本节主要介绍线程的方法:
currentThread()、isAlive()、sleep()、getId()
1. currentThread() 方法:返回代码段正在被哪个线程调用
例1:
/**
* @ClassName GetThreadName
* @Description 获取正在被哪个线程调用
*/
public class GetThreadName {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
/*
运行结果:说明 main 方法被名为 main 的线程调用
main
*/
}/**
* @ClassName MyThread
* @Description 线程 构造函数和run方法分别输出调用者
*/
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public MyThread() {
System.out.println("构造方法被:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 调用");
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run方法被:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 调用");
}
}/**
* @ClassName MyThreadTest
* @Description 测试start() 和 run() 方法的实际调用者
*/
public class MyThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
//1-调用start() 方法
myThread.start();
/*
运行结果:
构造方法被:main 调用
run方法被:Thread-0 调用
*/
//2-调用run() 方法
//myThread.run();
/*
运行结果:
构造方法被:main 调用
run方法被:main 调用
*/
}
}
例3:
2. isAlive() 方法:判断当前线程是否处于活动状态。活动状态指 线程已经启动且尚未终止。线程处于正在运行或者准备开始运行的状态,则认为线程是"存活"的。
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
public MyThread2() {
System.out.println("Constructor --- begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName() = " + this.getName());
System.out.println("Constructor --- end");
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("run --- begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName() = " + this.getName());
System.out.println("run --- end");
}
}public class MyThread2Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread2 myThread2 = new MyThread2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread2);
t1.setName("AAA");
t1.start();
}
/*
运行结果:
Constructor --- begin
Thread.currentThread().getName() = main
this.getName() = Thread-0
Constructor --- end
-------------------------------------------
run --- begin
Thread.currentThread().getName() = AAA
this.getName() = Thread-0
run --- end
*/
}2. isAlive() 方法:判断当前线程是否处于活动状态。活动状态指 线程已经启动且尚未终止。线程处于正在运行或者准备开始运行的状态,则认为线程是"存活"的。
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run=" + this.isAlive());
}
}public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
System.out.println("begin == " + myThread.isAlive());
myThread.start();
//Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("end == " + myThread.isAlive());
/*
运行结果:
1. 没有sleep
begin == false
end == true
run=true
2. 有sleep
begin == false
run=true
end == false
*/
}
}
如果
加上
sleep() 方法,那么线程已经运行完,所以输出 end == false。
例2:
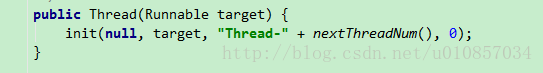
Thread-0 是 线程在初始化时设置的,所以 this.getName() = Thread-0。此时 MyThread2 线程并没有 start(),所以 this.isAlive() = false。
/**
* @ClassName MyThread2
* @Description 测试 Thread.currentThread 和 this 的区别
*/
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
public MyThread2() {
System.out.println("Constructor --- begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = " + Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
System.out.println("this.getName() = " + this.getName());
System.out.println("this.isAlive() = " + this.isAlive());
System.out.println("Constructor --- end");
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("run --- begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = " + Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
System.out.println("this.getName() = " + this.getName());
System.out.println("this.isAlive() = " + this.isAlive());
System.out.println("run --- end");
}
}public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread2 mt = new MyThread2(); // 1
Thread t1 = new Thread(mt); //2
System.out.println("main begin t1 isAlive = " + t1.isAlive());
t1.setName("AAA"); //3
t1.start(); //4
System.out.println("main end t1 isAlive = " + t1.isAlive());
}
/*
运行结果:
Constructor --- begin
Thread.currentThread().getName() = main
Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = true
this.getName() = Thread-0
this.isAlive() = false
Constructor --- end
main begin t1 isAlive = false
main end t1 isAlive = true
-------------------------------------------
run --- begin
Thread.currentThread().getName() = AAA
Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = true
this.getName() = Thread-0
this.isAlive() = false
run --- end
*/
}
这里说明一下:
步骤1,main方法实例化 MyThread2 类,所以是由 main 线程调用的 MyThread2 构造方法。上半部分结果中的 Thread.currentThread() 指的就是 main 线
程,
Thread.currentThread().getName() = main,此时 main 线程是活动的,即
Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = true。而在构造方法中 this 指的是 MyThread2 这个对 象,那么为什么 this.getName() = Thread-0 呢?我们看一下 Thread 源码:

步骤2、3、4:
步骤2中创建了一个新线程并将之前创建的 MyThread2 线程对象作为 target 传入 t1,此时 t1 的 run() 方法其实是调用 target.run(),即调用的是 MyThread2 的 run() 方法。run() 方法中 this 指的是 MyThread2 而不是 t1。
Thread.currentThread() 在 t1.start() 之后就是 t1了,所以 Thread.currentThread().getName() = AAA,Thread.currentThread().isAlive() = true。而this.getName() = Thread-0 ,this.isAlive() = false。
3. sleep() 方法:在指定的毫秒数内让当前“正在执行的线程”休眠,“正在执行的线程”指 this.currentThread() 返回的线程。
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run threadName = " + this.currentThread().getName() + " begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("run threadName = " + this.currentThread().getName() + " end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("begin = " + beginTime);
myThread.run(); //运行结果1
// myThread.start(); //运行结果2
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("end = " + endTime + " , use time = " + (endTime - beginTime));
/*
运行结果1:main线程直接调用 run() 方法,所以 sleep()也是main线程,总共用时2s多
begin = 1502868769857
run threadName = main begin
run threadName = main end
end = 1502868771887 , use time = 2030
运行结果2:main线程 和 myThread 线程同时执行,main 线程统计时间,而myThread 中间暂停了2s
begin = 1502869043441
end = 1502869043442 , use time = 1
run threadName = Thread-0 begin
run threadName = Thread-0 end
*/
}
}public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName() + " --- getId() = " + this.currentThread().getId());
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(mainThread.getName() + " --- getId() = " + mainThread.getId());
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
/*
运行结果:
main --- getId() = 1
Thread-0 --- getId() = 10
*/
}
}




















 933
933











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








