线程池:创建一定数量(建议:CPU个数 * 2)的线程去执行很多个任务,它通常面向的是一个队列。
一个典型的用法是,有许多个任务远超过线程池数量,将任务放进队列,多个线程则不断的从队列中取出任务执行,直到所有任务都完成,线程可以终止或者睡眠等待新任务的到来。
线程池的伸缩性对性能有较大的影响。
- 创建太多线程,将会浪费一定的资源,有些线程未被充分使用。
- 銷毀太多執行緒,將導致之後浪費時間再次創建它們。
- 创建线程太慢,将会导致長時間的等待,性能變差。
- 銷毀執行緒太慢,导致其它執行緒资源饥饿。
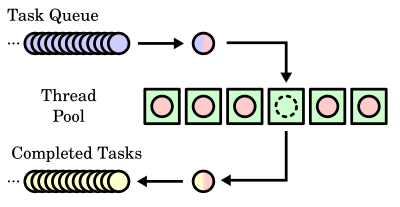
这里有个线程池的实现:
// spthread.h
#ifndef __spthread_hpp__
#define __spthread_hpp__
#ifndef WIN32
/// pthread
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
typedef void * sp_thread_result_t;
typedef pthread_mutex_t sp_thread_mutex_t;
typedef pthread_cond_t sp_thread_cond_t;
typedef pthread_t sp_thread_t;
typedef pthread_attr_t sp_thread_attr_t;
#define sp_thread_mutex_init(m,a) pthread_mutex_init(m,a)
#define sp_thread_mutex_destroy(m) pthread_mutex_destroy(m)
#define sp_thread_mutex_lock(m) pthread_mutex_lock(m)
#define sp_thread_mutex_unlock(m) pthread_mutex_unlock(m)
#define sp_thread_cond_init(c,a) pthread_cond_init(c,a)
#define sp_thread_cond_destroy(c) pthread_cond_destroy(c)
#define sp_thread_cond_wait(c,m) pthread_cond_wait(c,m)
#define sp_thread_cond_signal(c) pthread_cond_signal(c)
#define sp_thread_attr_init(a) pthread_attr_init(a)
#define sp_thread_attr_setdetachstate pthread_attr_setdetachstate
#define SP_THREAD_CREATE_DETACHED PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED
#define sp_thread_self pthread_self
#define sp_thread_create pthread_create
#define SP_THREAD_CALL
typedef sp_thread_result_t ( * sp_thread_func_t )( void * args );
#define sp_sleep(x) sleep(x)
#else ///
// win32 thread
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <process.h>
typedef unsigned sp_thread_t;
typedef unsigned sp_thread_result_t;
#define SP_THREAD_CALL __stdcall
typedef sp_thread_result_t ( __stdcall * sp_thread_func_t )( void * args );
typedef HANDLE sp_thread_mutex_t;
typedef HANDLE sp_thread_cond_t;
typedef DWORD sp_thread_attr_t;
#define SP_THREAD_CREATE_DETACHED 1
#define sp_sleep(x) Sleep(1000*x)
int sp_thread_mutex_init( sp_thread_mutex_t * mutex, void * attr )
{
*mutex = CreateMutex( NULL, FALSE, NULL );
return NULL == * mutex ? GetLastError() : 0;
}
int sp_thread_mutex_destroy( sp_thread_mutex_t * mutex )
{
int ret = CloseHandle( *mutex );
return 0 == ret ? GetLastError() : 0;
}
int sp_thread_mutex_lock( sp_thread_mutex_t * mutex )
{
int ret = WaitForSingleObject( *mutex, INFINITE );
return WAIT_OBJECT_0 == ret ? 0 : GetLastError();
}
int sp_thread_mutex_unlock( sp_thread_mutex_t * mutex )
{
int ret = ReleaseMutex( *mutex );
return 0 != ret ? 0 : GetLastError();
}
int sp_thread_cond_init( sp_thread_cond_t * cond, void * attr )
{
*cond = CreateEvent( NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL );
return NULL == *cond ? GetLastError() : 0;
}
int sp_thread_cond_destroy( sp_thread_cond_t * cond )
{
int ret = CloseHandle( *cond );
return 0 == ret ? GetLastError() : 0;
}
/*
Caller MUST be holding the mutex lock; the
lock is released and the caller is blocked waiting
on 'cond'. When 'cond' is signaled, the mutex
is re-acquired before returning to the caller.
*/
int sp_thread_cond_wait( sp_thread_cond_t * cond, sp_thread_mutex_t * mutex )
{
int ret = 0;
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( mutex );
ret = WaitForSingleObject( *cond, INFINITE );
sp_thread_mutex_lock( mutex );
return WAIT_OBJECT_0 == ret ? 0 : GetLastError();
}
int sp_thread_cond_signal( sp_thread_cond_t * cond )
{
int ret = SetEvent( *cond );
return 0 == ret ? GetLastError() : 0;
}
sp_thread_t sp_thread_self()
{
return GetCurrentThreadId();
}
int sp_thread_attr_init( sp_thread_attr_t * attr )
{
*attr = 0;
return 0;
}
int sp_thread_attr_setdetachstate( sp_thread_attr_t * attr, int detachstate )
{
*attr |= detachstate;
return 0;
}
int sp_thread_create( sp_thread_t * thread, sp_thread_attr_t * attr,
sp_thread_func_t myfunc, void * args )
{
// _beginthreadex returns 0 on an error
HANDLE h = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex( NULL, 0, myfunc, args, 0, thread );
return h > 0 ? 0 : GetLastError();
}
#endif
#endif
/**
* threadpool.h
*
* This file declares the functionality associated with
* your implementation of a threadpool.
