Thread 方法中提供了几种方法能够使线程停止?
1. 调用线程 stop() 方法; 2. 线程抛出异常 3. 调用线程 interrupt() 方法 4.使用 return
| 方法 | stop() | 抛出异常 | interrupt | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 线程是否停止 | 停止 | 停止 | 不会立即停止 | 停止 |
| 锁释放 | 立即释放 | 立即释放 | 不会释放锁,除非线程执行完或者由于其他原因导致锁被释放 | 立即释放 |
| 使用建议 | 不建议使用 | 不建议使用 | 一般使用这种 | 可以使用 |
一一举例:
1. stop()方法,会立即停止线程,并且释放掉线程持有的锁。使用不当会造成数据异常,该方法已被废弃,不建议使用。
public class StopMethod2StopThread {
public static Object lockA = new Object();
public static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//A线程锁住 id对象
synchronized (lockA) {
System.out.println("ThreadA get lockA...");
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000;i ++) {
//表名线程还在运行
System.out.println("i = " + i);
if (i == 100) {
//线程A停10s
Thread.currentThread().sleep(10000);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
public static class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lockA) {
System.out.println("ThreadB get lockA...");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
threadA.start();
//主线程停1s,然后开启B线程
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
//启动B线程
threadB.start();
//线程A是否还存活
System.out.println("ThreadA is alive? " + threadA.isAlive());
//调用stop()方法,线程A是否还存活?其持有的锁 lockA 是否被释放?
//如果 lockA 未被释放,那么线程B应该执行不了输出语句
threadA.stop();
System.out.println("ThreadA is alive? " + threadA.isAlive());
}
}执行结果:

2. 抛出异常
public class ThrowException2StopThread {
static Object lock = new Object();
//线程A
static class ThreadA implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//持有对象锁
synchronized (lock) {
//线程A休眠5s,让线程B启动等待锁
System.out.println("ThreadA get lock, sleep 5s!");
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
System.out.println("ThreadA i = " + i);
if (i == 20) {
System.out.println("throw exception here");
int j = 1 / 0;
}
}
}
}
}
//线程B
static class ThreadB implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("ThreadB get lock!");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(threadA);
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(threadB);
//线程A启动后,拿到锁开始休眠5s
thread1.start();
//主线程休眠1s,然后启动线程B,确保线程A先拿到锁
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
thread2.start();
}
}运行结果:线程A先运行拿到锁,线程B运行后等待锁;线程A休眠结束后开始运行,i=20时,线程A抛出异常,这时线程B拿到了锁

3. interrupt() 方法,仅修改了线程中断标志位(interrupt flag),将其修改为中断。至于线程会不会立刻停止,要看线程怎么写。在Java中线程是协作式的。
public class InterruptMethod2StopThread {
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
threadA.start();
threadA.interrupt();
}
}运行结果:程序一直运行到结束

A. 那么interrupt() 方法该怎么使用呢?当调用线程A的 interrupt() 方法后,需要我们在线程A中写代码捕获本线程的中断标志位(),然后停止线程。
public class InterruptMethod2StopThread {
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
boolean isInterrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
if (isInterrupted) {
System.out.println("isInterrupted = " + isInterrupted);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
threadA.start();
//让线程A先跑起来
Thread.sleep(20);
threadA.interrupt();
}
}运行结果:线程A在判断到 isInterrupted() = true时,我们在for循环中停止了循环执行。

B. 除了上面出现的 interrupt()、isInterrupted() 方法外,Thread类中还提供了 interrupted() 静态方法,该方法跟 isInterrupted() 有何区别? interrupted() 方法调用后会将中断标志位设置成 false,而 isInterrupted() 方法调不会对中断标志位产生任何作用。
我们看一下 Thread类 中这两个方法的实现:


两个方法都调用了 isInterrupted(boolean) 方法,这个方法是 Thread类的本地方法:

用代码测试一下 interrupted() 方法对中断标志位产生的影响:
public class InterruptMethod2StopThread {
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
// boolean isInterrupted = Thread.currentThread().in();
boolean isInterrupted = Thread.interrupted();
if (isInterrupted) {
System.out.println("isInterrupted = " + isInterrupted);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
threadA.start();
//让线程A先跑起来
Thread.sleep(20);
threadA.interrupt();
}
}运行结果:跟上一次相比,第二次我们判断线程中断标志位是发现,中断标志位 由 true 变为 false了。

C. 下面我们测试一下调用 interrupt() 方法是否会释放线程持有的锁:
public class InterruptMethodAndLock {
static Object lock = new Object();
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("ThreadA get lock");
while (!isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("ThreadA is running in while");
}
System.out.println("ThreadA out of while");
while (true) {
System.out.println("ThreadA is running whileB");
}
}
}
}
static class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("ThreadB get lock");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
threadA.start();
//让线程A先运行
Thread.sleep(10);
//启动线程B
threadB.start();
//调用线程A的中断方法
threadA.interrupt();
}
}运行结果:线程B一直没有拿到锁

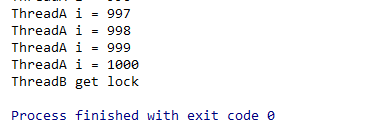
4. return 后是否会释放线程持有的锁:其实比较明显了,return就相当于线程的 run() 执行完,自然会释放锁。
public class ReturnAndLock {
static Object lock = new Object();
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("ThreadA get lock");
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
System.out.println("ThreadA i = " + i);
if (i == 1000) {
return;
}
}
}
System.out.println("多此一举的打印");
}
}
static class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("ThreadB get lock");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
threadA.start();
//让线程A先运行
Thread.sleep(10);
//启动线程B
threadB.start();
}
}运行结果:线程B拿到了锁





















 4698
4698











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








