3<<8);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
j=8*i;
intput[63-i]=(char)((a&(p1<<j))>>j);
}
}
main()
{
unsigned long H0=0x67452301,H1=0xefcdab89,H2=0x98badcfe,H3=0x10325476,H4=0xc3d2e1f0;
unsigned long A,B,C,D,E,temp,temp1,temp2,temp3,k,f;int i,flag;unsigned long w[80];
unsigned char input[64]; long x;int n;
printf("input message:\n");
scanf("%s",input);
n=strlen(input);
if(n<57)
{
x=n*8;
ms_len(x,input);
if(n==56)
for(i=n;i<60;i++)
input[i]=0;
else
{
input[n]=128;
for(i=n+1;i<60;i++)
input[i]=0;
}
}
creat_w(input,w);
/*for(i=0;i<80;i++)
printf("%lx,",w[i]);*/
printf("\n");
A=H0;B=H1;C=H2;D=H3;E=H4;
for(i=0;i<80;i++)
{
flag=i/20;
switch(flag)
{
case 0: k=0x5a827999;f=(B&C)|(~B&D);break;
case 1: k=0x6ed9eba1;f=B^C^D;break;
case 2: k=0x8f1bbcdc;f=(B&C)|(B&D)|(C&D);break;
case 3: k=0xca62c1d6;f=B^C^D;break;
}
/*printf("%lx,%lx\n",k,f); */
temp1=A<<5;
temp2=A>>27;
temp3=temp1|temp2;
temp=temp3+f+E+w[i]+k;
E=D;
D=C;
temp1=B<<30;
temp2=B>>2;
C=temp1|temp2;
B=A;
A=temp;
printf("%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx\n",A,B,C,D,E);
}
H0=H0+A;
H1=H1+B;
H2=H2+C;
H3=H3+D;
H4=H4+E;
printf("\noutput hash value:\n");
printf("%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx",H0,H1,H2,H3,H4);
getch();
}
这里对算法验证过程做一个记录说明:
Visual Studio 2005,文件》新建》项目》Visual c++》Win32控制台应用程序,输入项目名称“SHA1”,完成;
把下载的代码贴到SHA1.cpp文件末尾,复制“int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])”,删除_tmain函数,替换“main()”;
编译代码,提示以下错误:
错误 2 error C3861: “strlen”: 找不到标识符 e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 43
错误 3 error C2664: “ms_len”: 不能将参数 2 从“unsigned char [64]”转换为“char []” e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 47
错误 4 error C3861: “getch”: 找不到标识符 e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 98
第一条是警告,可以不处理
警告 1 warning C4996: 'scanf': This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using scanf_s instead. To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS. See online help for details. e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 42
双击错误2,定位到错误位置,在“strlen"上单击鼠标右键》Refactor》Add Include,如下图:
如果没有这一项,那应该是没有安装VC助手的原因;
双击错误3,定位到错误位置,在变量input前加(char*)强制转换;
双击错误4,定位到错误位置,在“getch"上单击鼠标右键》Refactor》Add Include;
按F6键编译项目,发现还有错误:
错误 2 error C2664: “strlen”: 不能将参数 1 从“unsigned char [64]”转换为“const char *” e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 45
双击错误2,定位到错误位置,在input前加(LPSTR)强制转换,编译,还有错误:
错误 2 error C2065: “LPSTR”: 未声明的标识符 e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 45
错误 3 error C2146: 语法错误 : 缺少“)”(在标识符“input”的前面) e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 45
错误 4 error C2059: 语法错误 : “)” e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 45
还是找不到标识符,方法一样:在“LPSTR"上单击鼠标右键》Refactor》Add Include;
再编译,又报错:
错误 4 error C4716: “ms_len”: 必须返回一个值 e:\devlop\sha1\sha1\sha1.cpp 38
定位到错误位置,仔细看了一下,这个函数的返回值应该没什么用,随便返回一个:return '0';
再编译,OK,终于生成成功了!
F5调试,输入:abcd,回车,哦,输出了好多东东,查看代码的输出调用,
找到92行应该没用,注释://printf("%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx\n",A,B,C,D,E);//输出编码过程,
最后得到的SHA1哈希值中还有逗号,找到100行,将printf("%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx,%lx",H0,H1,H2,H3,H4);格式化字符串中的逗号去掉;
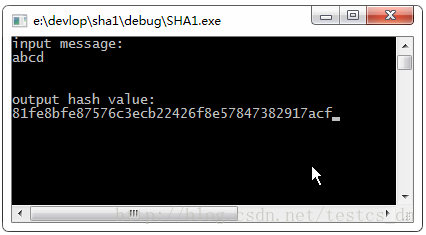
再编译,F5调试,输入:abcd,回车,结果如下图:
得到的结果对不对呢,找到一个在线SHA1加密工具,输入abcd,结果如下:
对比一下,OK,结果一至。
修改后的SHA-1算法:
// SHA1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <wtypes.h>
void creat_w(unsigned char input[64],unsigned long w[80])
{
int i,j;unsigned long temp,temp1;
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
j=4*i;
w[i]=((long)input[j])<<24 |((long)input[1+j])<<16|((long)input[2+j])<<8|((long)input[3+j])<<0;
}
for(i=16;i<80;i++)
{
w[i]=w[i-16]^w[i-14]^w[i-8]^w[i-3];
temp=w[i]<<1;
temp1=w[i]>>31;
w[i]=temp|temp1;
}
}
char ms_len(long a,char intput[64])
{
unsigned long temp3,p1; int i,j;
temp3=0;
p1=~(~temp3<<8);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
j=8*i;
intput[63-i]=(char)((a&(p1<<j))>>j);
}
return '0';
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
unsigned long H0=0x67452301,H1=0xefcdab89,H2=0x98badcfe,H3=0x10325476,H4=0xc3d2e1f0;
unsigned long A,B,C,D,E,temp,temp1,temp2,temp3,k,f;int i,flag;unsigned long w[80];
unsigned char input[64]; long x;int n;
printf("input message:\n");
scanf("%s",input);
n=strlen((LPSTR)input);
if(n<57)
{
x=n*8;
ms_len(x,(char*)input);
if(n==56)
for(i=n;i<60;i++)
input[i]=0;
else
{
input[n]=128;
for(i=n+1;i<60;i++)
input[i]=0;
}
}
creat_w(input,w);








 本文介绍了如何使用C语言实现SHA-1算法,并详细记录了解决在Visual Studio 2005中编译时遇到的错误过程。通过添加必要的头文件和类型转换,最终成功编译并验证了算法的正确性。同时指出,该代码仅适用于输入长度小于57个字符的情况,超过该长度将无法正确加密。提供了修改后的源码下载链接以及相关参考资料。
本文介绍了如何使用C语言实现SHA-1算法,并详细记录了解决在Visual Studio 2005中编译时遇到的错误过程。通过添加必要的头文件和类型转换,最终成功编译并验证了算法的正确性。同时指出,该代码仅适用于输入长度小于57个字符的情况,超过该长度将无法正确加密。提供了修改后的源码下载链接以及相关参考资料。

 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1075
1075

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