*/
#ifndef __threadpool_h__
#define __threadpool_h__
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
// maximum number of threads allowed in a pool
#define MAXT_IN_POOL 200
// You must hide the internal details of the threadpool
// structure from callers, thus declare threadpool of type "void".
// In threadpool.c, you will use type conversion to coerce
// variables of type "threadpool" back and forth to a
// richer, internal type. (See threadpool.c for details.)
typedef void *threadpool;
// "dispatch_fn" declares a typed function pointer. A
// variable of type "dispatch_fn" points to a function
// with the following signature:
//
// void dispatch_function(void *arg);
typedef void (*dispatch_fn)(void *);
/**
* create_threadpool creates a fixed-sized thread
* pool. If the function succeeds, it returns a (non-NULL)
* "threadpool", else it returns NULL.
*/
threadpool create_threadpool(int num_threads_in_pool);
/**
* dispatch sends a thread off to do some work. If
* all threads in the pool are busy, dispatch will
* block until a thread becomes free and is dispatched.
*
* Once a thread is dispatched, this function returns
* immediately.
*
* The dispatched thread calls into the function
* "dispatch_to_here" with argument "arg".
*/
int dispatch_threadpool(threadpool from_me, dispatch_fn dispatch_to_here,
void *arg);
/**
* destroy_threadpool kills the threadpool, causing
* all threads in it to commit suicide, and then
* frees all the memory associated with the threadpool.
*/
void destroy_threadpool(threadpool destroyme);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
/**
* threadpool.c
*
* This file will contain your implementation of a threadpool.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include "spthread.h"
typedef struct _thread_st {
sp_thread_t id;
sp_thread_mutex_t mutex;
sp_thread_cond_t cond;
dispatch_fn fn;
void *arg;
threadpool parent;
} _thread;
// _threadpool is the internal threadpool structure that is
// cast to type "threadpool" before it given out to callers
typedef struct _threadpool_st {
// you should fill in this structure with whatever you need
sp_thread_mutex_t tp_mutex;
sp_thread_cond_t tp_idle;
sp_thread_cond_t tp_full;
sp_thread_cond_t tp_empty;
_thread ** tp_list;
int tp_index;
int tp_max_index;
int tp_stop;
int tp_total;
} _threadpool;
threadpool create_threadpool(int num_threads_in_pool)
{
_threadpool *pool;
// sanity check the argument
if ((num_threads_in_pool <= 0) || (num_threads_in_pool > MAXT_IN_POOL))
return NULL;
pool = (_threadpool *) malloc(sizeof(_threadpool));
if (pool == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out of memory creating a new threadpool!\n");
return NULL;
}
// add your code here to initialize the newly created threadpool
sp_thread_mutex_init( &pool->tp_mutex, NULL );
sp_thread_cond_init( &pool->tp_idle, NULL );
sp_thread_cond_init( &pool->tp_full, NULL );
sp_thread_cond_init( &pool->tp_empty, NULL );
pool->tp_max_index = num_threads_in_pool;
pool->tp_index = 0;
pool->tp_stop = 0;
pool->tp_total = 0;
pool->tp_list = ( _thread ** )malloc( sizeof( void * ) * MAXT_IN_POOL );
memset( pool->tp_list, 0, sizeof( void * ) * MAXT_IN_POOL );
return (threadpool) pool;
}
int save_thread( _threadpool * pool, _thread * thread )
{
int ret = -1;
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &pool->tp_mutex );
if( pool->tp_index < pool->tp_max_index ) {
pool->tp_list[ pool->tp_index ] = thread;
pool->tp_index++;
ret = 0;
sp_thread_cond_signal( &pool->tp_idle );
if( pool->tp_index >= pool->tp_total ) {
sp_thread_cond_signal( &pool->tp_full );
}
}
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &pool->tp_mutex );
return ret;
}
sp_thread_result_t SP_THREAD_CALL wrapper_fn( void * arg )
{
_thread * thread = (_thread*)arg;
_threadpool * pool = (_threadpool*)thread->parent;
for( ; 0 == ((_threadpool*)thread->parent)->tp_stop; ) {
thread->fn( thread->arg );
if( 0 != ((_threadpool*)thread->parent)->tp_stop ) break;
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &thread->mutex );
if( 0 == save_thread(pool, thread ) ) {
sp_thread_cond_wait( &thread->cond, &thread->mutex );
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &thread->mutex );
} else {
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &thread->mutex );
sp_thread_cond_destroy( &thread->cond );
sp_thread_mutex_destroy( &thread->mutex );
free( thread );
break;
}
}
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &pool->tp_mutex );
pool->tp_total--;
if( pool->tp_total <= 0 ) sp_thread_cond_signal( &pool->tp_empty );
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &pool->tp_mutex );
return 0;
}
int dispatch_threadpool(threadpool from_me, dispatch_fn dispatch_to_here, void *arg)
{
int ret = 0;
_threadpool *pool = (_threadpool *) from_me;
sp_thread_attr_t attr;
_thread * thread = NULL;
// add your code here to dispatch a thread
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &pool->tp_mutex );
while( pool->tp_index <= 0 && pool->tp_total >= pool->tp_max_index ) {
sp_thread_cond_wait( &pool->tp_idle, &pool->tp_mutex );
}
if( pool->tp_index <= 0 ) {
_thread * thread = ( _thread * )malloc( sizeof( _thread ) );
memset( &( thread->id ), 0, sizeof( thread->id ) );
sp_thread_mutex_init( &thread->mutex, NULL );
sp_thread_cond_init( &thread->cond, NULL );
thread->fn = dispatch_to_here;
thread->arg = arg;
thread->parent = pool;
sp_thread_attr_init( &attr );
sp_thread_attr_setdetachstate( &attr, SP_THREAD_CREATE_DETACHED );
if( 0 == sp_thread_create( &thread->id, &attr, wrapper_fn, thread ) ) {
pool->tp_total++;
printf( "create thread#%ld\n", thread->id );
} else {
ret = -1;
printf( "cannot create thread\n" );
sp_thread_mutex_destroy( &thread->mutex );
sp_thread_cond_destroy( &thread->cond );
free( thread );
}
} else {
pool->tp_index--;
thread = pool->tp_list[ pool->tp_index ];
pool->tp_list[ pool->tp_index ] = NULL;
thread->fn = dispatch_to_here;
thread->arg = arg;
thread->parent = pool;
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &thread->mutex );
sp_thread_cond_signal( &thread->cond ) ;
sp_thread_mutex_unlock ( &thread->mutex );
}
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &pool->tp_mutex );
return ret;
}
void destroy_threadpool(threadpool destroyme)
{
_threadpool *pool = (_threadpool *) destroyme;
// add your code here to kill a threadpool
int i = 0;
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &pool->tp_mutex );
if( pool->tp_index < pool->tp_total ) {
printf( "waiting for %d thread(s) to finish\n", pool->tp_total - pool->tp_index );
sp_thread_cond_wait( &pool->tp_full, &pool->tp_mutex );
}
pool->tp_stop = 1;
for( i = 0; i < pool->tp_index; i++ ) {
_thread * thread = pool->tp_list[ i ];
sp_thread_mutex_lock( &thread->mutex );
sp_thread_cond_signal( &thread->cond ) ;
sp_thread_mutex_unlock ( &thread->mutex );
}
if( pool->tp_total > 0 ) {
printf( "waiting for %d thread(s) to exit\n", pool->tp_total );
sp_thread_cond_wait( &pool->tp_empty, &pool->tp_mutex );
}
for( i = 0; i < pool->tp_index; i++ ) {
free( pool->tp_list[ i ] );
pool->tp_list[ i ] = NULL;
}
sp_thread_mutex_unlock( &pool->tp_mutex );
pool->tp_index = 0;
sp_thread_mutex_destroy( &pool->tp_mutex );
sp_thread_cond_destroy( &pool->tp_idle );
sp_thread_cond_destroy( &pool->tp_full );
sp_thread_cond_destroy( &pool->tp_empty );
free( pool->tp_list );
free( pool );
}
/**
* threadpool_test.c
*
* Just a regression test for the threadpool code.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include "spthread.h"
extern int errno;
void mylog( FILE * fp, const char *format, /*args*/ ...)
{
va_list ltVaList;
va_start( ltVaList, format );
vprintf( format, ltVaList );
va_end( ltVaList );
fflush( stdout );
}
void dispatch_threadpool_to_me(void *arg) {
int seconds = (int) arg;
fprintf(stdout, " in dispatch_threadpool %d\n", seconds);
fprintf(stdout, " thread#%ld\n", sp_thread_self() );
sp_sleep(seconds);
fprintf(stdout, " done dispatch_threadpool %d\n", seconds);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
threadpool tp;
tp = create_threadpool(2);
fprintf(stdout, "create thread over...\n");
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 3\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 3);
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 6\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 6);
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 7\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 7);
fprintf(stdout, "**main** done first\n");
sp_sleep(20);
fprintf(stdout, "\n\n");
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 3\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 3);
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 6\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 6);
fprintf(stdout, "**main** dispatch_threadpool 7\n");
dispatch_threadpool(tp, dispatch_threadpool_to_me, (void *) 7);
fprintf(stdout, "**main done second\n");
destroy_threadpool( tp );
//sp_sleep(20);
return -1;
}






















 133
133

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








